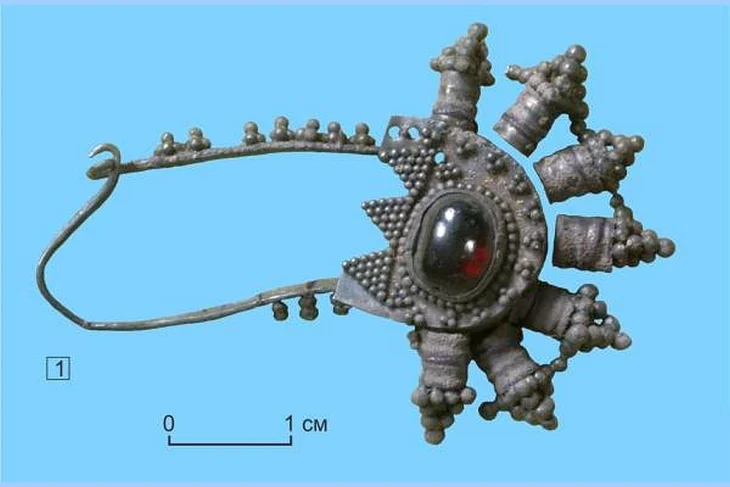
Archaeologists discovered rare makeup products of 10 different colors and different sorts of hair accessories and jewelry during excavations at the ancient Roman city of Aizanoi in Türkiye’s Kütahya province, reports said Saturday.
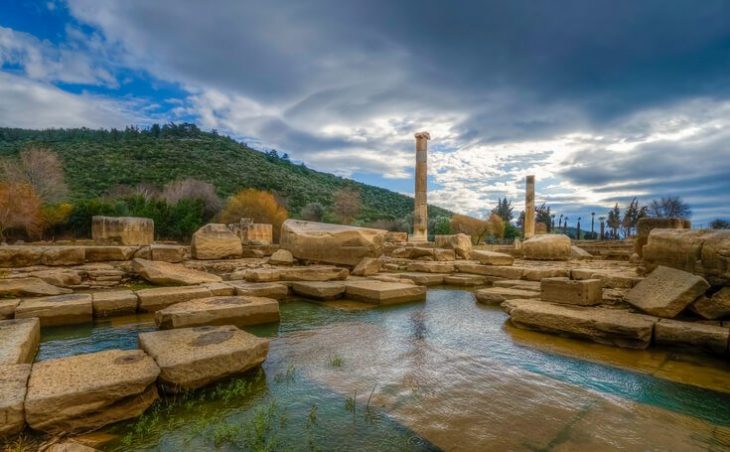
The Aizanoi ancient city is located in the inner Western Anatolia Region, 48 km Southwest of the Kütahya Province, and within the boundaries of the Çavdarhisar district.
The city was re-discovered by the European travellers in 1824 and surveyed and identified between the years of 1830 and 1840. The scientific excavations within Aizanoi were launched in 1926 by D. Krencker and M. Schede on behalf of the German Archeological Institute and presently the excavation works are being carried out by the Dumlupınar University (DU).
Aizanoi is one of the most significant cities of the Roman Period with the Zeus Temple, the Complex of Stadium-Theatre, and the Macellum.
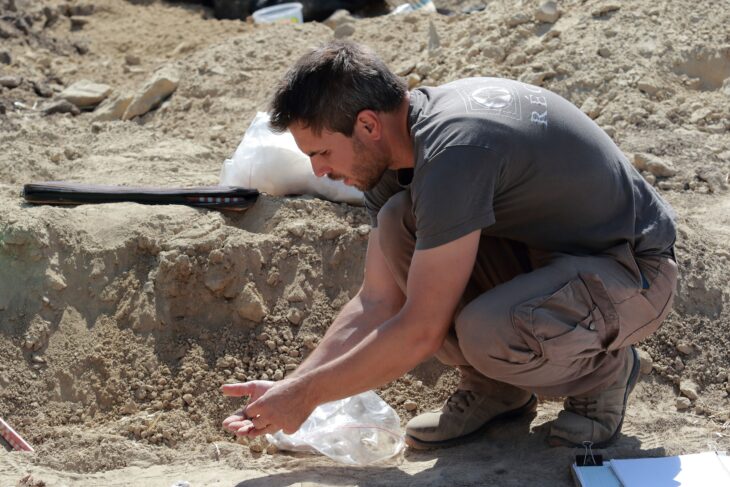
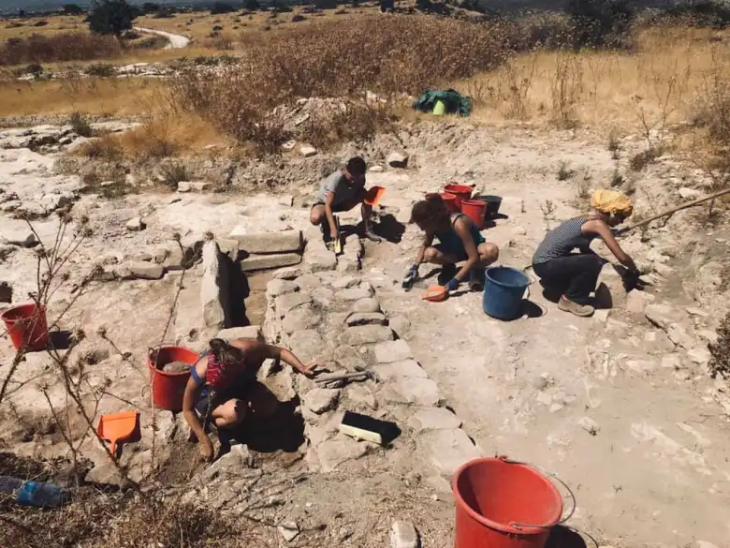
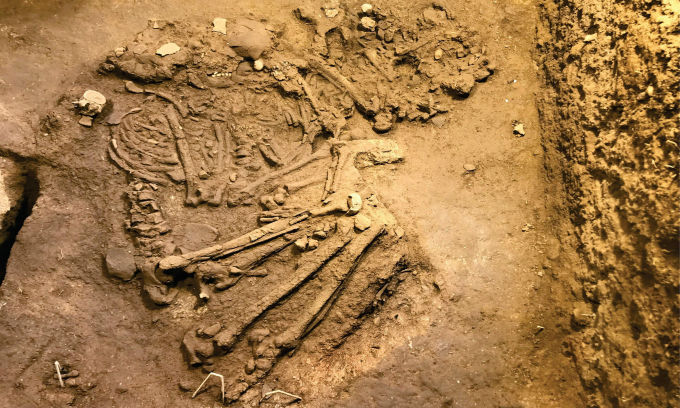
The excavations, which have been carried out in collaboration with the Kütahya Governorate and Dumlupınar University, were conducted east of the Temple of Zeus, Professor Gökhan Coşkun, the head of the Archaeology Department at DU, told Anadolu Agency (AA).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
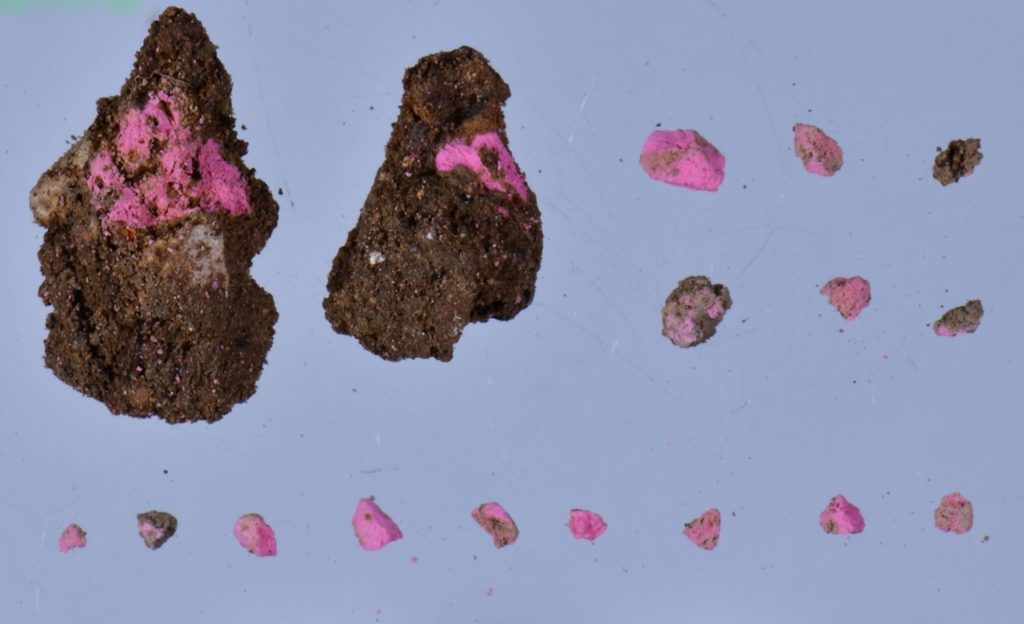
Coşkun said they discovered the remnants of a cosmetics and jewelry shop while excavating 2,000-year-old shops in the ancient city’s marketplace. “We found out that the shop sold perfume, jewelry, and makeup products,” he said, adding that they found many perfume bottles, pieces of jewelry, and makeup.
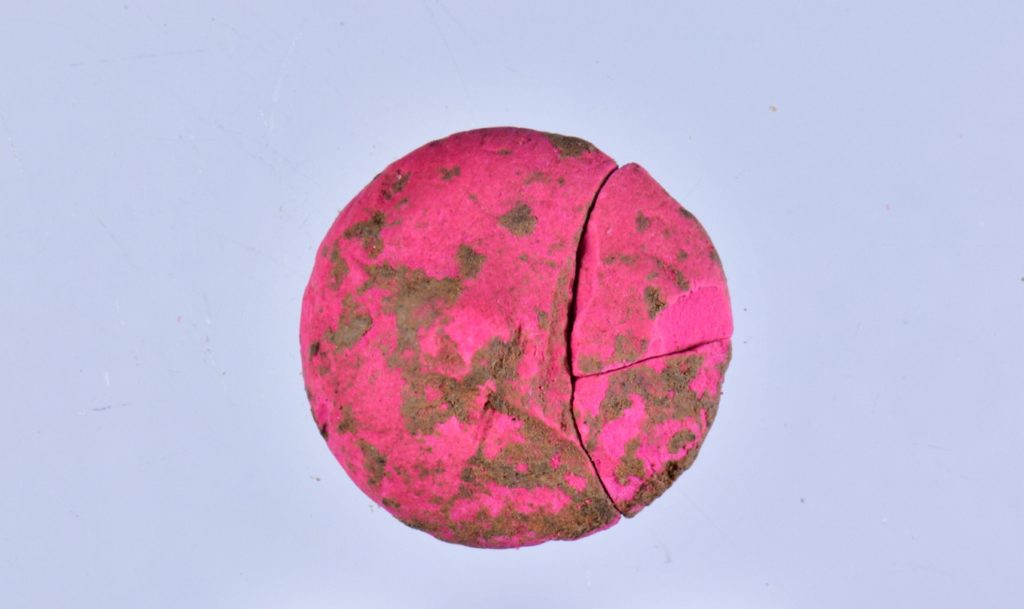
The professor noted that they discovered blusher and eye shadows in the excavations.
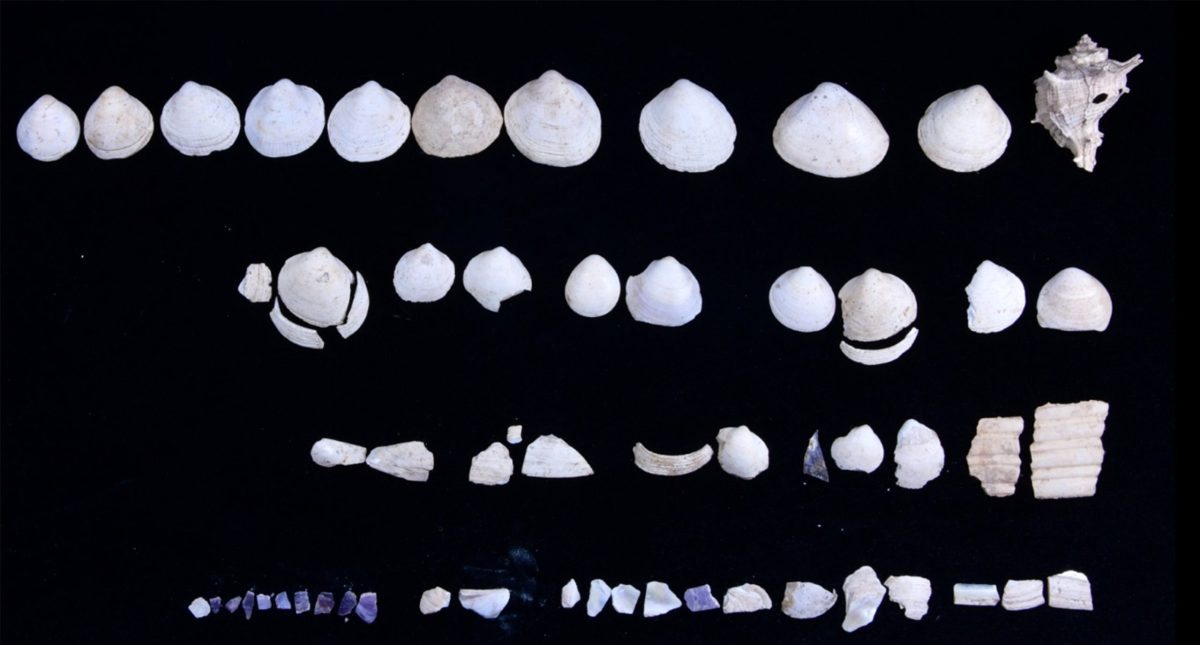
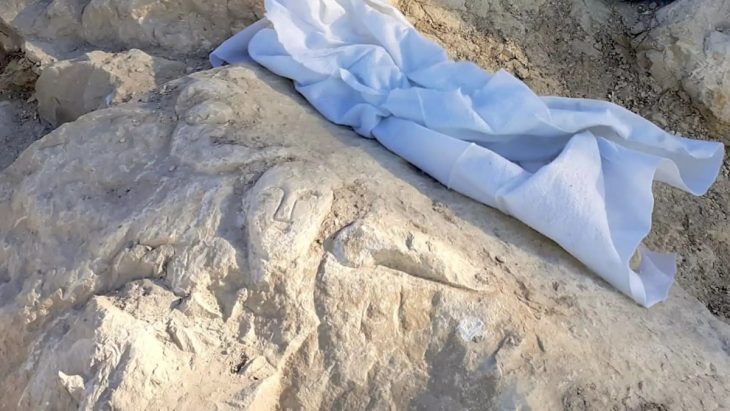
“We know that ancient Romans stored their eyeshadows and blushes in oyster shells and we found numerous oyster shells in the shops we were carrying out excavations in,” Coşkun said. The professor said that archaeologists discovered makeup products of 10 different colors and different sorts of hair accessories and jewelry.
Regular excavations have been carried out at the site since 1970.
Cover Photo: 2,000-year-old oyster shells used to store makeup products found during excavations in Kütahya. AA