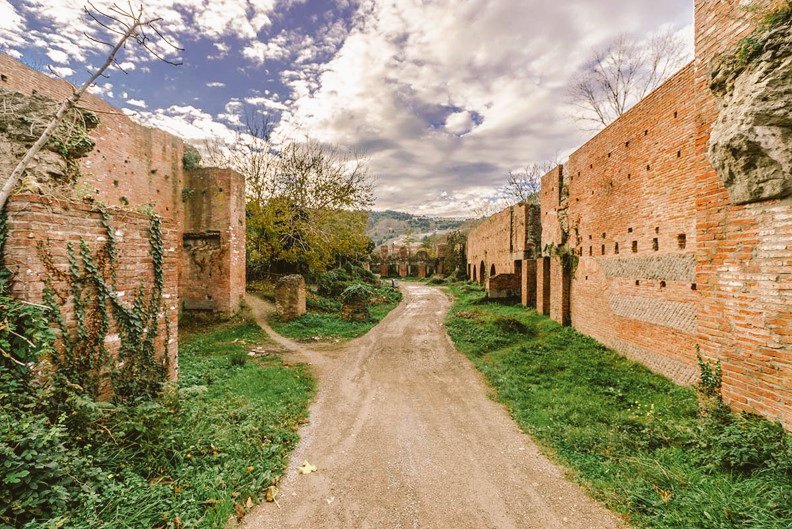
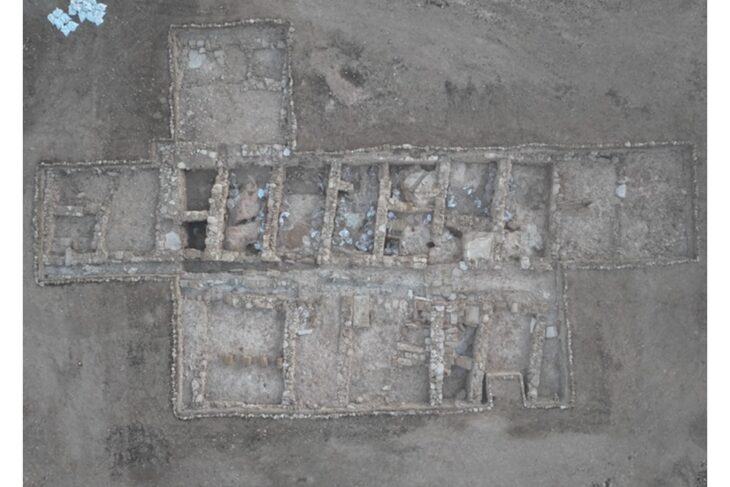
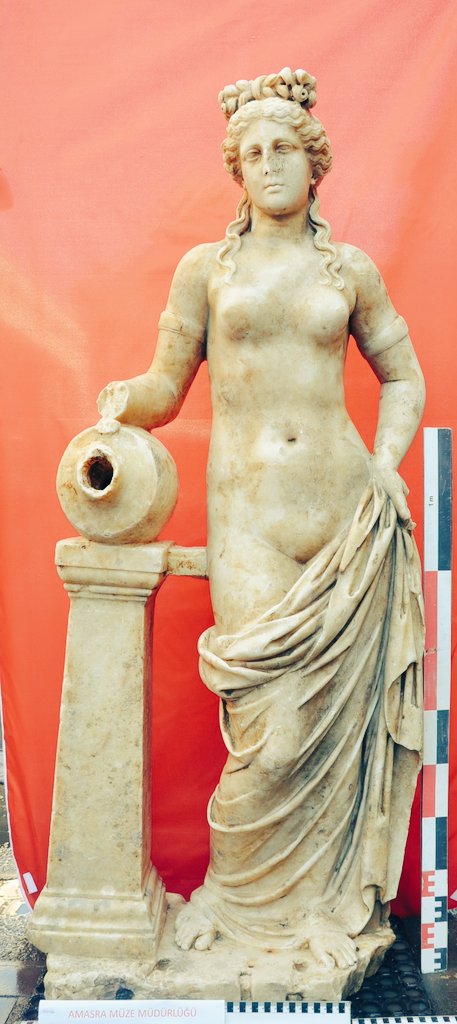
Excavations in the ancient city of Amastris, located in the Black Sea province of Bartın’s Amasra district, have unearthed a statue of a nymph thought to be 1800 years old. The artifact is set to be exhibited in the Amasra Museum soon.
Amasra’s coast was host to the Phoenician colony, Sesamus, in the 12th century B.C. The colony’s heyday was during the rule of Iranian Princess Amastris. It was among the most important of the Byzantine fortress harbors on the south shore of the Black Sea.
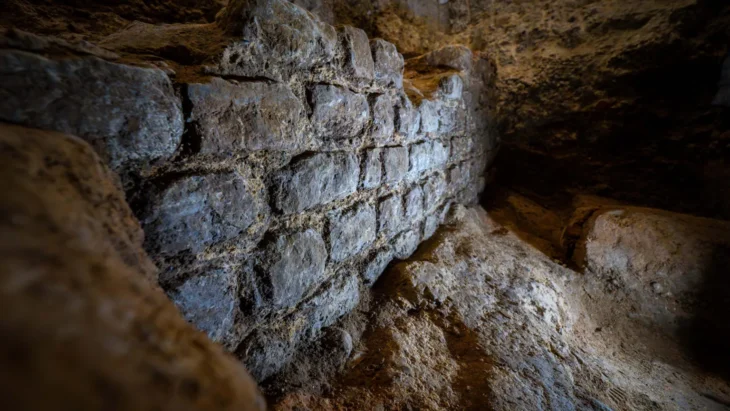
The site of the excavation was donated to the Ministry of National Education in 2014 and construction started for the building of a school on the land in 2017 when some remains believed to belong to the Roman period were discovered, upon which the construction works were stopped and the area was taken under protection.
Excavations are carried out under the direction of the Amasra Museum Directorate and the scientific consultancy of Bartın University.
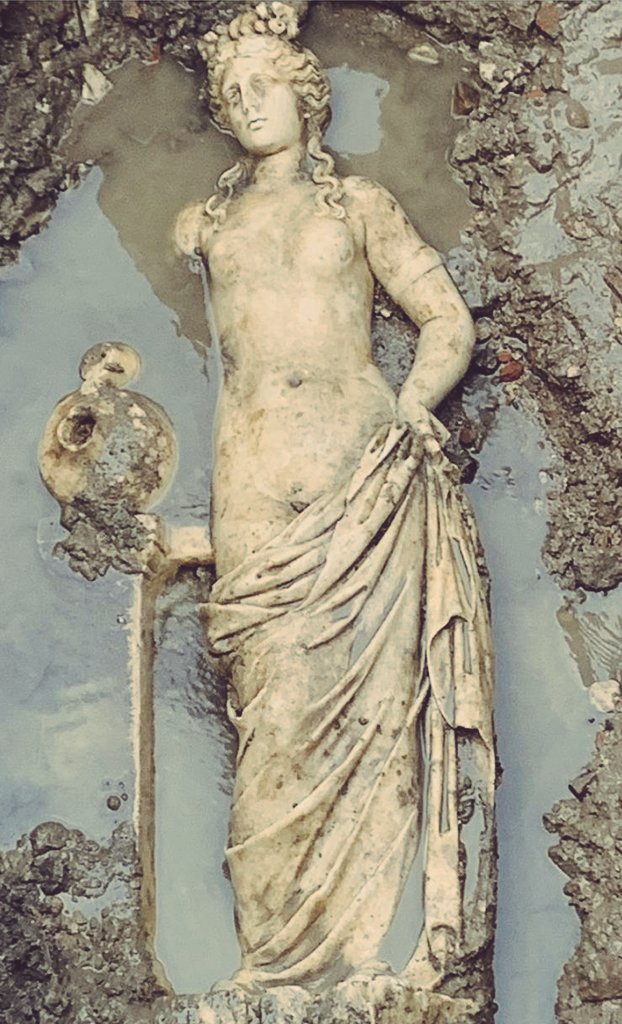

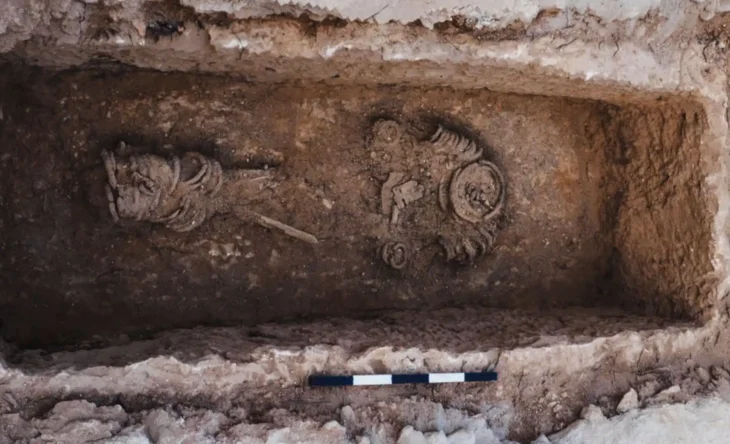
During the excavations carried out under the direction of Amasra Museum Director Zübeyde Kuru, a statue of a water nymph, thought to be 1800 years old, was found 3 meters below the surface.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In the statement made on the social media account of the Excavations and Research Department of the General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, the following statements were made:
“In our excavations in Bartın, Amasra, Gymnasium, a 1.53-centimeter-high statue belonging to the 2nd century AD and considered to be a Nymphe (water nymph) was unearthed.”

Situated in the ancient region of Paphlagonia, the original city seems to have been called Sesamus and it was mentioned by Homer.
The place derived its name Amastris from Amastris, the niece of the last Persian king Darius III, who was the wife of Dionysius, tyrant of Heraclea, and after his death the wife of Lysimachus.
Amastris (ca. 340/39-285/84), was first married to Craterus, then to Dionysius of Heraclea, and finally to Lysimachus. She was the mother of four known children; was supposedly divorced when Lysimachus married Arsinoe; Amastris founded an eponymous city in Paphlagonia; she was the first queen to issue coins in her name; and was allegedly murdered by her sons for interfering in their affairs.