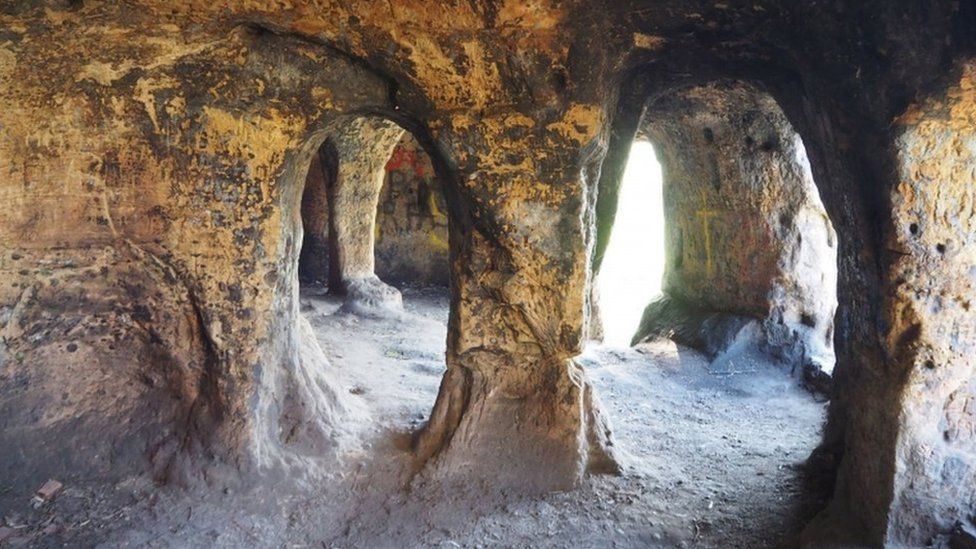
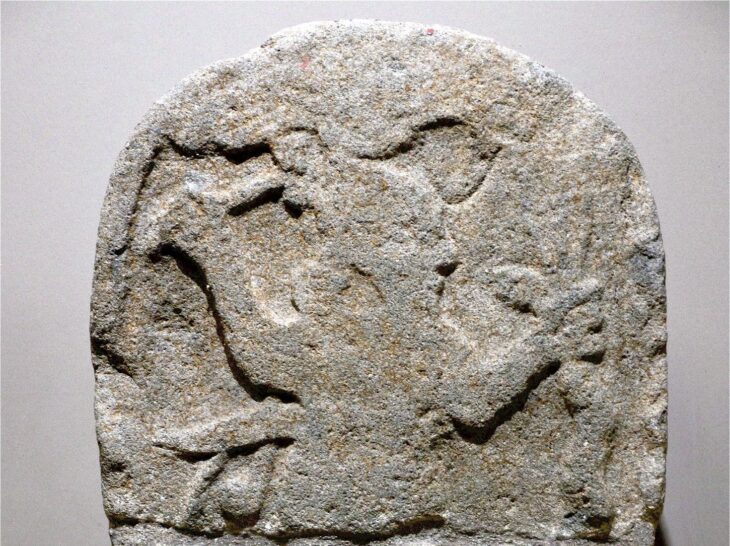
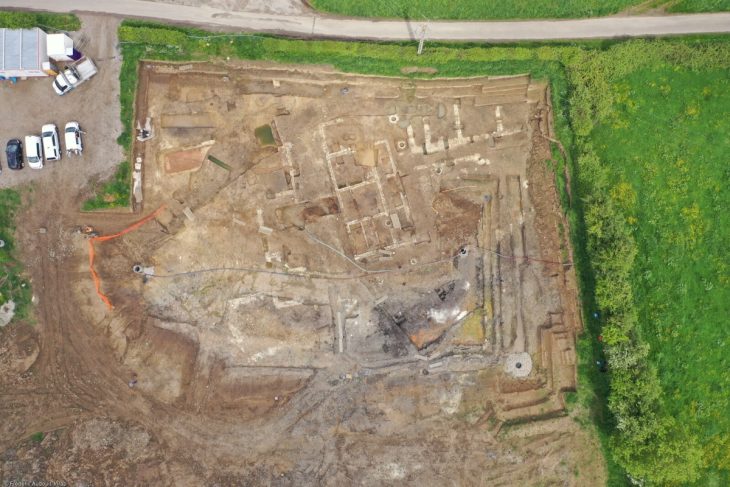
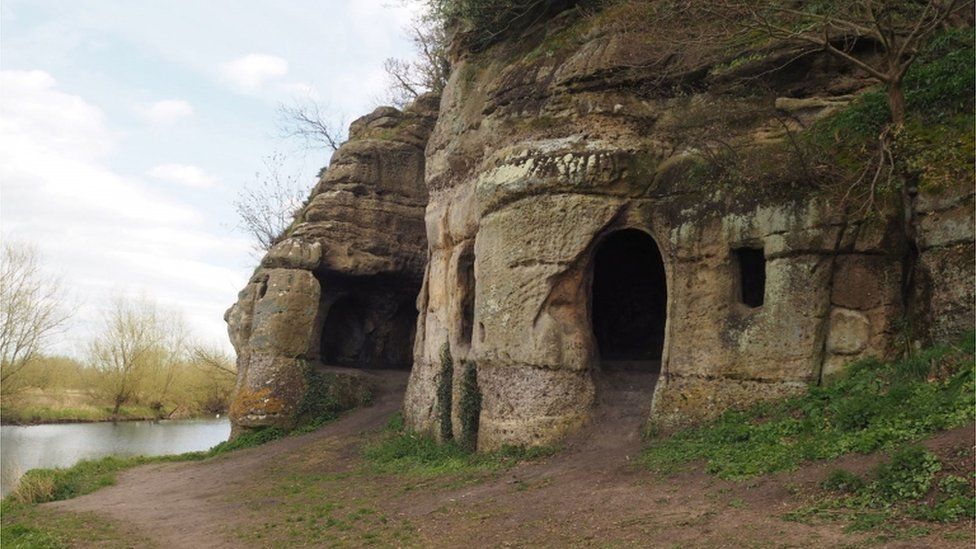
A nearly complete Anglo-Saxon house, considered to date from the early ninth century and might have been the abode of a king, has been unearthed in a sandstone cave long thought to be 18th-century folly.
According to new research, the house, which features a modest oratory – or chapel – is more likely to date from the early Middle Ages.
Experts said the caves could be the UK’s oldest intact domestic dwelling.
Working with colleagues from Wessex Archaeology, archaeologists from the Royal Agricultural University’s (RAU) newly-formed Cultural Heritage Institute performed a thorough survey of the grade II listed Anchor Church Caves between Foremark and Ingleby in south Derbyshire.

Edmund Simons, the principal investigator of the project, said: “Our findings demonstrate this odd little rock-cut building in Derbyshire is more likely from the ninth century than from the 18th Century, as everyone had originally thought. (İtv.com)
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“This makes it probably the oldest intact domestic interior in the UK – with doors, floor, roof, windows, etc – and, what’s more, it may well have been lived in by a king who became a saint.”
Researchers say that the narrow doorways and windows in the residence are very similar to Saxon architecture.
The team stated that although such cases are often associated with medieval hermits, there is also a legendary connection between the Anchor Church cave and St. Hardulph.

A fragment from a 16th-century printed book states that “At that time, St. Hadulf had a cell on a cliff not far from the Trent River.” Local folklore believed that these caves were where Hadulf lived. Modern scholarship identifies Hardulph with King Eardwulf who was deposed as king of Northumbria in 806. Hardulph died around 830 and was buried in Britten on the hills of Leicestershire, just 5 miles from the cave.
It is believed that some of the surviving sculptures in the village’s Church of St Mary and St Hardulph, which was founded as a monastery in the seventh century, came from his shrine.
Mr. Simons said: “The architectural similarities with Saxon buildings, and the documented association with Hardulph/Eardwulf, make a convincing case that these caves were constructed, or enlarged, to house the exiled king.
“It was not unusual for deposed or retired royalty to take up a religious life during this period, gaining sanctity and in some cases canonization.
“Living in a cave as a hermit would have been one way this could have been achieved.
This project has so far identified more than 20 other sites in the West Midlands that could date from as early as the 5th century.