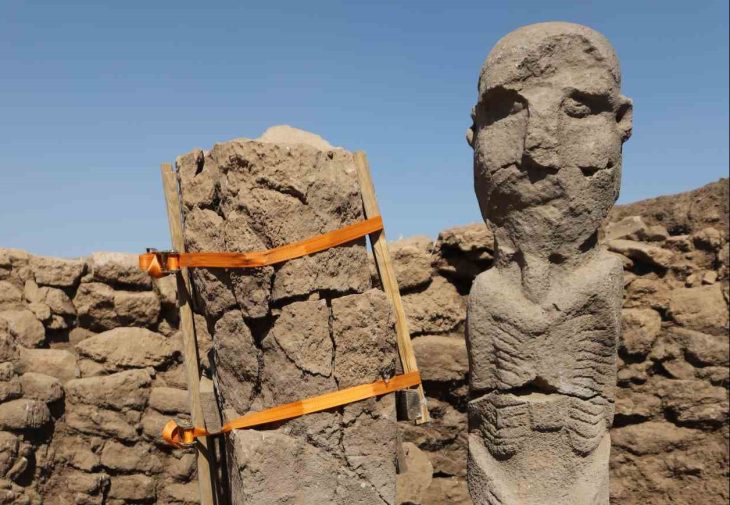
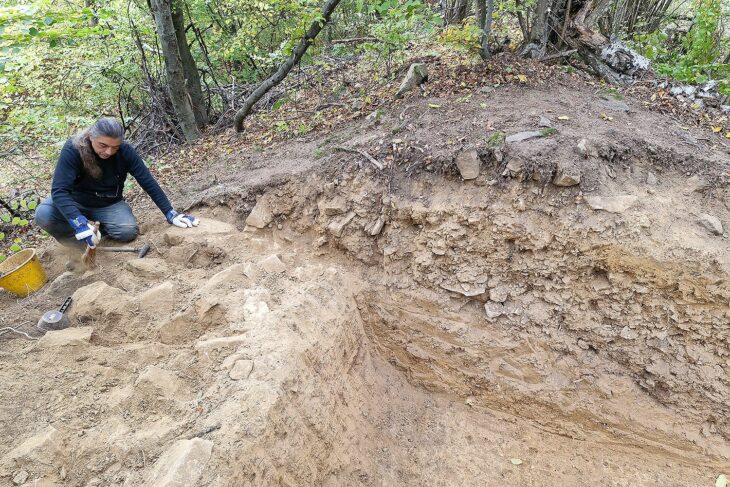
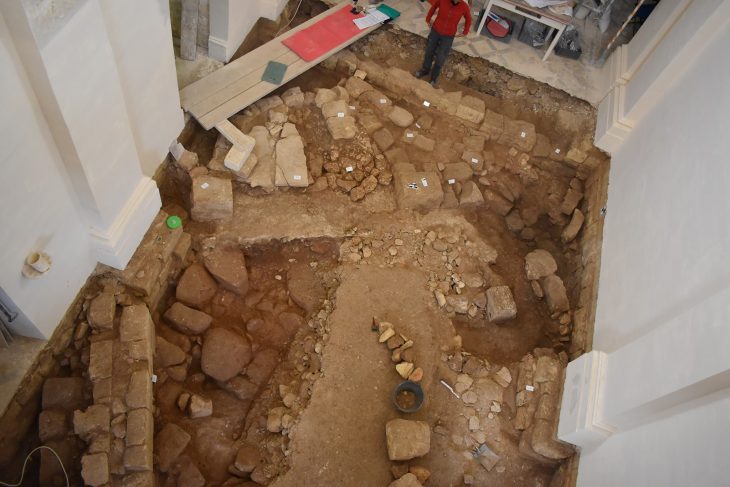
Archaeological excavations at Midas Castle in Yazılıkaya Midas Valley in the Han district of Eskişehir, located in northwest Turkey, will be resumed after 71 years by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism and Anadolu University.
The first archaeological excavations in Midas Castle, at the southern end of the Yazılıkaya Midas Valley in the Han district of Eskişehir, were started in 1936 by Albert Gabriel, the director of this institute, on behalf of the French Archeology Institute in Istanbul.
Short-term excavations were carried out until 1939 under the supervision of Albert Gabriel and E. Haspels.
Turkish scientist Halet Çambel also participated in the work in the castle. Excavation and cleaning work at Pişmiş Castle, 2 kilometers northeast of here, and Midas Castle excavations ended in 1939 with the start of the 2nd World War. Excavations continued in 1949 and 1951 by the French Archeology Institute after the war.

New excavations will begin in Midas Castle, where one of the most important religious monuments of the Phrygians is Yazılıkaya Monument, under the chairmanship of Anadolu University Archeology Department Lecturer Associate Professor Yusuf Polat. Archaeological data to be obtained from Yazılıkaya Midas Kale is expected to provide more information about the Phrygians.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Phrygian Culture Keeps Its Mysterious
Stating that as a result of the excavations, parts of the Phrygian culture that remained in the dark can also be brought to light, Polat used the following statements:
The fact that the information about the Phrygians in the ancient written sources is scarce and in some cases contains contradictory statements is the main reason why this culture still remains a mystery to a large extent. The fact that the written documents are scarce and the existing inscriptions are both short and most of the inscriptions are votive inscriptions does not help to break up the veil of secrecy.
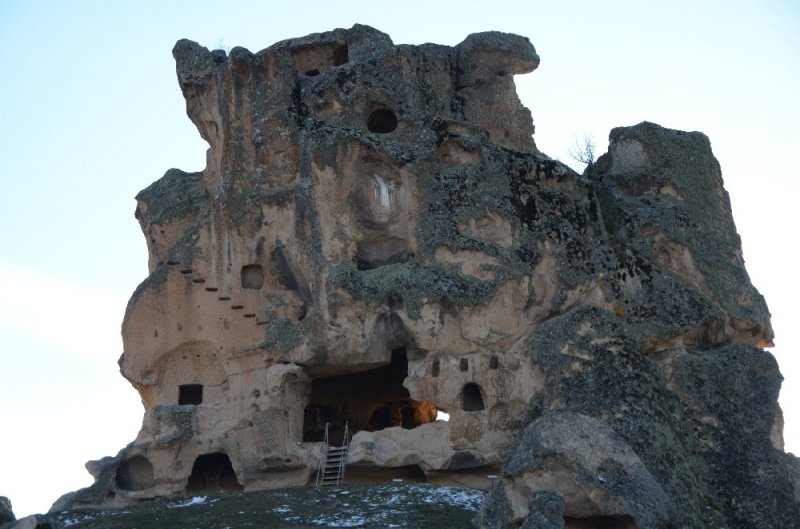

The scarcity of archaeological excavations and research in the areas where Phrygian culture spread also plays a role in the limited information about this culture. Although the Midas Valley is a special and religious area with cult monuments belonging to the Phrygian period, it is a settlement that has the potential to illuminate the obscure part of this culture, with all kinds of archaeological data to be obtained thanks to new excavations in this area.
Cover Photo: Yazılıkaya Monument