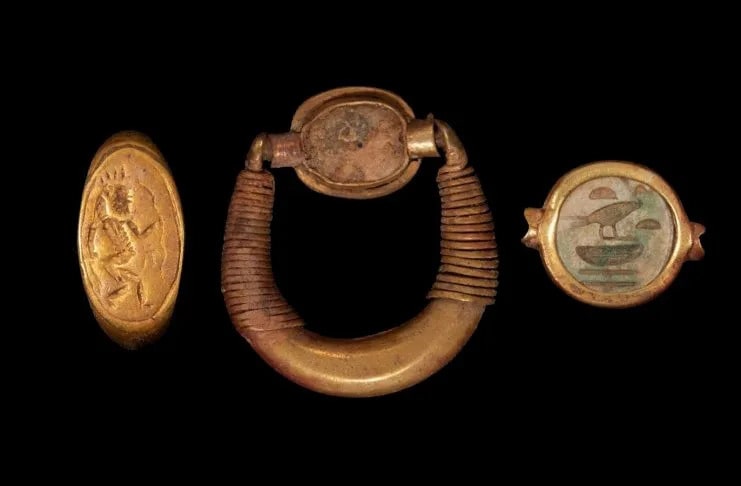
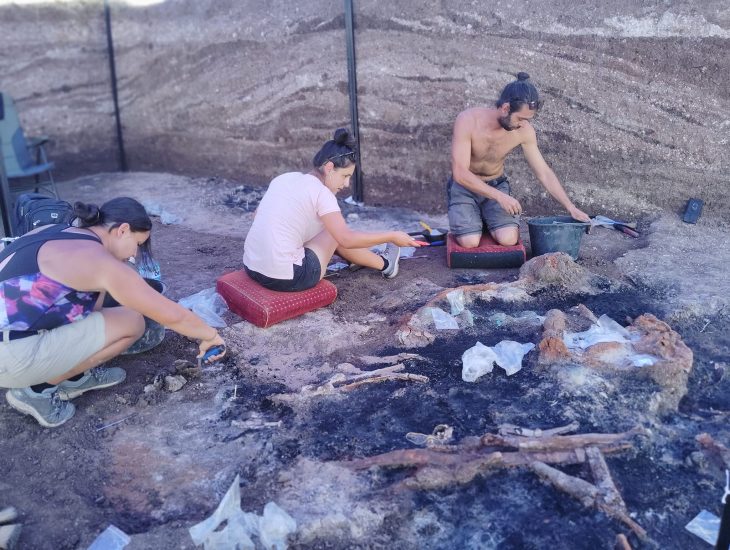
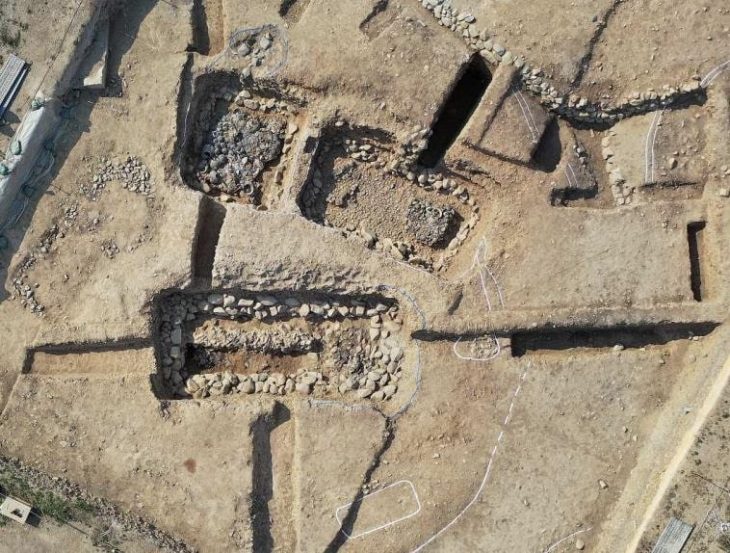
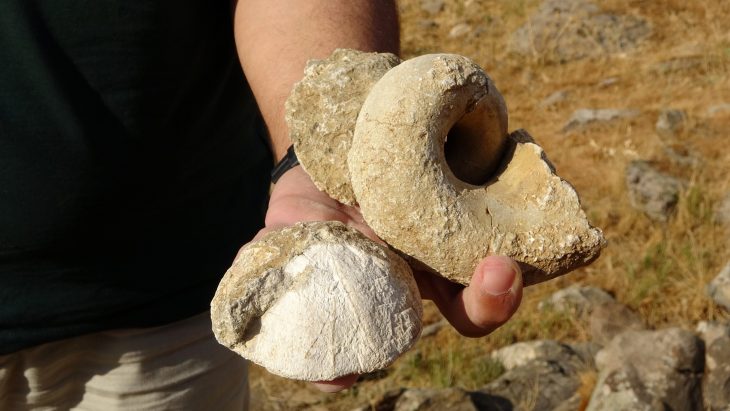
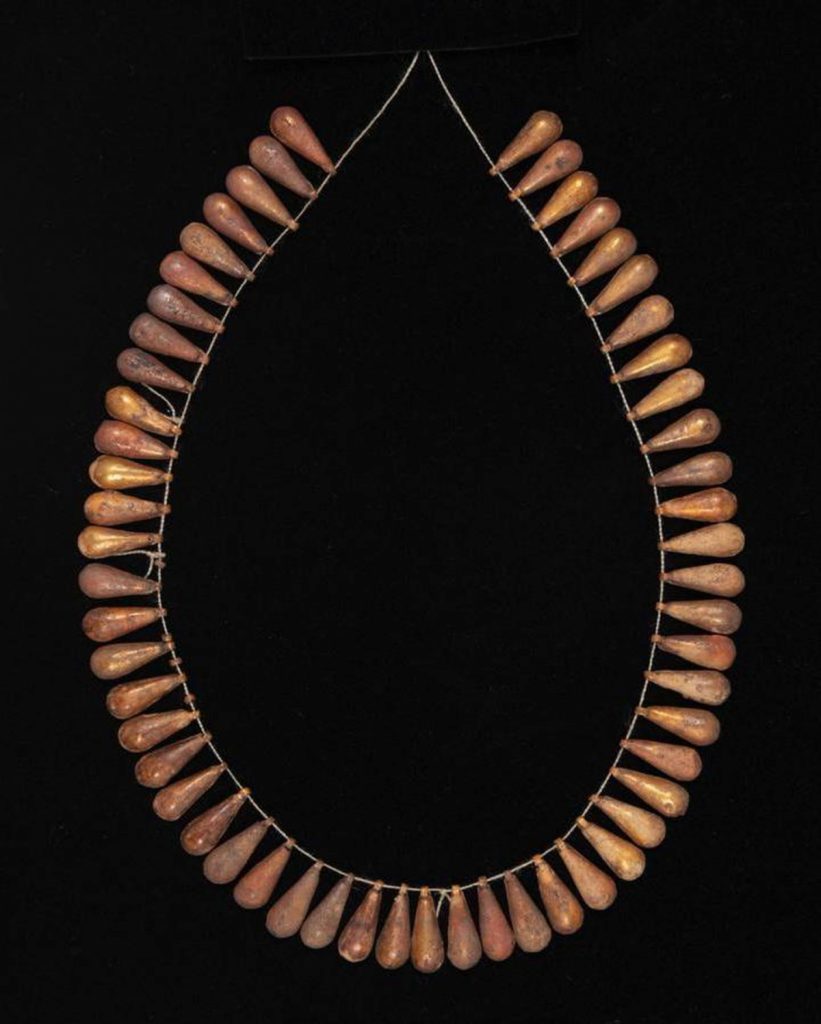
Archaeologists discovered a collection of ornate jewelry at the Tell El-Amarna necropolis on the Nile River’s eastern bank in modern-day Minya, Egypt. Finds comprises three rings and one necklace.
The necropolis was the burial ground for the city of Amarna, constructed in 1346 BC to serve as the capital city of the Pharaoh Akhenaten, the 10th ruler of the late Eighteenth Dynasty.
A team of Egyptian and English archaeologists discovered a young woman wrapped in textile and plant-fiber matting and buried wearing a necklace with petal-shaped pendants as well as three rings made of gold and soapstone during excavations at the Amarna North Desert Cemetery.

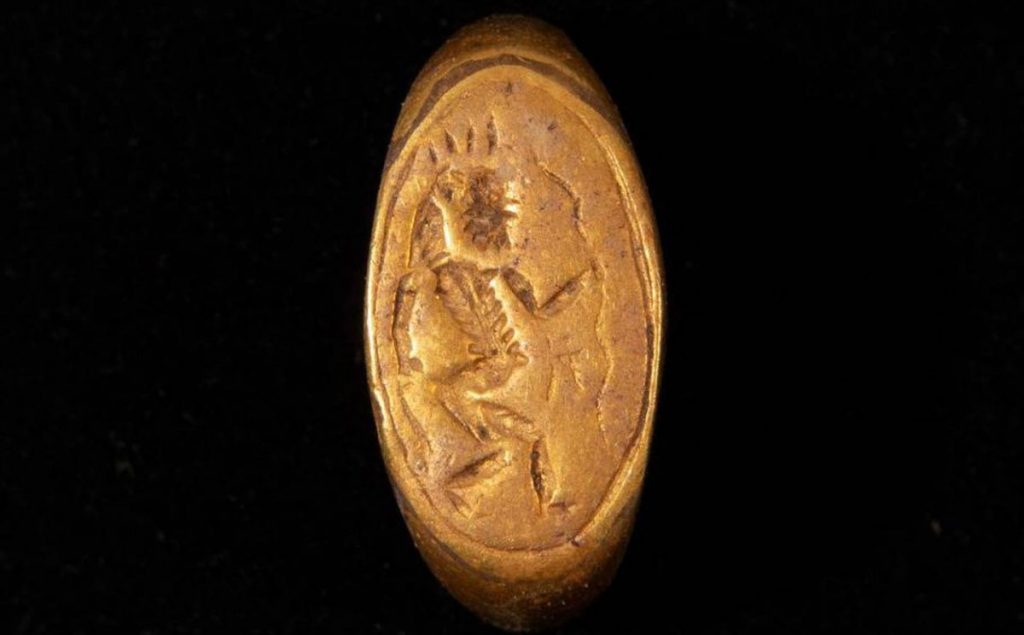
The image of the ancient Egyptian deity Bes—who, with his feminine counterpart Beset, was worshiped as a protector of households, particularly mothers, children, and childbirth—was depicted on one of the rings. The other two are inscribed with a phrase in hieroglyphics that translates into “lady of the two lands”, presumably referring to Egypt’s lower and upper kingdoms.
The young woman was placed among a small number of burial shafts, tombs, and pit graves dating to the 18th dynasty (1550–1292 BCE).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Dr. Anna Stevens, from the Department of Archaeology at the University of Cambridge, said: “her burial is located at the Amarna North Desert Cemetery in the low desert west of the North Tombs. It includes a small number of burial shafts and tombs, as well as pit graves.”

She added a number of artifacts had been discovered and extensive restoration work conducted on various relics in the area.
Since 2005, the Amarna project has been researching the necropolis of Amarna, with ongoing excavations being supported by scientists from an archaeological mission at Tel El-Amarna that has been directed by the University of Cambridge since 1977.
Today, the city is home to a number of temples dedicated to Aten as well as several royal residences that continue to attract large crowds.
Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
Cover Photo: Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities