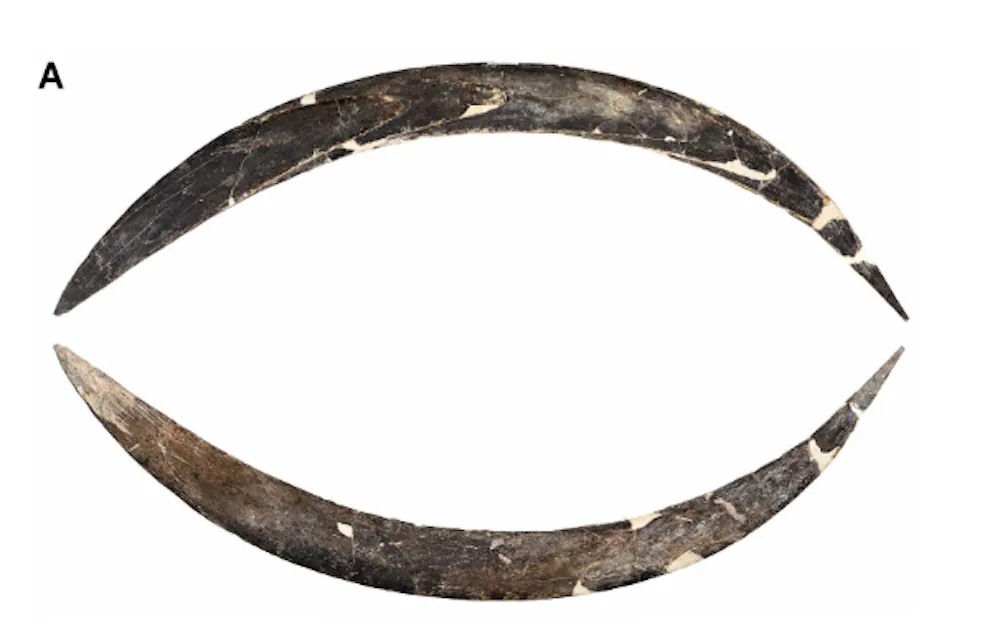
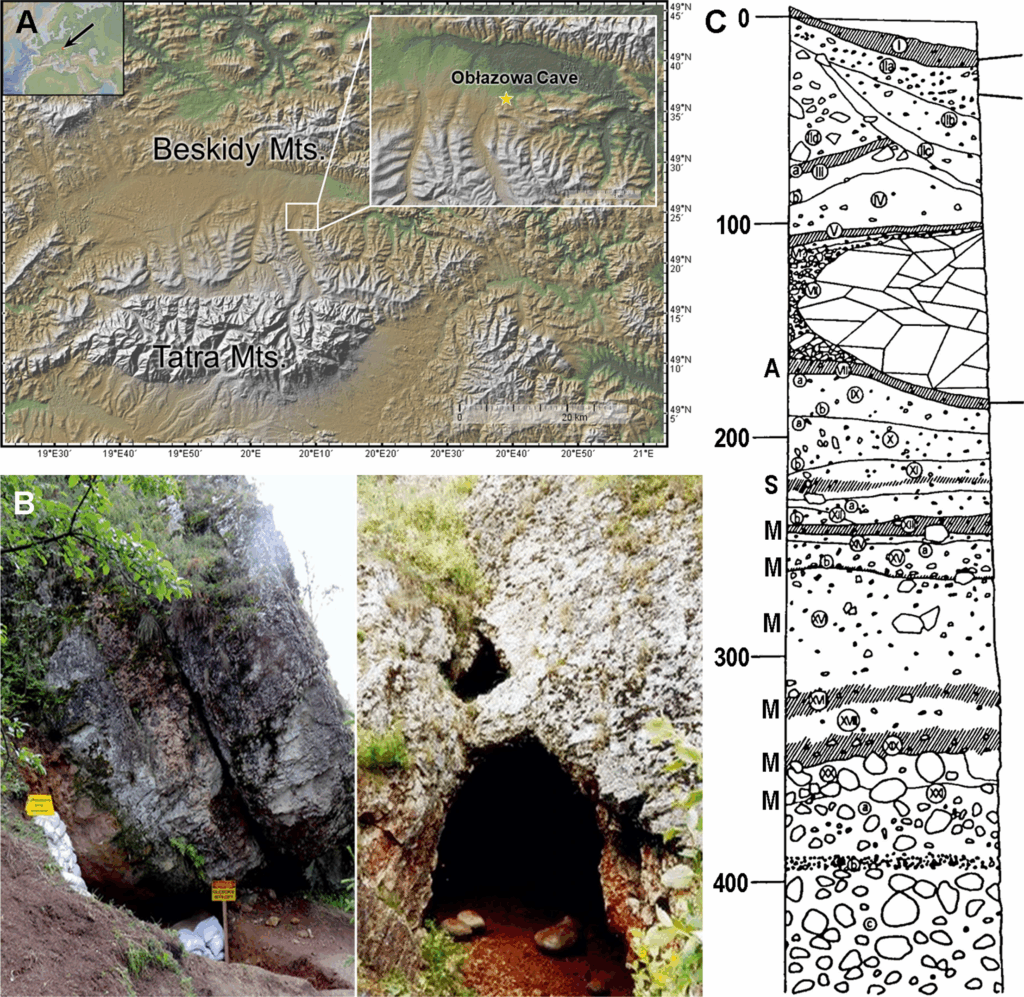
An international team of scientists has uncovered the oldest known boomerang in Europe, a 72-centimeter tool meticulously carved from mammoth ivory, found in Obłazowa Cave in southern Poland. Radiocarbon dating places this artifact between 42,290 and 39,280 years ago, making it one of the earliest examples of Upper Paleolithic technology and early Homo sapiens hunting tools.
Unlike traditional wooden boomerangs, this exceptional prehistoric hunting weapon was designed as a non-returning boomerang, optimized for precision throws rather than aerodynamic returns. Its large size and curvature demonstrate advanced craftsmanship skills during the Late Pleistocene, reflecting the technical ingenuity of early modern humans in Central Europe.
Wear pattern analysis indicates that the boomerang was frequently used by a right-handed individual, providing valuable insights into the daily life and tool use of Paleolithic humans. The boomerang was found alongside a human phalanx identified as Homo sapiens through genetic and morphological analysis, as well as decorative artifacts like shell pendants and bone beads, suggesting possible symbolic or ritual significance.
Due to contamination during restoration, direct radiocarbon dating of the boomerang was not possible. Instead, scientists used Bayesian modeling on associated animal bones and human remains from the same stratigraphic layer to date the artifact precisely. This approach places the boomerang firmly within the Upper Paleolithic period, between 42,290 and 39,280 calibrated years BP.

This discovery challenges the long-held belief that boomerangs and similar throwing tools were unique to Aboriginal Australians or later cultures in Egypt. Instead, it reveals that early Homo sapiens in Europe independently developed complex hunting technologies and symbolic behavior much earlier than previously thought. Isotope analyses of animal remains found at Obłazowa Cave indicate a varied diet, including reindeer, horses, and musk oxen, reflecting adaptive strategies in cold-steppe environments.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The mammoth ivory boomerang from Obłazowa Cave significantly reshapes our understanding of prehistoric innovation, demonstrating that early modern humans possessed advanced technological skills and cultural complexity in Europe around 40,000 years ago. This artifact offers a rare glimpse into the cognitive and adaptive abilities of our ancestors during a pivotal era of human evolution.
Furthermore, this find adds valuable evidence to the ongoing discussion about the interaction and coexistence between Homo sapiens and Neanderthals in Europe. The presence of advanced tools alongside human remains suggests that modern humans brought technological advantages that may have contributed to the eventual replacement of Neanderthals. This insight shifts the timeline for modern human migration and technological development in Central Europe during the Upper Paleolithic.
Additionally, the deliberate selection of mammoth ivory and the transportation of this heavy material over long distances highlight strategic planning and resource investment by early humans. The absence of carving debris in the cave indicates that the boomerang was likely crafted elsewhere and brought to Obłazowa Cave, emphasizing its cultural and possibly symbolic importance beyond mere hunting utility.
The discovery of this ancient boomerang underscores the sophistication of Upper Paleolithic hunting tools and supports the idea that early modern humans in Europe developed symbolic expression and technological innovation independently of other regions such as Australia or Egypt. It also illustrates their adaptability to harsh climates and diverse ecosystems, enhancing our understanding of human resilience during the Late Pleistocene.
Talamo S, Casaccia N, Richards MP, Wacker L, Tassoni L, Nadachowski A, et al. (2025) Boomerang and bones: Refining the chronology of the Early Upper Paleolithic at Obłazowa Cave, Poland. PLoS One. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0324911
Cover Image Credit: The oldest boomerang in the world. Credit: Archaeological Museum in Kraków