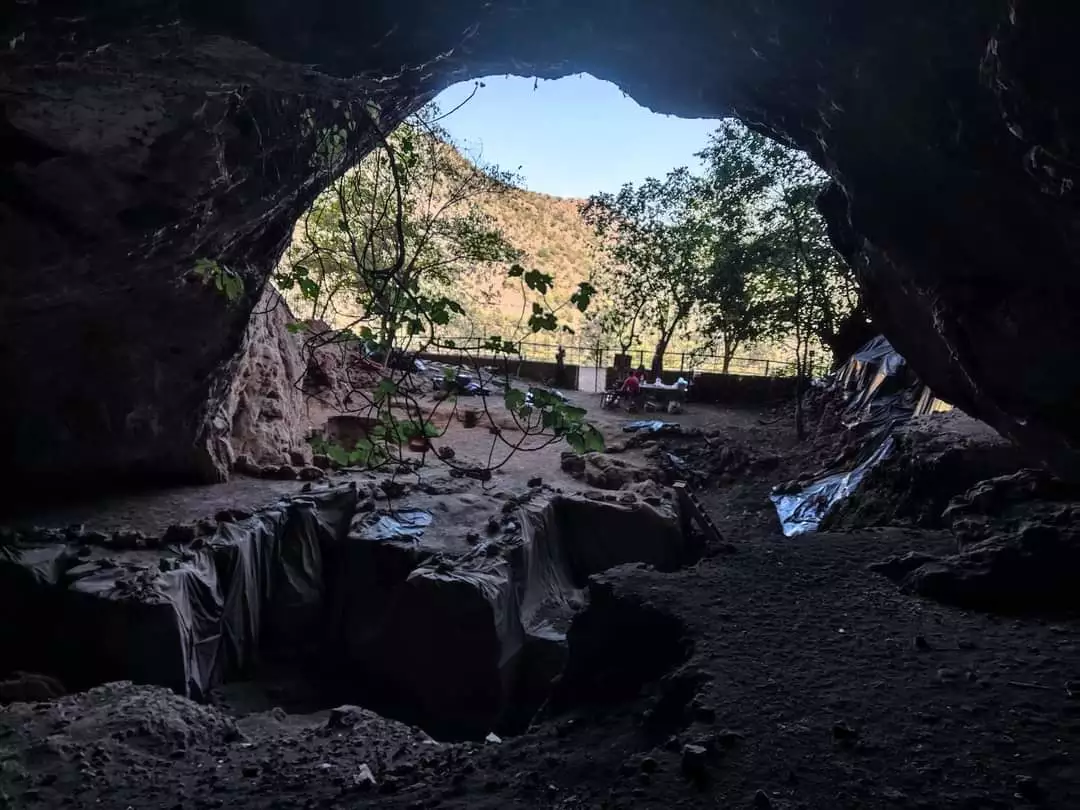
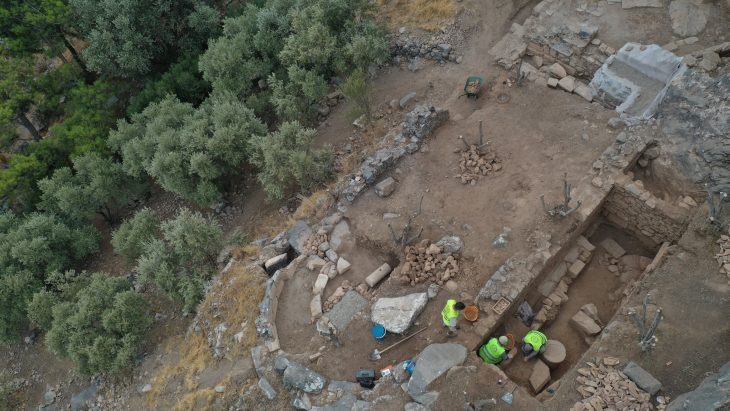
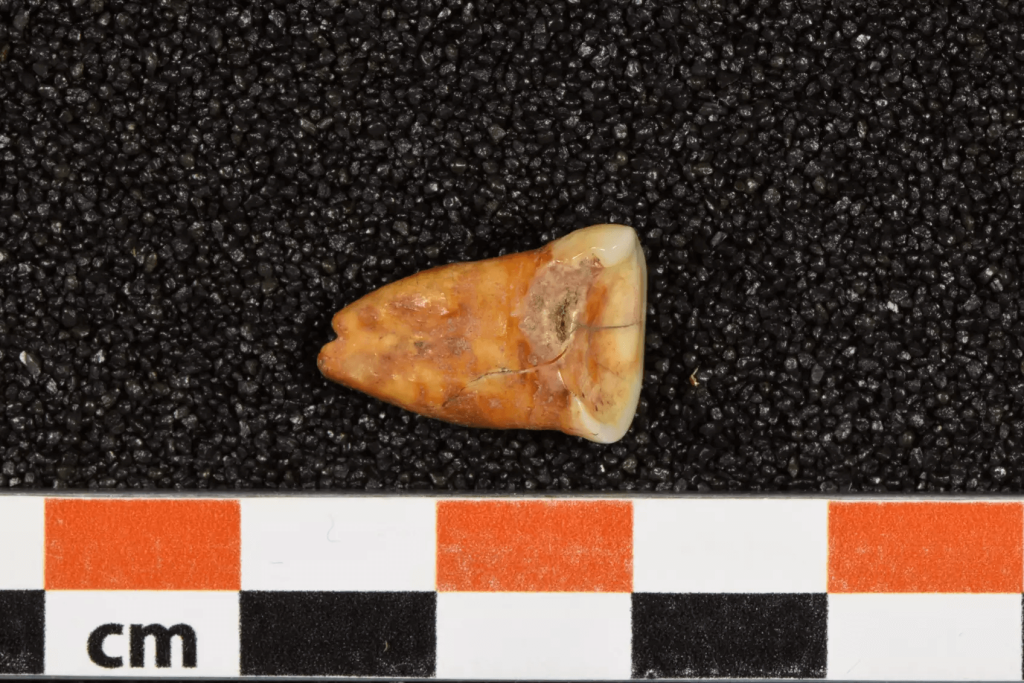
It has long been accepted wisdom that hunter-gatherer societies lived primarily off of meat. But fresh data from an innovative study reveals an unexpected shift in the dietary habits of prehistoric human populations in Morocco, pointing to a clear preference for plant-based diets more than 15,000 years ago.
A new study provides strong isotopic evidence of plant preference among 15,000-year-old hunter-gatherers in Morocco. This is the first time a significant amount of plant consumption has been measured for a pre-agricultural population, shedding new light on the dietary practices of ancient human societies.
Conducted by an international team of scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (Leipzig, Germany), Géoscience et Environnement Toulouse (Toulouse, France), and the Institut National des Sciences de l’Archéologie et du Patrimoine (Rabat, Morocco), the study examines the diet of individuals associated with the Iberomaurusian culture discovered in the cave of Taforalt, Morocco. Using a comprehensive multi-isotopic approach, including zinc and strontium isotope analysis in dental enamel, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur analysis in collagen, as well as amino acid analysis of human and faunal remains, the researchers uncovered surprising insights into ancient dietary practices.
The study’s major conclusions clearly show that the diet of these hunter-gatherers included a significant proportion of plants belonging to Mediterranean species, predating the advent of agriculture in the region by several millennia. Archaeobotanical remains found at the site, such as acorns, pine nuts, and wild pulses, further support this notion. Moreover, the study suggests that plant foods were also introduced into infant diets and may have served as weaning products for this human population. This finding has significant implications, as it suggests the potential for earlier weaning practices in pre-agricultural communities compared to previously thought norms for hunter-gatherer societies.

Complex dietary practices of pre-agricultural societies
This challenges the prevailing notion of a diet heavily based on animal protein among pre-agricultural human groups and raises questions about the lack of agricultural development in North Africa at the beginning of the Holocene. Zineb Moubtahij, first author of the study, explains: “Our findings not only provide insights into the dietary practices of pre-agricultural human groups but also highlight the complexity of human subsistence strategies in different regions. Understanding these patterns is crucial to unraveling the broader story of human evolution.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Furthermore, this study is the first to use zinc isotopes preserved in enamel to determine the diet of ancient populations in Africa. North Africa is a key region for the study of human evolution and modern human dispersal. Having a tool that allows us to further explore human diet deep in time in this region will provide valuable insights into human dietary patterns and adaptability in different environments.
Moving forward, the research team hopes to explore additional Paleolithic sites in North Africa and use innovative techniques to gain a deeper understanding of ancient dietary practices and their implications for human evolution.
Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology
Cover Photo: Inside view of the Taforalt Cave in Morocco.© Abdeljalil Bouzouggar