The University of Alicante Institute for Archeology and Historical Heritage (INAPH) Researchs discovered a collection of buried Roman antiquities going back to 100 BC at the recent Catlar’s Menorcan excavation site.
The island of Menorca (Minorca) is one of Spain’s Balearic islands in the Mediterranean.
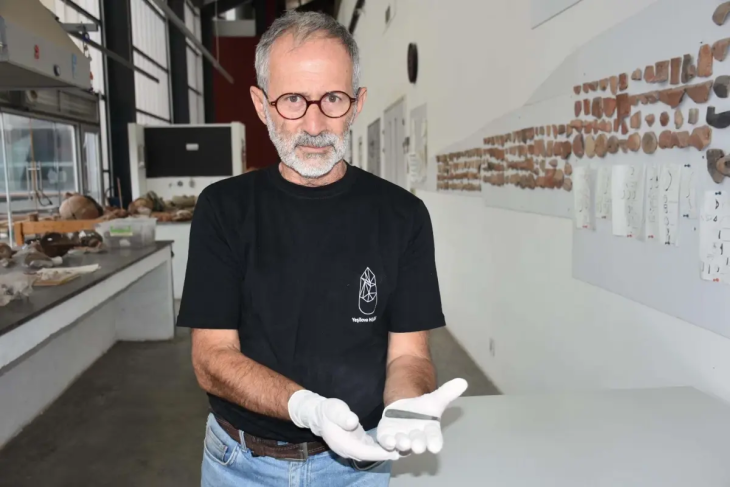
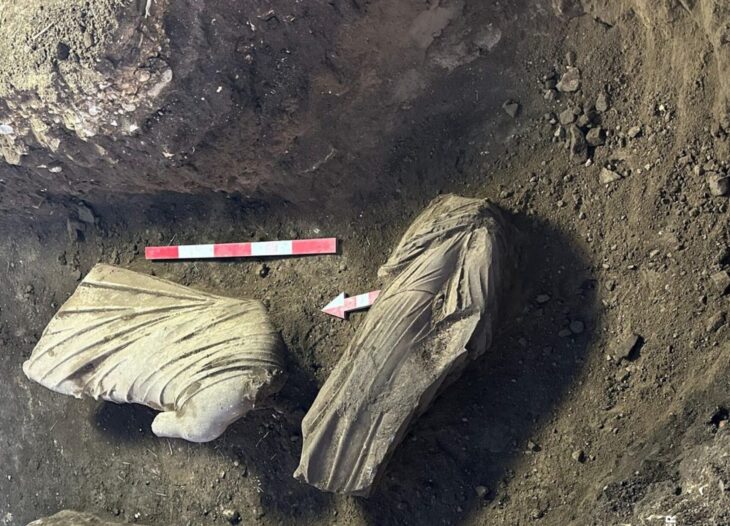
Fernando Prados, researcher, and director of the Modular Project: Phoenician-Punic Architecture at the Alicante University Archeology and Historical Heritage Research Institute (INAPH), briefed on the discoveries of the sixth season and said that they brought an “outstanding” collection to the Ciutadella Museum.
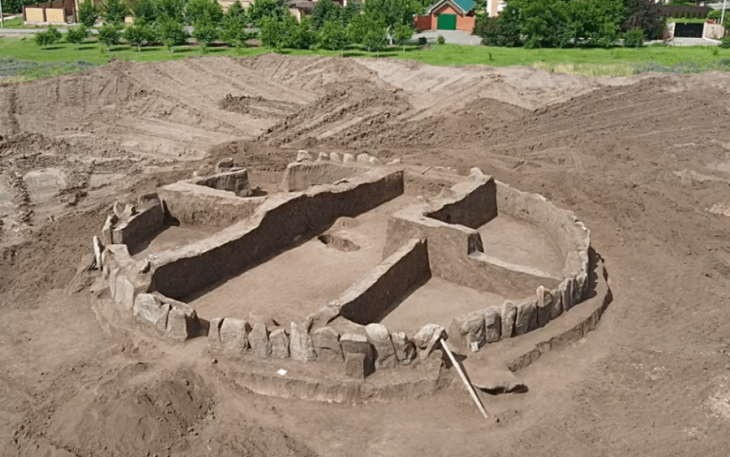
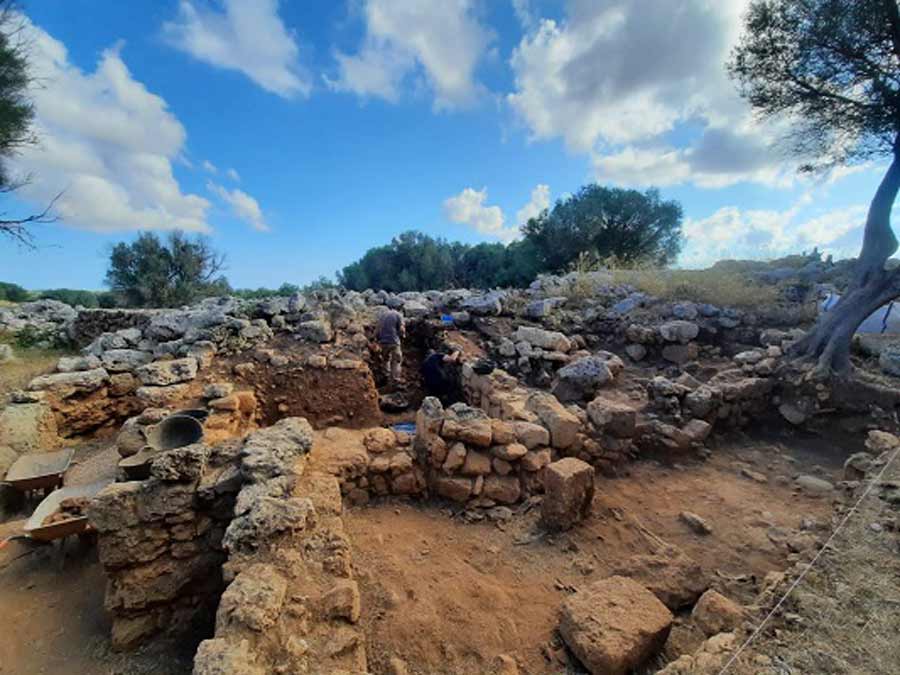
One year after being unable to excavate due to the COVID-19 pandemic, archaeologists have resumed work in the Crooked Gateway area. This kind of door is a characteristic of Punic culture, and it was used as a defense system to prevent possible siege by the Romans.
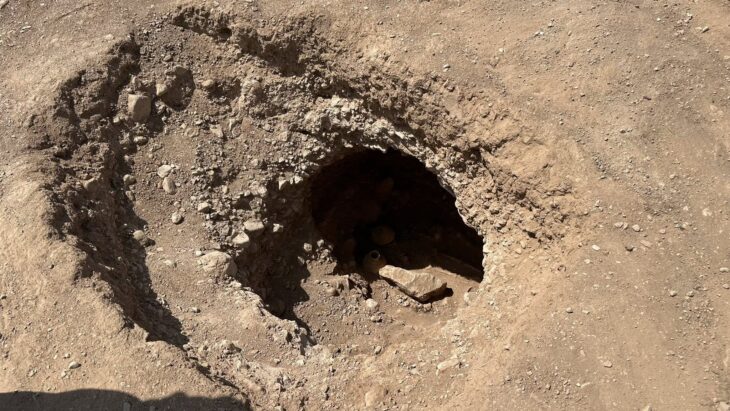
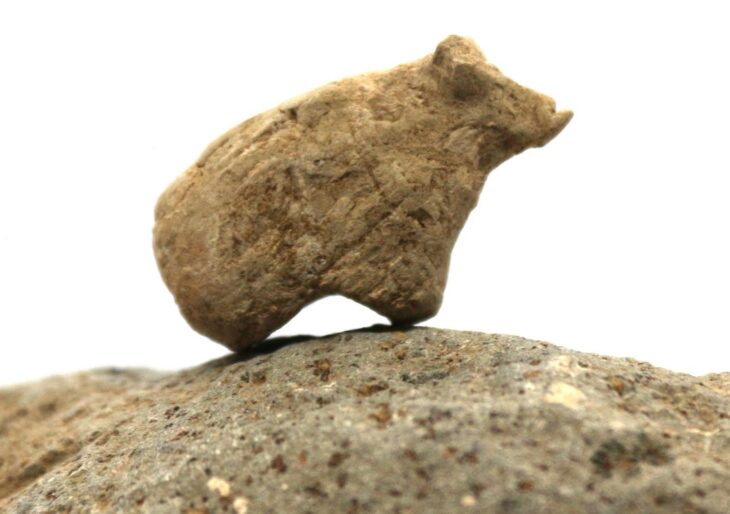
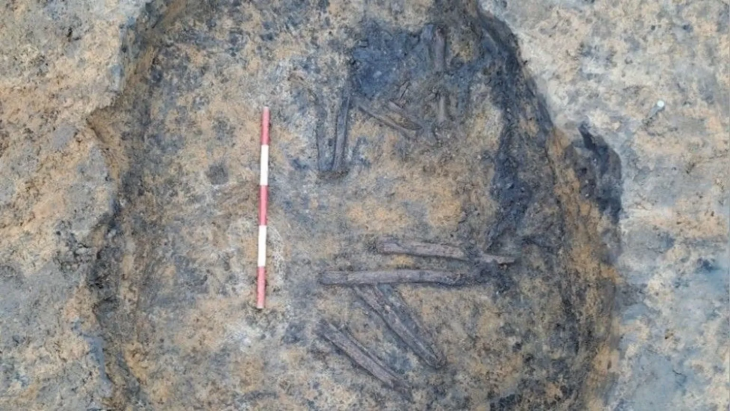
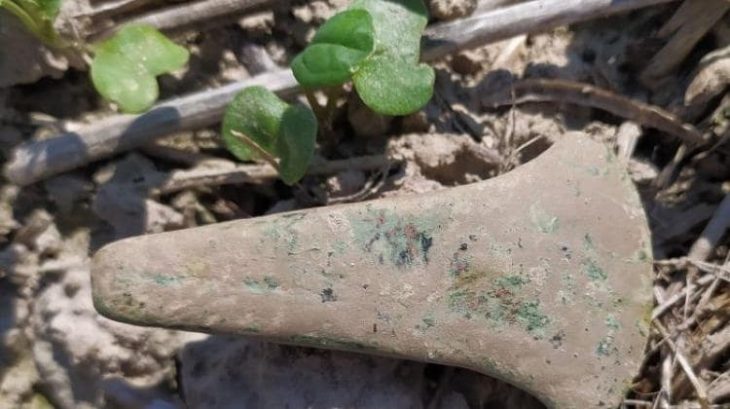
The discovery of this blind gate means a huge leap in Menorca’s historical knowledge. Excavation of the gate and the street leading to the gate led to the discovery of a material store buried above the ground. A large number of typical items carried by Roman soldiers were found: weapons, knives, three arrows, spearheads, projectiles, surgical tools, bronze spatula probes, etc.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Although finding this sort of material is not rare, it is unusual for it to be in such pristine shape.
Their location next to the Son Catlar gate is significant because it shows they were buried as talismans or good luck charms.
As Prados said, might be related to the mystical protective properties ascribed to it by the Romans when closing doors against bad spirits.
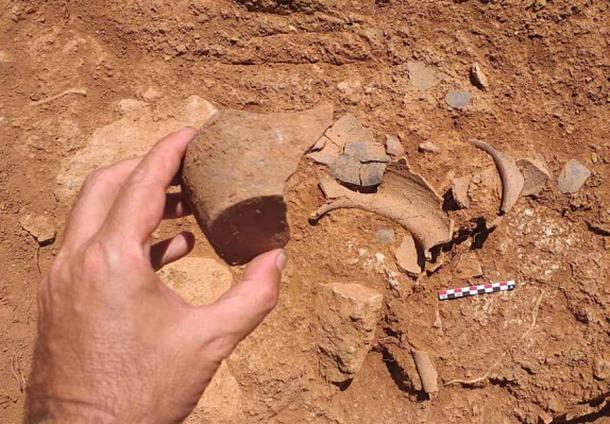

Roman soldiers were very superstitious and used to perform these rituals. At that time, the world of doors was full of magic. The Romans gave city gates a sacred value, and to completely seal a city gate would require certain magical actions.
According to the UA researcher, the conservation of the full perimeter of the wall at Son Catlar makes the site a source of considerable importance since it gives a great lot of opportunity for researching the archaeology of conflict and war.
The Modular Project’s research program on the island is supported financially by the Menorca government, INAPH, and the Cap Blanch campground, as well as logistically by the Ciutadella municipal council and the Mart I Bella Historical-Archaeological Association.
Between the first century BC and the first millennium AD, the Romans were one of many foreign empires and kingdoms that conquered the Balearic island nations, including Menorca.