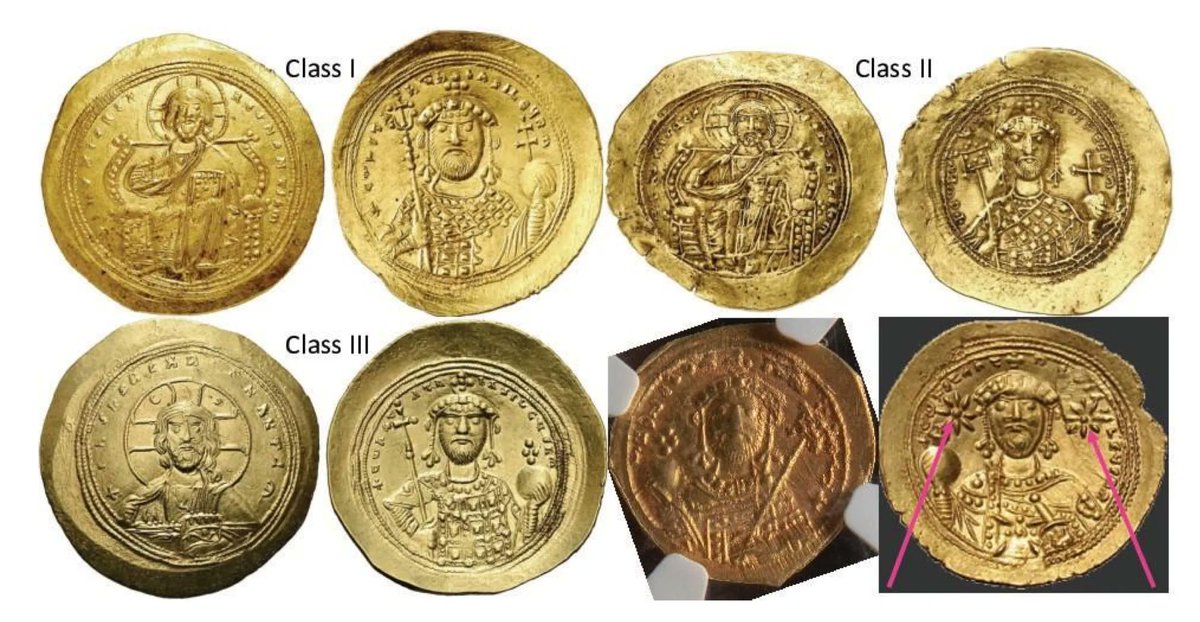
SN 1054 was one of the most spectacular astronomical events of all time. The supernova explosion eventually formed what is today known as the M1—the Crab Nebula. But in 1054 AD, the year it occurred, it was an ultrabright star in the sky and one of only eight recorded supernovae in the history of the Milky Way. However, it was only noted by half of the literate world. Primarily written about in the East, especially in China, SN 1054 was almost wholly absent from the Western record—except, potentially, for a subtle hint at it in the most unlikely of place: some Byzantine coins.
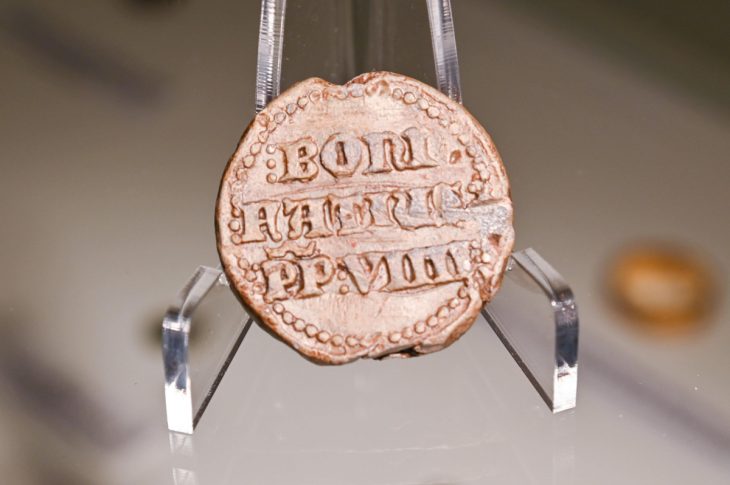
At least, that is the new theory according to a multinational group of researchers in the European Journal of Science and Theology. They found that a special version of a coin minted by Byzantine Emperor Constantine IX showed two stars around the emperor’s head—potentially representing a nod to the existence of SN 1054, despite any written evidence for the supernova’s existence elsewhere in the Christian world.
Scholars in Japan, China, and the Islamic world had no problem noticing the new bright star in the sky. So why didn’t the Christians? There has been an ongoing debate in the history of astronomy community surrounding this question for decades, with no definitive answer. However, the general consensus is that Christian scholars feared that pointing out a change in what, at the time, were thought to be the perfect and inviolable heavens would cause too much of a ruckus within the church. Theological doctrine held sway in the Christian world at the time, and calling into question any part of that doctrine could lead to excommunication or even death. It would have to be a brave scholar to risk such a fate for no tangible reward.
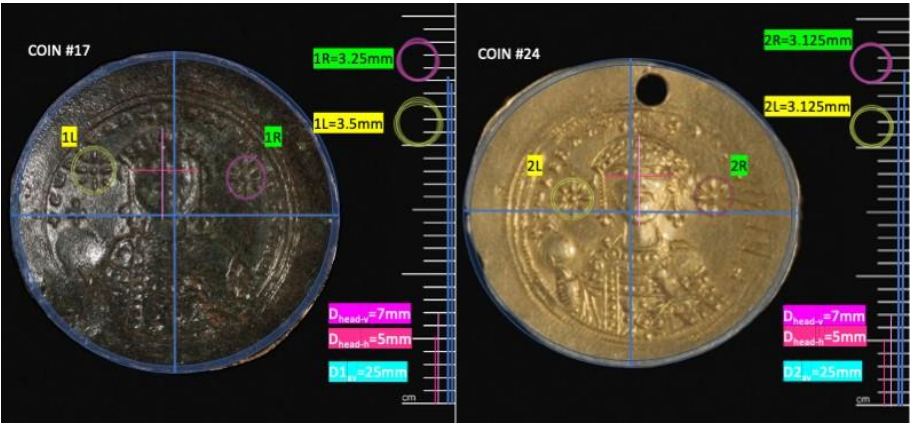
Which makes it even more interesting that a metalworker, or maybe one of the otherwise cowed scholars, might have had the nerve to do so. The researchers found a special edition of a coin, known in the technical jargon as the Constantine IX Monomachos Class IV coin, which has two stars compared to the single star noticeable on the other three classes of coins minted during the monarch’s reign.
The Class IV is thought to be minted between the summer of 1054 and the spring of 1055 and has two noticeable stars on either side of the monarch’s head. One star is thought to represent Venus, the Morning Star, while the monarch’s head itself is believed to represent the sun. The other star, though, could potentially represent the “guest star” (as Chinese observers called it) of the SN 1054 supernova.
What’s more, the size of the stars differs slightly between the 36 coins of that vintage the researchers were able to find in museums around the world. The researchers also hypothesize that the changing size of the star could reflect the gradual dimming of the supernova in the sky during this period.
If so, it would be a subtle but effective nod to the striking astronomical reality going on overhead at the time. But, as with much ancient history, it is hard to separate fact from speculation. The authors themselves point out that they don’t know how many Class IV coins were minted, nor their precise dates and they have no concrete proof that the second star represents a fantastic astronomical event. But, many romantics would like to think that, after whoever minted the coins took what might have been considered a massive risk at the time, a team of scholars over 1000 years later finally truly grasped why they did so. We can certainly appreciate that story, even if the factual basis for it is still up in the air.
Lead Image: Coins minted during the reign of Constantine IX
















