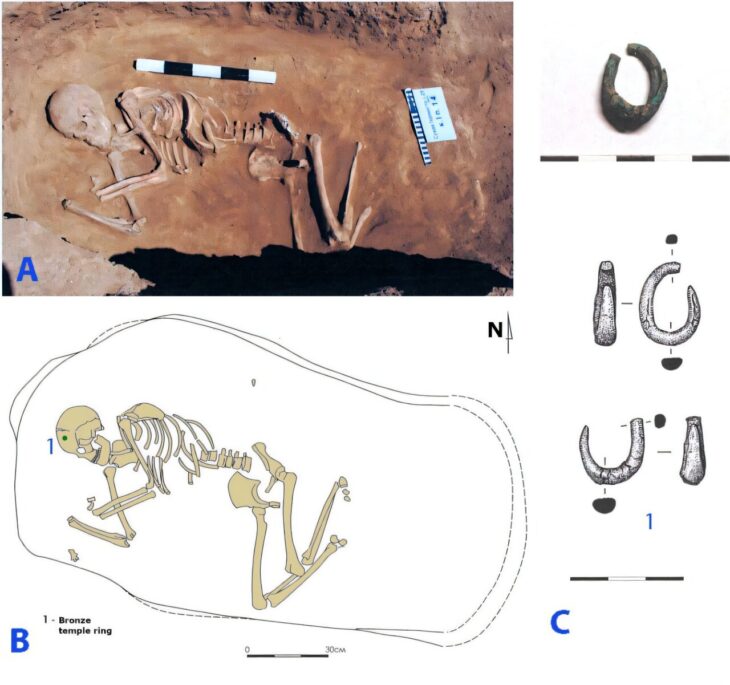
The population of the Copper Age mega-sites in what is now Ukraine and Moldova had a predominantly vegetarian diet.
In the Black Sea region, more precisely in today’s Ukraine and Moldova, the mega-settlements of the Cucuțeni-Tripolje culture emerged around 6,000 years ago. With an area of up to 320 hectares and around 15,000 inhabitants, they were not only the largest settlements of their time, but are also considered the oldest cities in Europe – even older than the urbanization in Mesopotamia. Providing these mega-settlements with food – a topic that has long puzzled researchers – is now the focus of a new study.
The study published by scientists from the SFB 1266 at the Kiel University (CAU) on December 18th in the renowned journal PNAS now provides answers. “The supply of the residents of the mega-settlements was based on extremely sophisticated food and pasture management,” says Kiel paleoecologist Doctor Frank Schlütz.
Almost everyone knows the stories about the comic character Popeye, the sailor, who supposedly owed his strength to his great love of spinach. As we know today, science has long overestimated the value of this vegetable. In complete contrast, peas are actually highly beneficial for human nutrition due to their high protein content. However, their importance has so far been greatly underestimated by science.
Even the early Trypillia farmers, who lived almost 7,000 years ago in what is now Ukraine and Moldova, valued a diet consisting mainly of grain and peas, which allowed them to largely do without meat. This is shown by the recent study by Kiel University, which was carried out under the direction of the archaeologist Professor Johannes Müller together with researchers from Ukraine and Moldova as part of the latest investigations into Trypillia societies.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
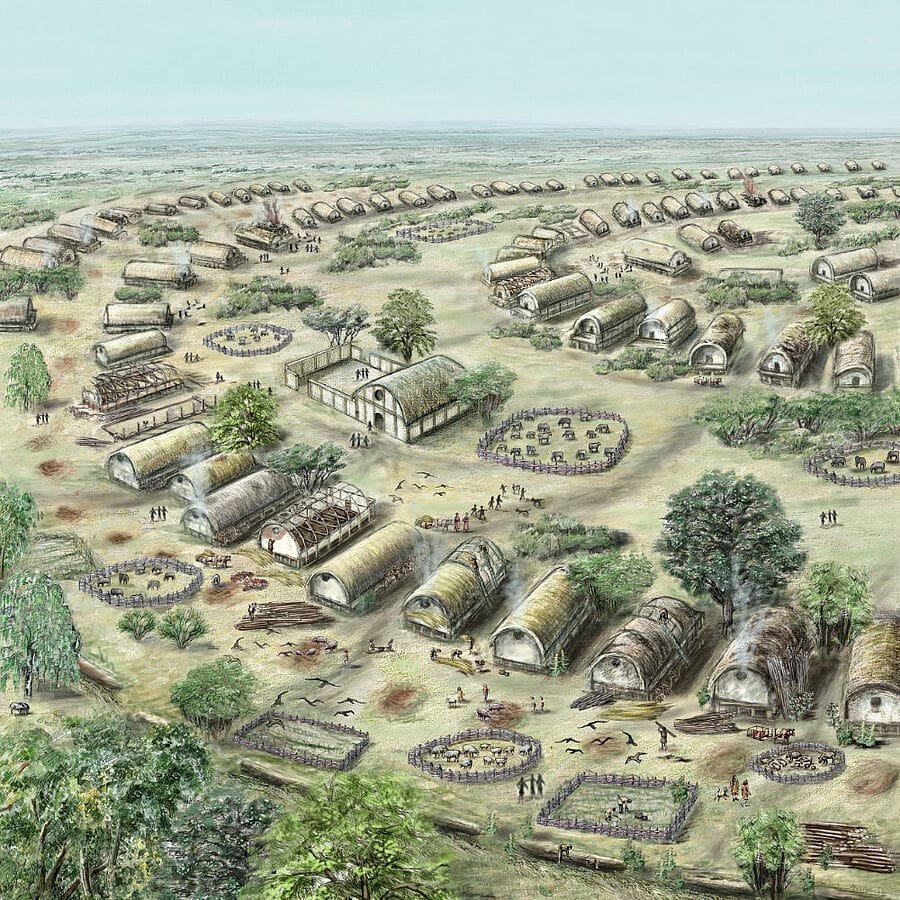

Early agriculture and mega-sites
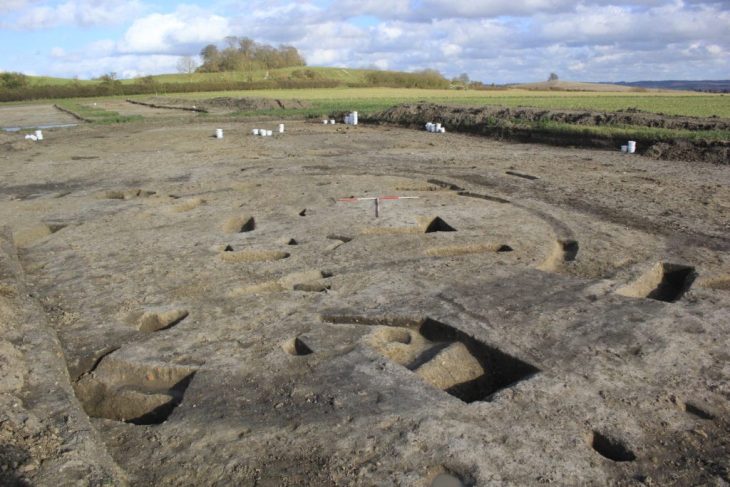
These societies based on agriculture and stockbreeding formed around 4800 BCE in the forest steppe north of the Black Sea. Starting around 4150 BCE, the people of the Trypillia society created huge planned settlements. With areas of up to 320 hectares, they were the size of a few hundred football fields. The settlements were laid out in an extremely planned manner. It is estimated that up to 15,000 people lived together in them. These mega-sites had a clearly structured layout with manageable neighbourhoods, including meeting houses, in which the people who came together were integrated and involved in social decision-making processes. The heyday of the Trypillia society with its gigantic settlements, compared to all other societies of the time, which are considered to be the earliest cities in Europe, lasted for about 500 years. It only collapsed when the population was cut off from communication structures and decision-making processes were centralised.
Analyses of carbon and nitrogen isotopes provide answers
Due to the size of the settlements, daily life in them was comparable to that of other agricultural towns, and the people were therefore largely farmers. But how could such large groups of people secure their food supply with Neolithic technology? “To answer this question, we have determined the carbon and nitrogen isotope composition of hundreds of samples over the last 10 years,” says Johannes Müller.
The archaeologists primarily measured animal and human bones that they excavated. “We then specifically supplemented this data with isotope measurements on charred peas and cereal grains from soil samples from various Trypillia settlements,” reports archaeobotanist Professor Wiebke Kirleis.
The isotopes can be used to make statements about how domestic animals were kept thousands of years ago, whether the cultivated crops were fertilised and what role plants and animals played in human nutrition.
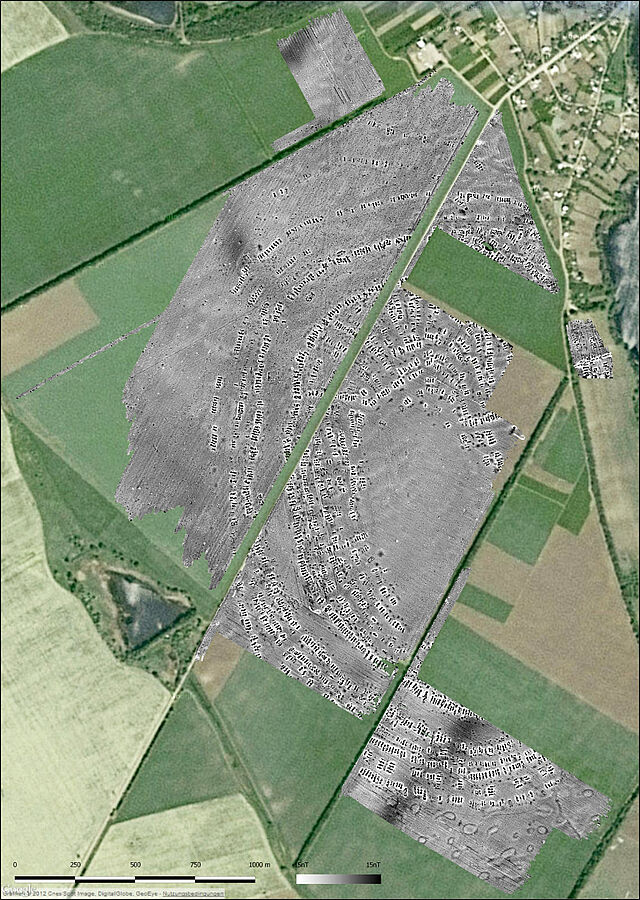

Almost exclusively vegetarian
“We concluded that a large proportion of the cattle and sheep were kept on fenced pastures. Moreover, the manure of the animals produced there was used by people to intensively fertilise the peas in particular,” says Frank Schlütz. Accordingly, peas and grains formed the main pillars of a human diet that was not only nutritious but, thanks to the peas, also balanced in terms of essential amino acids. The resulting pea straw was probably used to feed the livestock on the pastures. Thanks to this close connection between crop production and stockbreeding, the people of the mega-sites were able to eat sufficiently and healthily. The labour-intensive and resource-consuming production of meat was largely eliminated. The reasons for the decline of the settlements were of a social nature, as the archaeologist Dr Robert Hofmann reveals: “As we know from previous studies, social tensions arose as a result of increasing social inequality. People turned their backs on large settlements and decided to live in smaller settlements again.” Around 3000 BCE, the Trypillia societies disappeared from the scene.
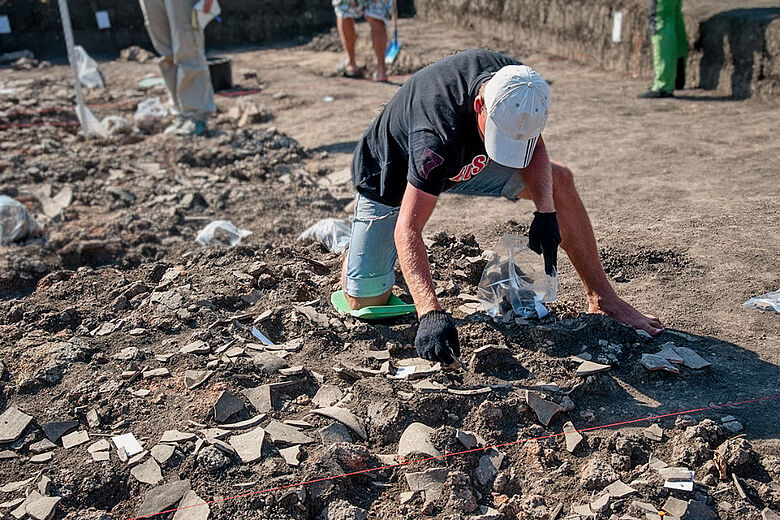
Cover Photo: During the archaeological excavation of the Trypillia settlement of Stolniceni, located in the northwest of Moldova, restorer Stanislav Fedorov recovered ceramic vessels from the remains of a house that burned down in the 4th millennium BC. © Prof. Dr. Johannes Müller, University of Kiel