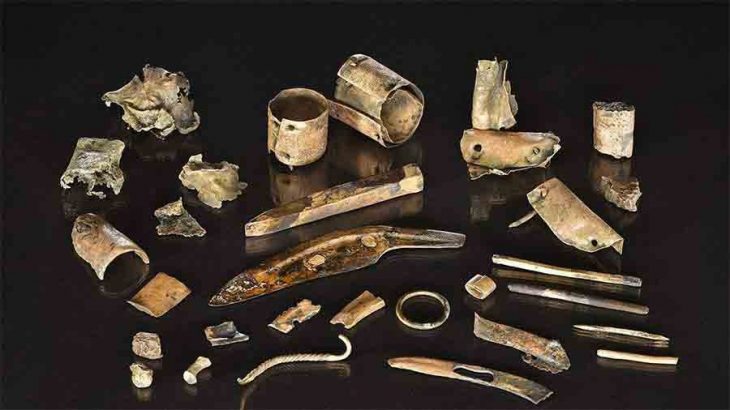
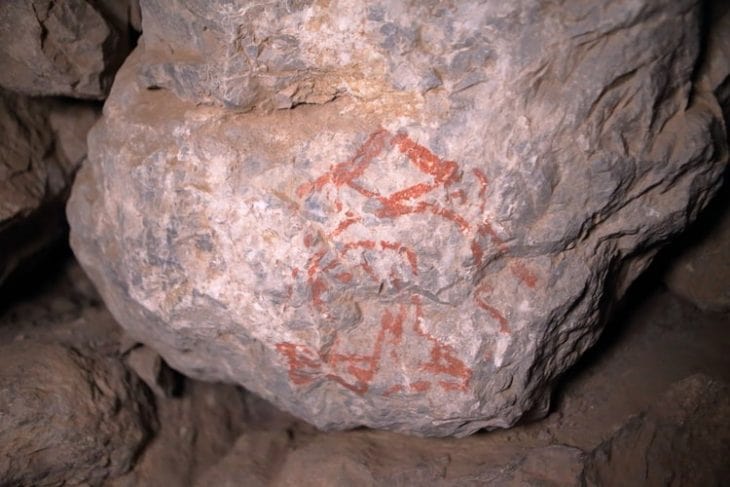
The Mayans excelled at agriculture, pottery, writing, calendars, and arithmetic, leaving an incredible quantity of spectacular architecture and symbolic artwork behind.
The ancient Maya, a varied collection of indigenous people who lived in modern-day Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras, had one of the most sophisticated and complex civilizations in the Western Hemisphere.
Mayan civilization lasted for over 2,000 years, but the period from about 300 A.D. to 900 A.D., known as the Classic Period, was its heyday.
The Maya gained a sophisticated grasp of astronomy during this period. They also discovered how to grow corn, beans, squash, and cassava in sometimes inhospitable environments; how to construct elaborate cities without the use of modern machinery; how to communicate with one another using one of the world’s first written languages; and how to measure time using not one, but two complicated calendar systems.
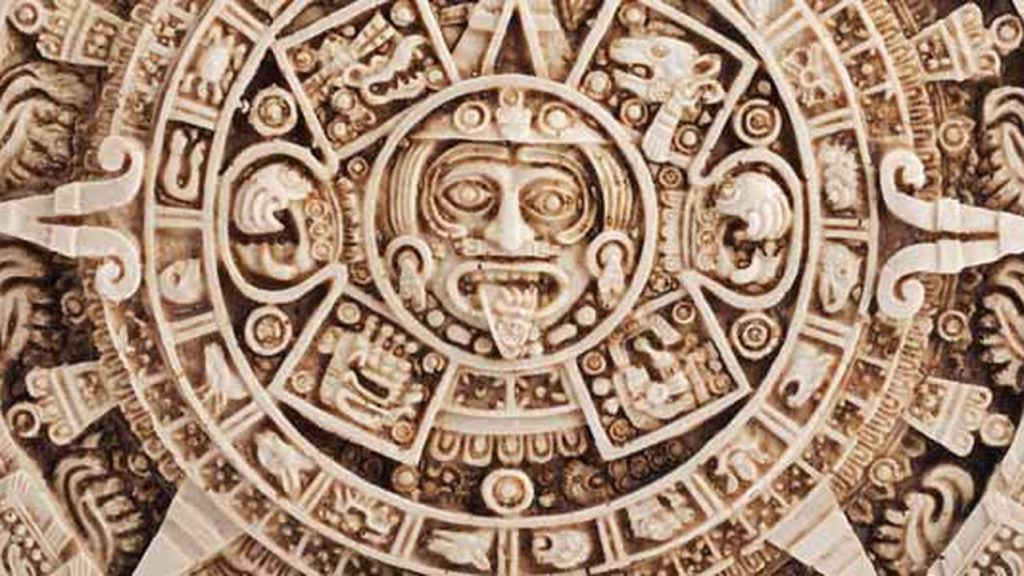

Beginning around 250 AD, the Classical Period was the golden age of the Mayan Empire. Classic Maya civilization reached nearly 40 cities and large populations, including Tikal, Uaxactún, Copán, Bonampak, Dos Pilas, Calakmul, Palenque, and Río Bec.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Excavations of Maya sites have unearthed plazas, palaces, temples, and pyramids. Supported by a large farming population, Mayan cities, although practicing a primitive “cut-and-burn” agriculture, also exhibited evidence of more advanced farming methods such as irrigation and terracing.
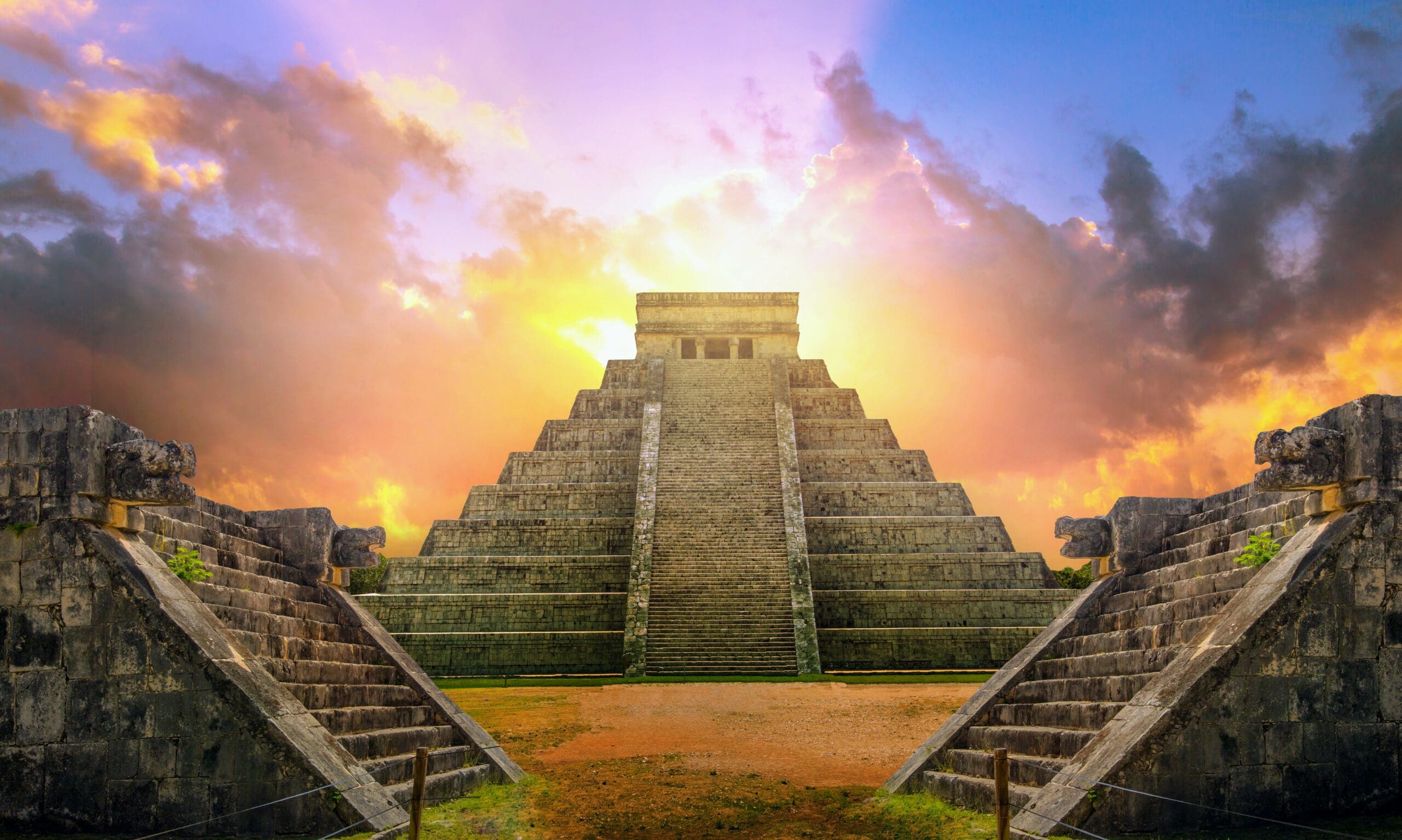
Many of the temples and palaces constructed by the Classic Maya had stepped pyramidal shapes, and they were ornamented with highly detailed reliefs and inscriptions. These structures have earned the Maya their reputation as the great artists of Mesoamerica.
The use of the zero and the creation of intricate calendar systems like the Calendar Round, based on 365 days, and later the Long Count Calendar, intended to last more than 5,000 years, were among the many mathematical and astronomical innovations made by the Maya under the guided of their religious ritual.
The Maya built their temples and other holy buildings using their sophisticated knowledge of astronomy. For instance, the site of the pyramid at Chichén Itzá in Mexico is determined by the position of the sun at the spring and fall equinoxes. On these two days, the pyramid’s shadow at dusk coincides with a sculpture of the Mayan snake god’s head. The snake seems to crawl down into the Earth as the sun sets; the shadow serves as the serpent’s body.
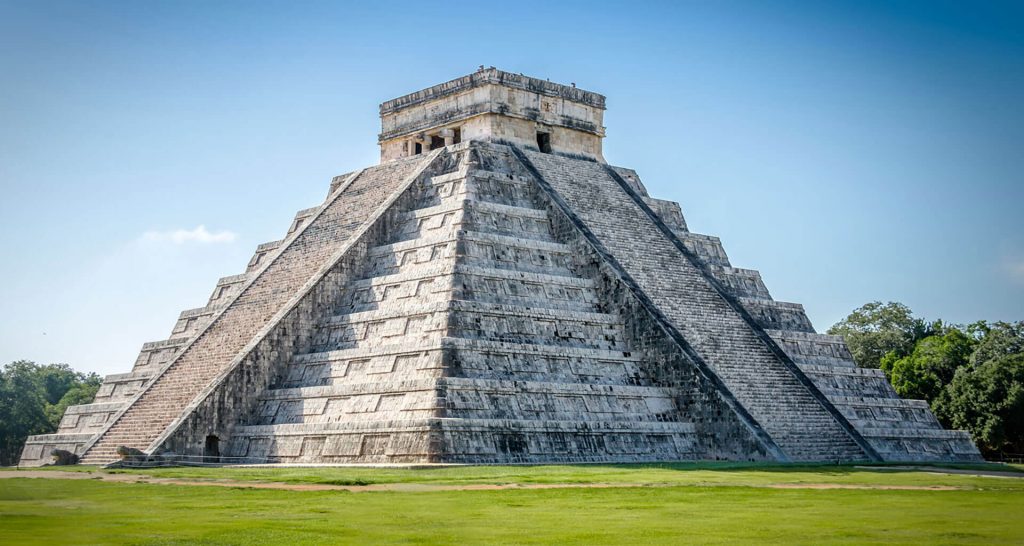

Surprisingly, the ancient Maya were able to construct complex temples and vast cities without the use of metal or the wheel, two things we would consider to be necessary building materials. They did, however, make use of a variety of other “new” inventions and technologies, particularly in the decorative arts. For instance, they created intricate looms for weaving fabric and created a variety of glittery paints using mica, a material that is still used in technology today.
Until recently, it was widely assumed that vulcanization—the process of mixing rubber with other materials to make it more durable—was developed in the nineteenth century by the American (from Connecticut) Charles Goodyear. Historians now believe that the Maya were manufacturing rubber items 3,000 years before Goodyear got his patent in 1843.
According to researchers, the Maya discovered this procedure by accident during a sacred rite in which they blended the rubber tree with the morning-glory plant. When the Maya discovered how durable and adaptable this new material was, they began to employ it in a number of ways, including the production of water-resistant fabric, adhesive, book bindings, figurines, and the giant rubber balls used in the ritual game known as pokatok.

Like many other great lost civilizations around the world, the Maya formalized their language into a codified writing system.
Similar to Ancient Egypt, their glyphs were utilized to express words, sounds, and syllables via the use of images and other symbols. Historians believe that the Mayans used around 800 glyphs to do this and, incredibly, 80% of their language can still be understood by their descendants today.
The Mayans also created a form of an early book that chronicled everyday life, news, the exploits of their gods, and many other things. Like every other sensible civilization, the Mayans were eager to record their history and accomplishments, even going so far as to jot down important occasions on pillars, walls, and enormous slabs of stone, much like the Ancient Egyptians and Romans did. Their books were written on bark and folded into fan-like structures.
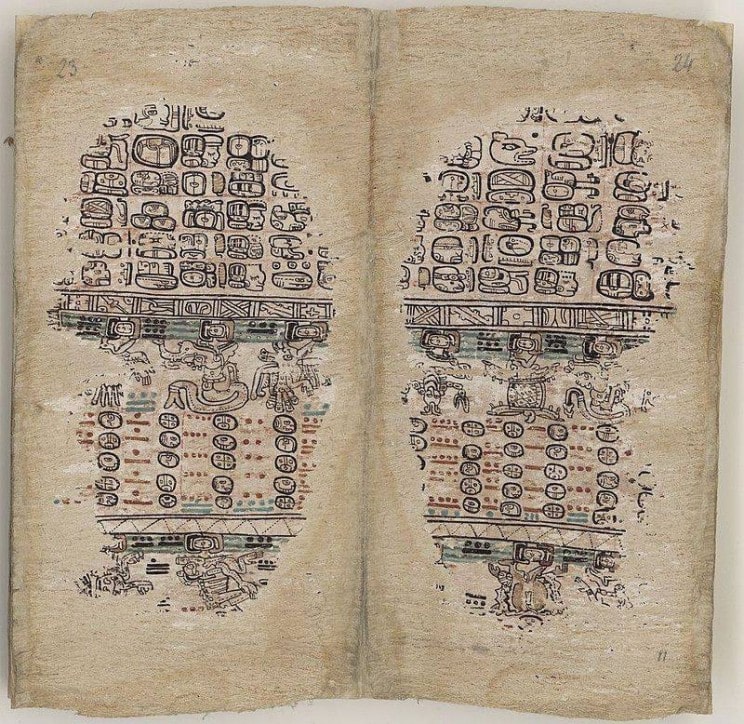

The Dresden Codex, the oldest surviving book written in the Americas, contains tables charting the movements of Venus, Mars, and the Moon. The Maya also calculated the occurrence of lunar eclipses based on observations and tracked the motion of Jupiter and Saturn.
Maya medicine was more advanced than one might think, and like other cultures, medicine was a mixture of religion and science.
The Mayans believed that imbalance and balance were the keys to good and bad health. Health and illness are correlated with balance. They held that a person’s diet, gender, and age were always determining factors in this. They knew about stitches and often used human hair to suture wounds. They also regularly made casts to speed the healing and recovery of fractures and other bone breakages.
By all accounts, they were particularly skilled at dentistry and used iron pyrite as tooth fillings. Mayan ‘witch doctors’ were also skilled in creating prosthetics made from jade and turquoise and used obsidian for making cuts.
Source: Adams, Richard E. W. (2005) [1977]. Prehistoric Mesoamerica (3rd ed.). Norman, Oklahoma: University of Oklahoma Press.