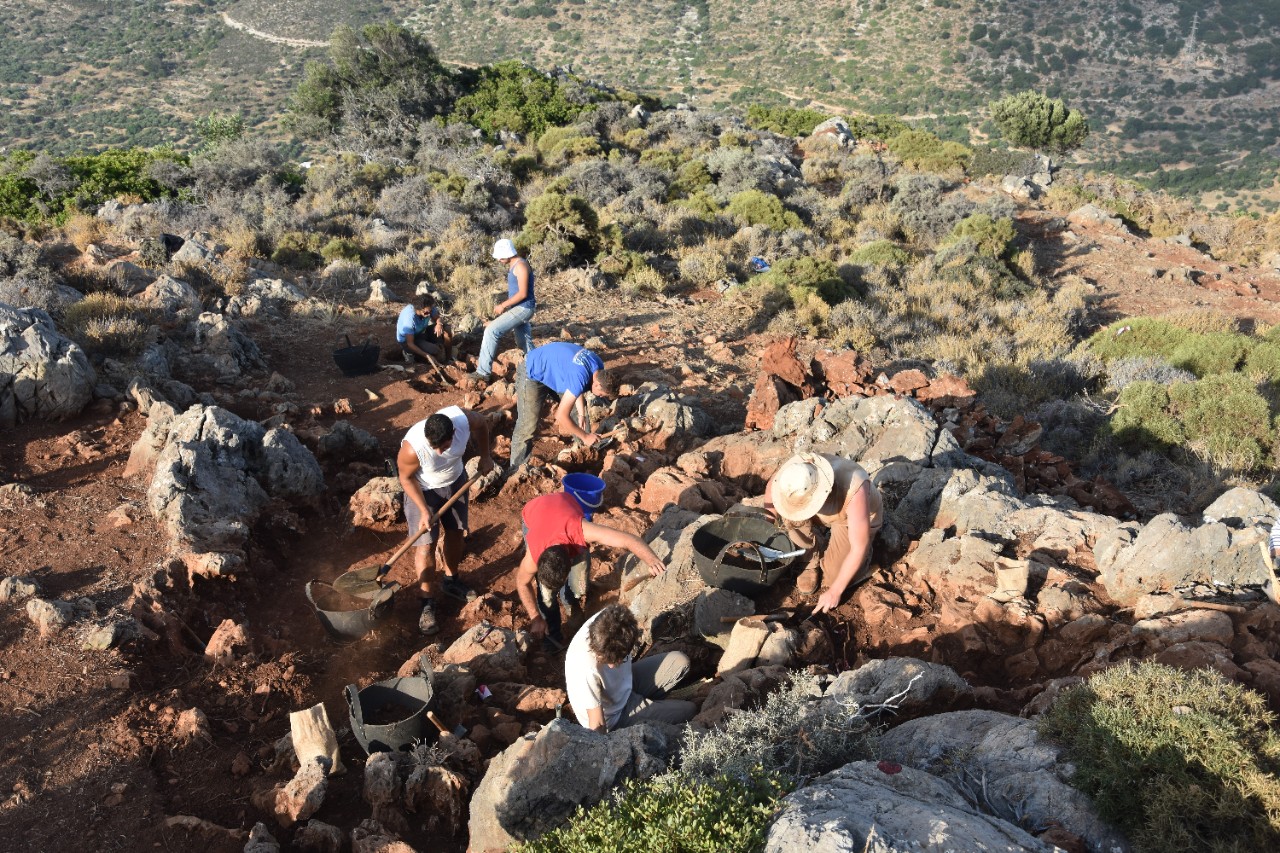
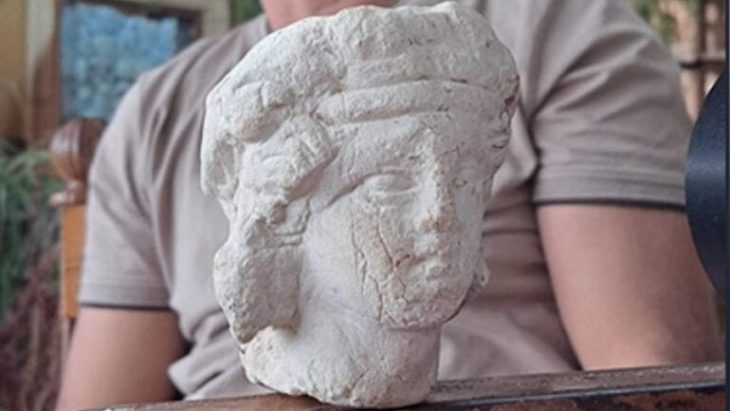
Perched high on the rugged slopes of Mount Anavlochos, overlooking the azure expanse of the Mediterranean Sea, lie the silent remnants of an ancient mystery. Hundreds of fragmented terracotta figurines, predominantly female and affectionately dubbed “the ladies of Anavlochos,” have been unearthed, offering a unique window into the mass production techniques and ritualistic practices of ancient Greece.
Dating back to between 900 and 350 BCE, these figurines provide valuable insights into the scale of pottery production and the nature of religious rituals in the ancient world.
Dr. Florence Gaignerot-Driessen, a Classics scholar from the University of Cincinnati, is spearheading an innovative archaeological project at this evocative Cretan site. By employing cutting-edge technologies such as 3D scanning and printing, her international team is meticulously piecing together the story held within these clay fragments.
The Anavlochos site, inhabited between 1200 and 650 BCE, offers a unique glimpse into the past. The figurines, many of which were deposited after the settlement was abandoned, include plaques featuring mythological creatures like sphinxes and representations of women in traditional attire.
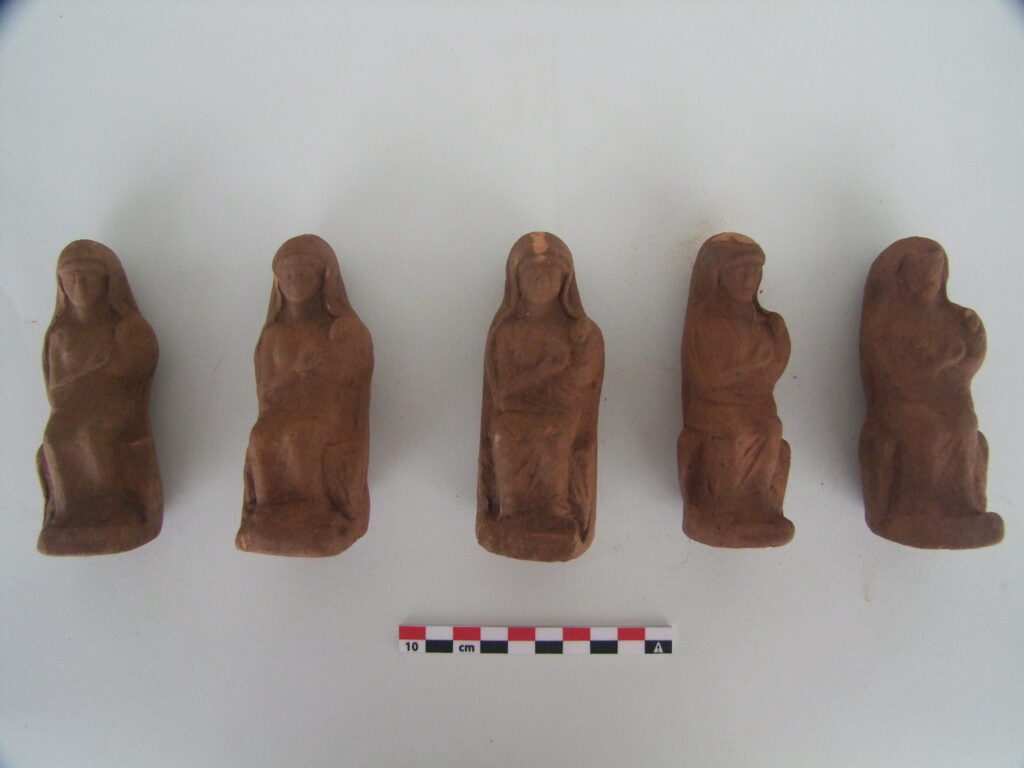

The sheer number of these votive offerings, discovered nestled within the bedrock crevices, suggests a production scale previously not fully understood for this type of artifact. “They weren’t crafted with meticulous detail, indicating they were likely intended for a broad audience,” explains Dr. Gaignerot-Driessen. “Their modest clay composition, rather than precious metals or ivory, further underscores their accessibility. It seems anyone, regardless of their social standing, could acquire and deposit one of these small effigies.”
Intriguingly, all the discovered figurines and plaques are broken. Dr. Gaignerot-Driessen and her colleagues are delving into whether this fragmentation was a deliberate act, perhaps an integral part of the ritual, or simply the result of centuries of weathering on the exposed mountainside.
To unravel these ancient manufacturing secrets, the research team is engaging in experimental archaeology. By creating precise 3D replicas of the original molds and figurines, they can physically recreate the production process. In the University of Cincinnati’s ceramics lab, Dr. Gaignerot-Driessen is working with clay to reconstruct the ancient techniques, hoping to discern whether the figurines were mass-produced using molds or individually modeled – a far more time-consuming process.
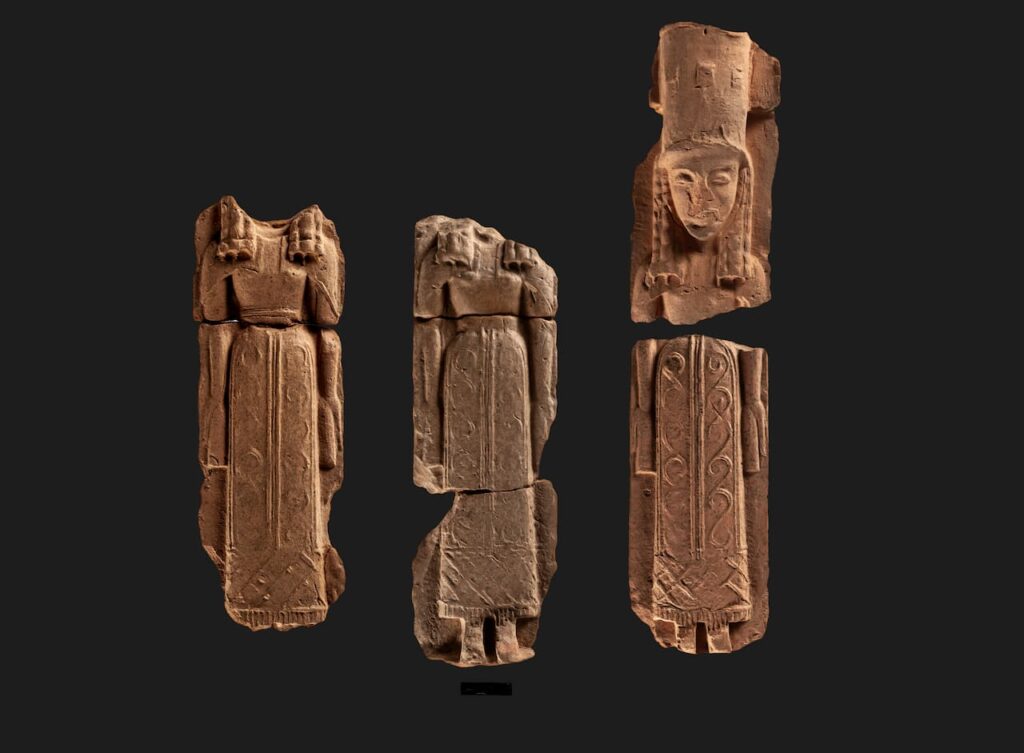

The style of the artifacts provides further clues about the cultural landscape of the time. Plaques depicting the mythical sphinx, a creature with a woman’s head and a lion’s body, reveal potential Near Eastern influences on early Greek culture. Similarly, depictions of women adorned in distinctive attire, including the high, cylindrical “polos” hat and the “epiblema” cloak, offer insights into seventh-century BCE fashion and iconography.
While no written accounts detail the specific rituals performed at Anavlochos, Dr. Gaignerot-Driessen theorizes that these offerings may have been connected to rites of passage or initiation ceremonies for women. “Perhaps young women or mothers offered these terracotta figures to a deity seeking protection during significant life stages,” she suggests.
This summer, Dr. Gaignerot-Driessen will lead a group of University of Cincinnati students to Crete for hands-on fieldwork. They will collaborate with specialists to analyze the excavated remains and even experiment with local clays to create and break their own replica figurines. This practical approach aims to shed light on whether the ancient artifacts were intentionally broken before deposition or fractured naturally over time.
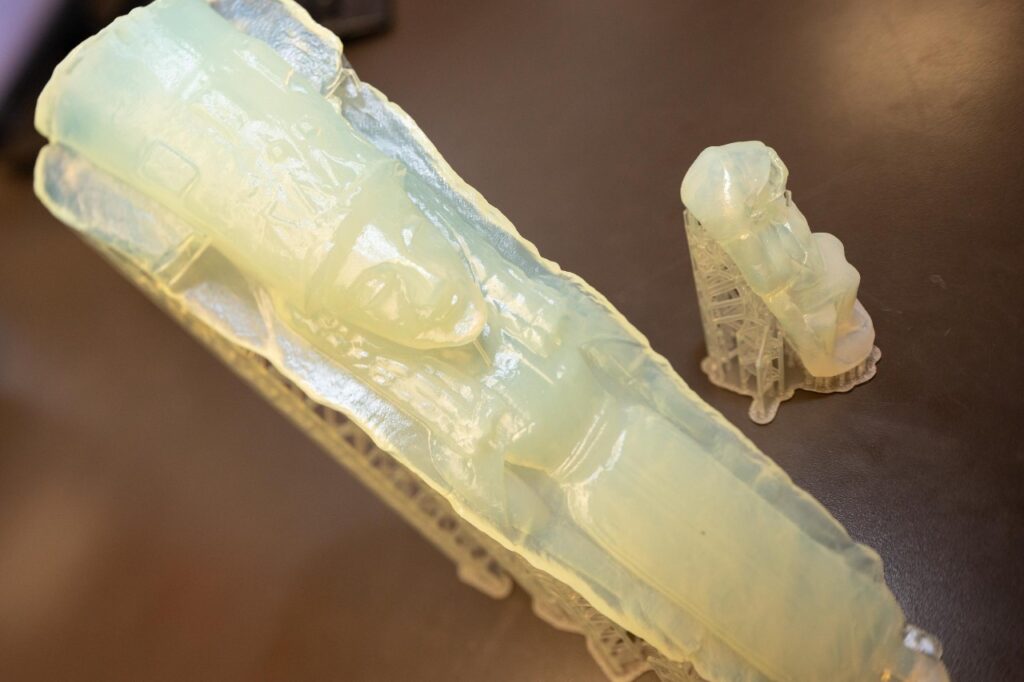

Nicholas Germann, manager of the University of Cincinnati’s Rapid Prototyping Center, highlights the innovative intersection of ancient artistry and modern technology in this project. “We’re essentially reverse-engineering a lost art,” he explains. “By recreating these artifacts with such precision, we can gain unprecedented insights into their creation and eventual degradation. It’s a remarkable blend of historical inquiry and cutting-edge science.”
As Gaignerot-Driessen notes, “This is experimental archaeology. We strive to bring the past back to life to gain a deeper understanding of ancient techniques and cultural significance.” The project not only bridges the gap between ancient and modern methodologies but also enriches our comprehension of the rituals and beliefs that shaped the lives of those who once inhabited Anavlochos.
The “ladies of Anavlochos,” silent sentinels of a bygone era, are slowly yielding their secrets, thanks to the dedication and ingenuity of researchers who are bridging the millennia with modern scientific tools. Their story promises to enrich our understanding of ancient Greek craftsmanship, ritual, and the lives of the people who once climbed this majestic mountain to leave their humble offerings.
Cover Image Credit: Florence Gaignerot-Driessen