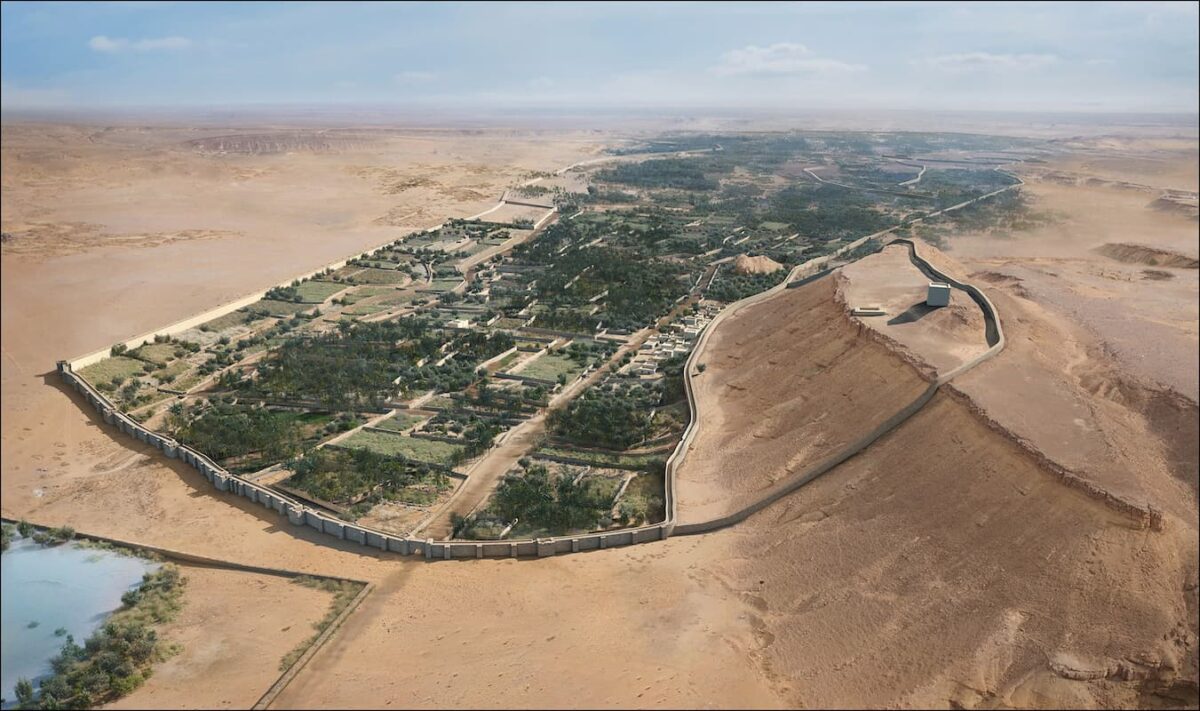
A groundbreaking archaeological discovery has revealed a vast network of ancient walled oases in the Arabian Desert, dating back over 4,000 years.
These fortified settlements—stretching from Tayma to Thaj—challenge the long-standing perception of Arabia as a land dominated solely by nomadic tribes. Instead, they highlight a complex and enduring model of oasis-based civilization, with sophisticated agricultural systems, social organization, and defensive infrastructure that supported life in one of the planet’s most extreme environments.
Fortified Settlements in the Heart of the Desert
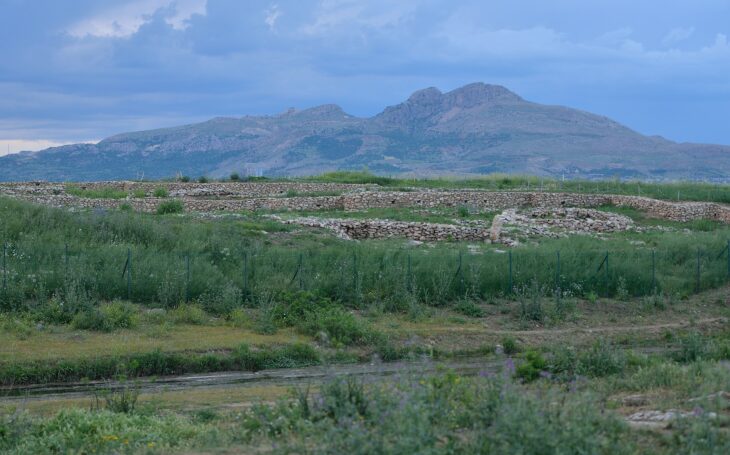
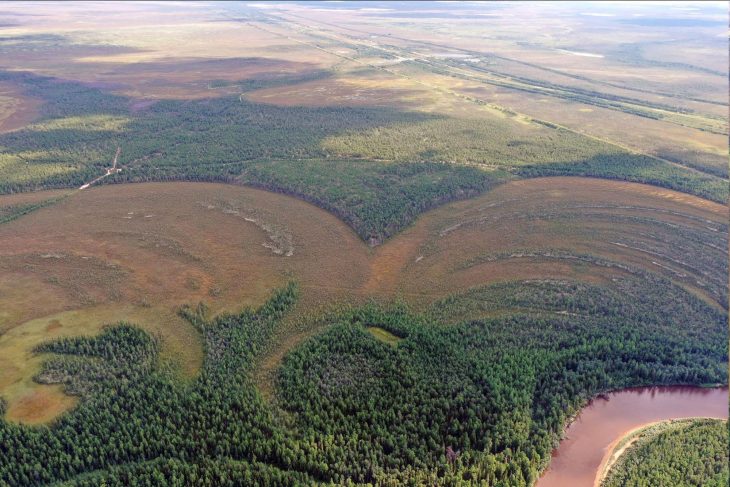
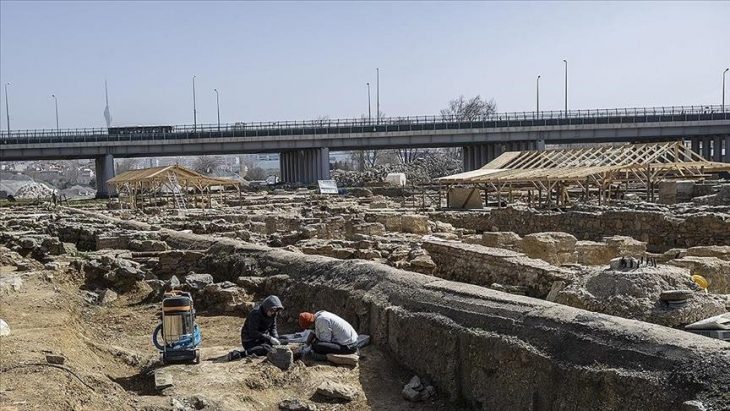
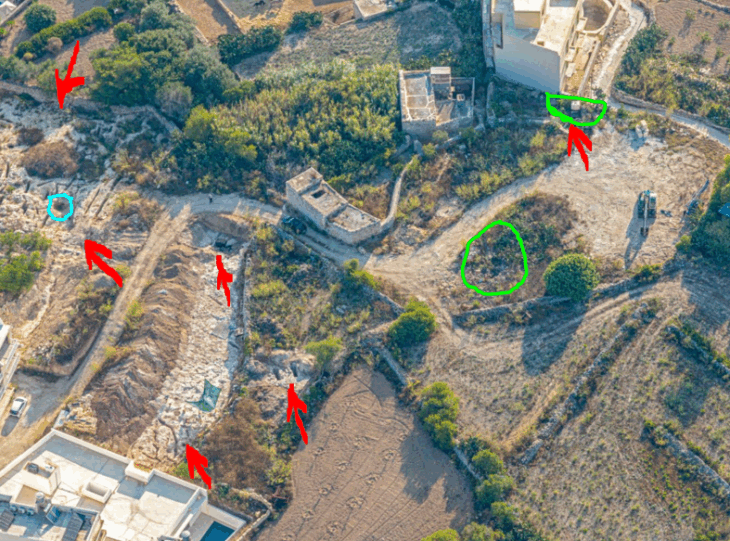
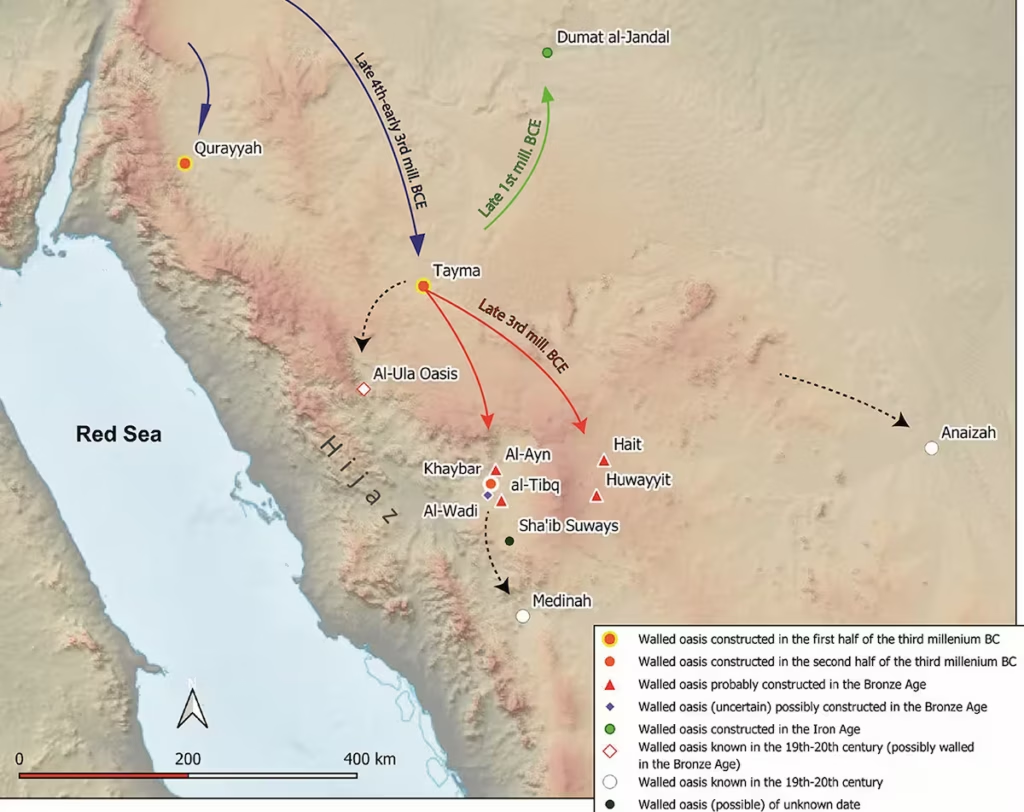
The research, led by an international team of archaeologists and published in the journal Antiquity, identifies at least ten major oases protected by extensive stone walls. Located between Tayma near the Jordanian border and Thaj on the Persian Gulf, these fortified sites once housed thriving communities. Some walls stretch up to eight kilometers and were up to two meters thick, incorporating defensive towers and entry gates.
Among the most prominent newly identified oases are Dumat al-Jandal, Khaybar, Hait, and Huwayyit. Dumat al-Jandal, revealed through 1960s aerial photography, is encircled by two-kilometer-long walls. At Khaybar, radiocarbon dating places the construction between 2250 and 1950 BCE. Here, the remnants of a once 14-kilometer-long wall, complete with nearly 180 bastions, reflect a monumental collective building effort.
Agricultural Innovation and Urban Planning
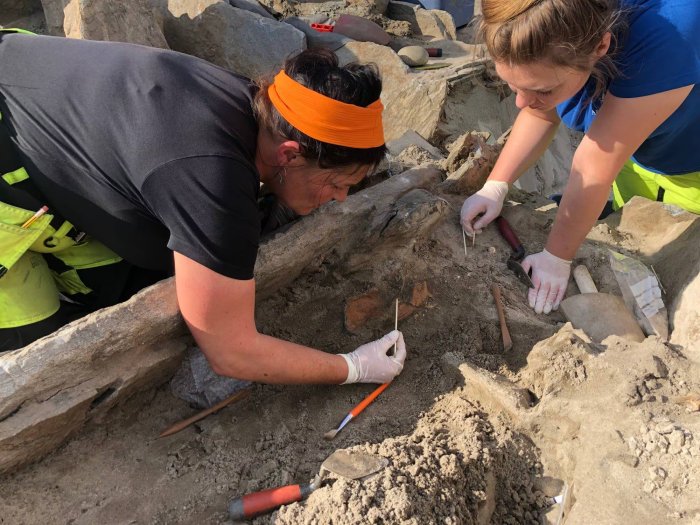
These walled oases were not merely defensive structures—they served as fully functional settlements with cultivated fields, date palm groves, livestock pens, and water wells. Archaeological evidence shows that residents developed advanced strategies to secure vital resources in the arid climate, including the protection of grain stores and herds of goats and sheep.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
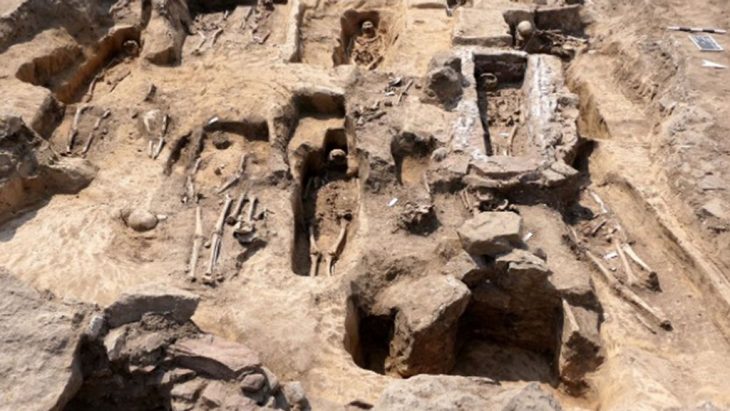
One standout site is al-Nataḥ, a 2.6-hectare fortified town within Khaybar oasis. Dating back to between 2400 and 1500 BCE, it likely housed up to 500 residents. Multi-story homes, urban planning, and even a surrounding necropolis point to what researchers call “slow urbanism”—a gradual yet deliberate shift from mobile to permanent settlement.
A Long-Term Settlement Model
The walled oases represent a socio-political and environmental strategy that persisted across millennia. Originating in the Bronze Age (3000–1200 BCE), this settlement pattern expanded during the Iron Age and later periods. Even as late as the 19th and 20th centuries, cities like Medina and al-Ula continued to use walled systems to protect agriculture from raids and natural threats.
This continuity suggests a remarkable level of societal organization. The ability to mobilize labor and maintain infrastructure across generations highlights the emergence of centralized authority and collective effort in pre-Islamic Arabia.
Rethinking the Arabian Desert’s History
The discovery fundamentally alters the historical narrative of Arabia. Rather than being dominated exclusively by nomadic tribes, the region was also home to complex, sedentary societies capable of urban development and long-term planning. These fortified oases likely played a crucial role in the rise of early Arab caravan kingdoms, serving as trade and cultural hubs across the peninsula.
The research underscores the region’s connections with the wider ancient world. Architectural parallels with the Mediterranean Levant suggest cultural exchanges and technological influence, reinforcing Arabia’s position in broader Bronze and Iron Age networks.

Ongoing Questions and Future Exploration
While the study provides crucial insights, it also raises new questions. How were labor and materials organized to construct such massive walls? What role did environmental changes, like drought or trade shifts, play in the rise and decline of these settlements? Researchers emphasize the need for further excavation and analysis to understand the full social, political, and environmental context.
As archaeologists continue to unearth more evidence, the Arabian Desert is slowly revealing a complex and deeply rooted human history—one of adaptation, resilience, and innovation.
Charloux, G., & Alonazi, M. (2025). The Walled Oases Complex in north-west Arabia: evidence for a long-term settlement model in the desert. Antiquity, 1–9. doi:10.15184/aqy.2025.10125
Cover Image Credit: M. Bussy & G. Charloux / Dumat al-Jandal Archaeological Project
















