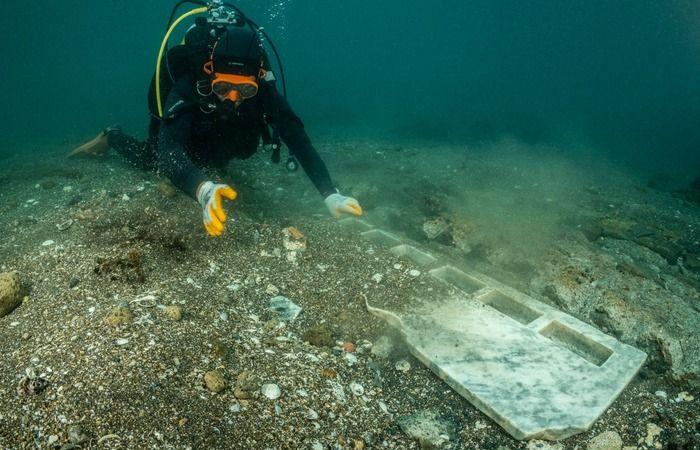
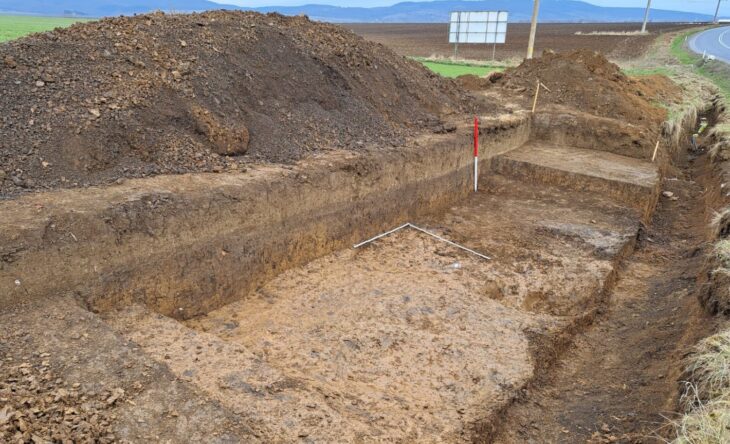
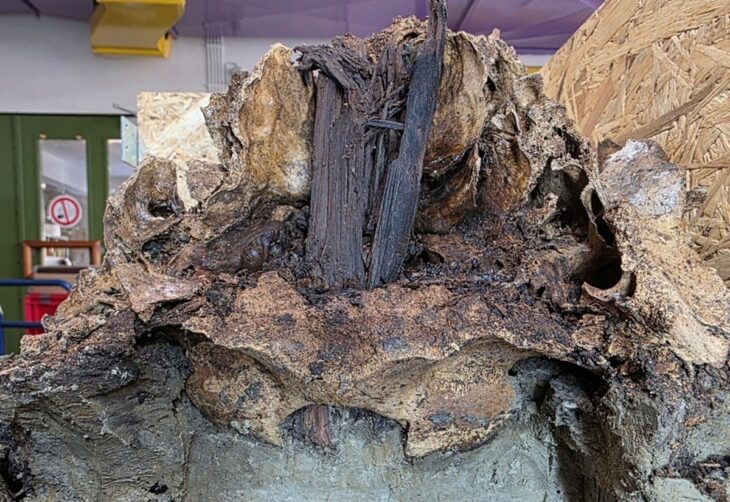
Off the coast of Pozzuoli on the Phlegrean Peninsula in Campania, Italy, underwater archaeologists have identified a sunken Nabataeans temple with the discovery of two Roman marble altars.
The Nabataean kingdom was a Roman ally that ruled a territory stretching from the Euphrates to the Red Sea during the Roman period. The kingdom, centered on the capital city of Petra, was stationed in the desert areas of the Arabian Peninsula, but had, since the early imperial age, established its base inside the Pozzuoli port, the largest commercial port of the Roman Mediterranean.
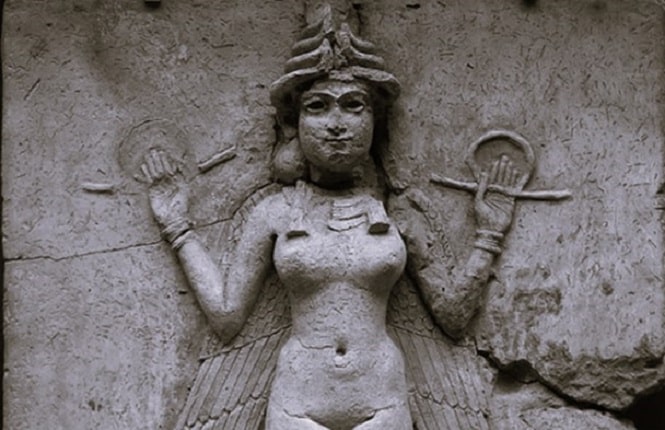
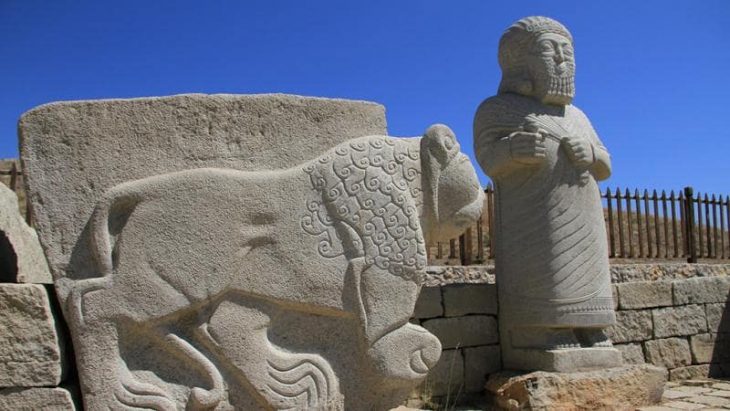
The Nabataeans established a base at Puteoli and constructed a shrine dedicated to the tutelary god, Dusares.
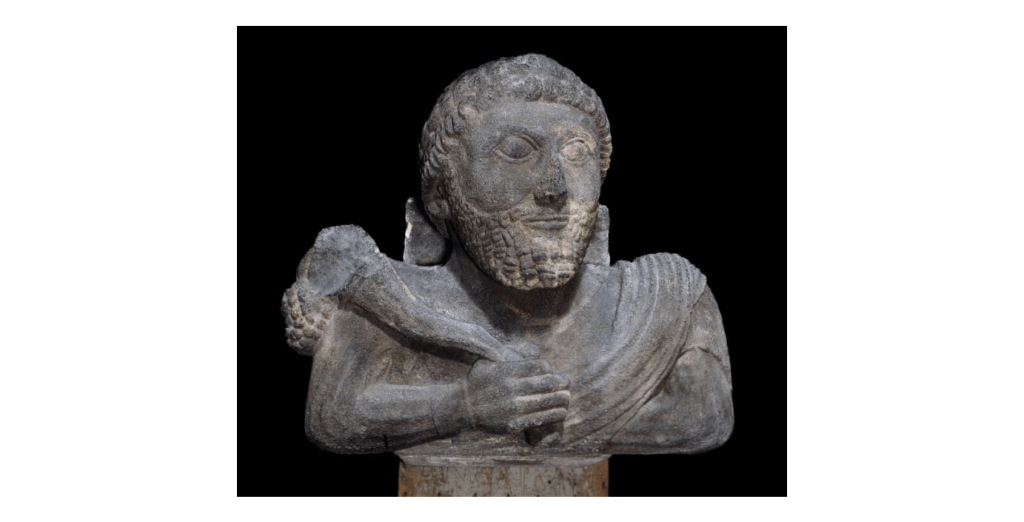
Amid the ruins of the ancient city of Puteoli (modern Pozzuoli), close to the columnade known as Tempio delle Ninfe, an altar and two cult bases bearing the inscription DVSARI SACRVM (‘Holy to Dusares’) were discovered in the middle of the 18th century. It was immediately clear that Nabataeans had once lived in Peteoli because Dusares was a deity that was exclusive to the Nabataeans. The Archaeological Museum of Naples currently has the altar and bases on display. At the same time, a massive bust of a god that is now housed in the Vatican Museum and has been theorized to be the Nabataean god Dusares was discovered in the vicinity of Puteoli.
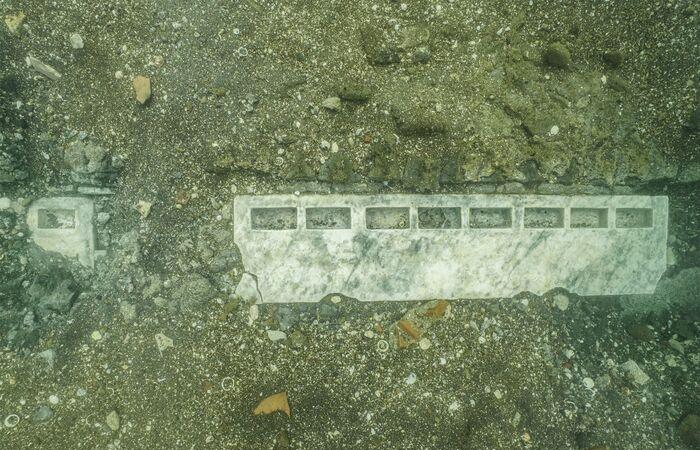

The location of the reference sanctuary remained approximate, today identified with precision topographical instruments that have allowed the Temple to be inserted into the broader topographical framework of the vicus Lartidianus.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The discovery of the altars, similar to the one kept in the Castello di Baia, is part of a fruitful research activity that will begin at the end of 2021, as part of an agreement between the Superintendency of Archaeology, Fine Arts, and Landscape for the Metropolitan Area of Naples and the University of Campania Vanvitelli, with the involvement of the Scuola Superiore Meridionale for the coordination of underwater activities, and with the valuable logistici.

Minister of Culture, Gennaro Sangiuliano, said: “Ancient Puteoli reveals another of its treasures which testifies to the richness and vastness of commercial, cultural and religious exchanges in the Mediterranean basin in the ancient world.”
In addition to the correct positioning of the Temple, the research has enabled the identification of rooms, warehouses, imperial administration buildings, and road axes of the ancient port.