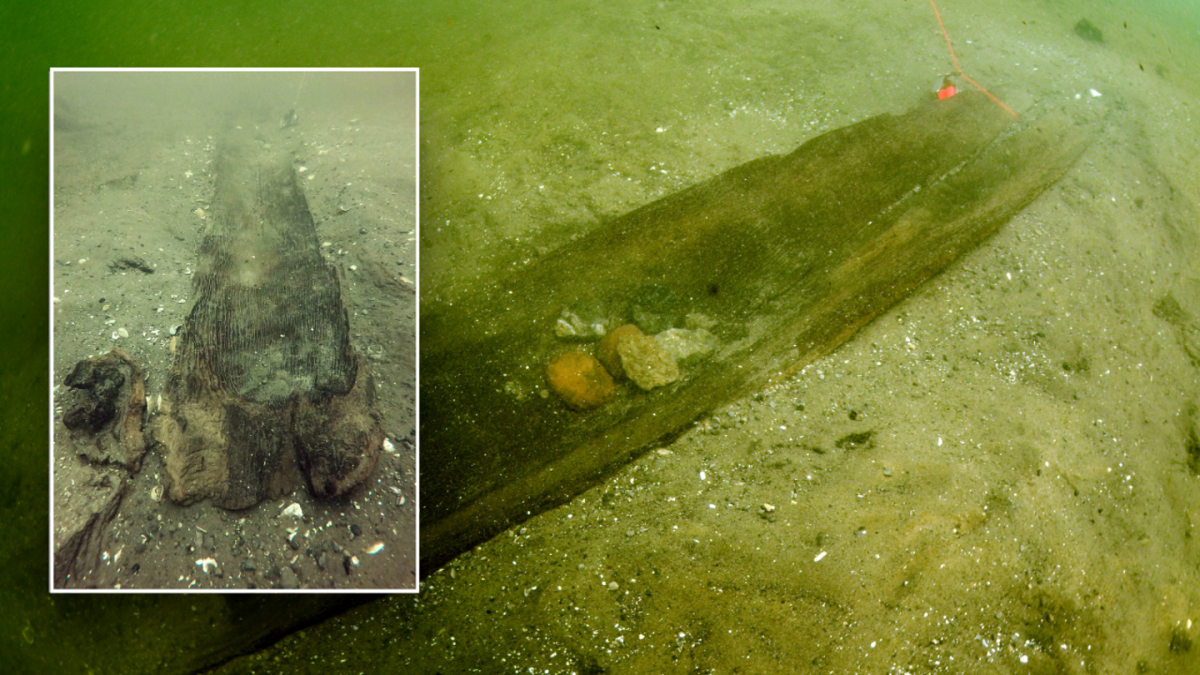
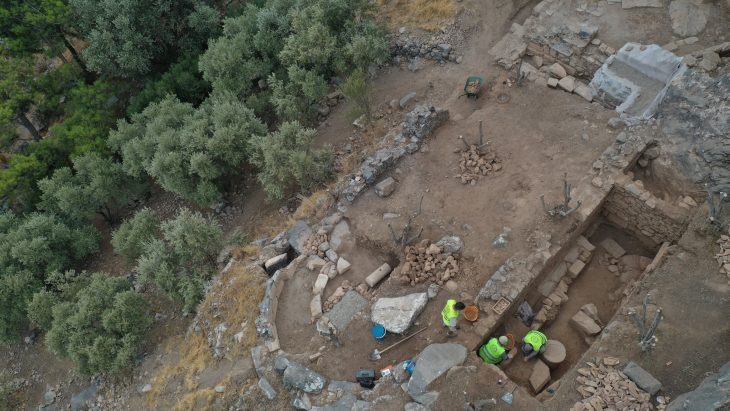
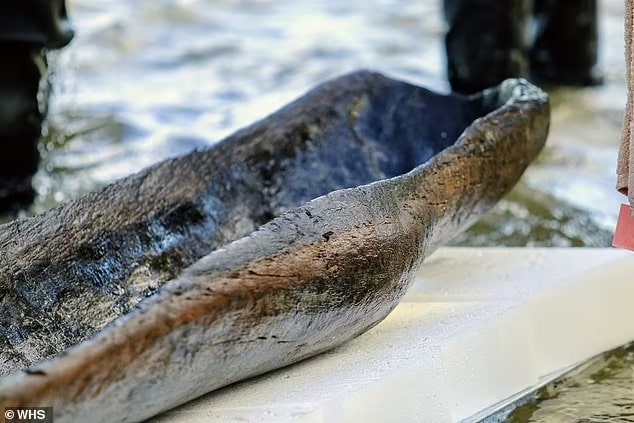
Historians from Wisconsin have reported the amazing finding of at least eleven prehistoric canoes in Lake Mendota, which is close to Madison. Among the important discoveries is a canoe from 2500 BC. The findings were announced in a press release by the Wisconsin Historical Society on May 23.
Two historic canoes were discovered in a lakeside cache in 2021 and 2022, according to the Wisconsin Historical Society. Since then, at least eleven more ancient canoes have since discovered by historians along what they believe to be an ancient shoreline that gradually submerged.
All the canoes varied in age, with the youngest one dating back to 1250 AD. The archaeologists explained that the canoes “may have been intentionally cached in the water during the winter months, a standard practice to keep canoes safe from freezing and warping.”
The oldest canoe was discovered through radiocarbon dating to be from 2500 B.C., which suggests it was constructed around the same time as Stonehenge. The canoe was built more than 1,700 years before the first inhabitants of Ancient Rome arrived and 2,500 years before Jesus was born.
The canoes were also discovered along a shoreline that has since been submerged, suggesting a previously unknown civilization once thrived in the area.
Dr Amy Rosebrough, State Archaeologist for the Wisconsin Historical Society mentioned that divers also found stone tools in the water, suggesting the presence of an ancient village site, which has yet to be located. “Even without finding the village, the discovery of these canoes and the tools found within the first canoe reminds us that people have lived and worked alongside the lake for thousands of years,”.

‘Seeing these canoes with one’s own eyes is a powerful experience, and they serve as a physical representation of what we know from extensive oral traditions that Native scholars have passed down over generations,’ said Tribal Historic Preservation Officer for the Ho-Chunk Nation Bill Quackenbush.
‘We are excited to learn all we can from this site using the technology and tools available to us, and to continue to share the enduring stories and ingenuity of our ancestors.’
While the Ho-Chunk tribe once lived in the area surrounding Lake Mendota, the Paleo-Indian people were the earliest inhabitants arriving around 12,000 years ago – the Ho-Chunk tribe migrated there no earlier than 800AD.
Divers have found stone tools in the water, and experts believe that the lake is filled with other hidden sites.
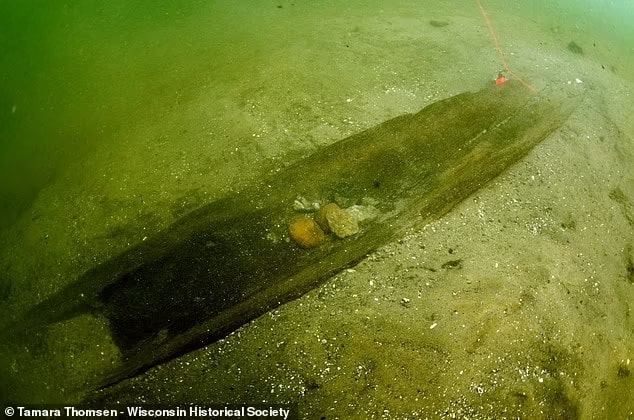

“Lake Mendota is a hard lake to work in, however,” Dr. Rosebrough admitted. “There is a limited window of visibility for diving missions, and we are exploring non-destructive remote sensing techniques that might help this summer.”
“Even without finding the village, the discovery of these canoes and the tools found within the first canoe that was found, human-worked stone tools called net sinkers, reminds us that people have lived and worked alongside the lake for thousands of years.”
Efforts are ongoing to explore the lake further, using non-destructive remote sensing techniques to uncover more about this prehistoric site.
Dr. Rosebrough added that, though the Great Lakes dwarf Lake Mendota, the south-central Wisconsin lake is small but mighty when it comes to archaeological potential.
Cover Photo: Wisconsin Historical Society