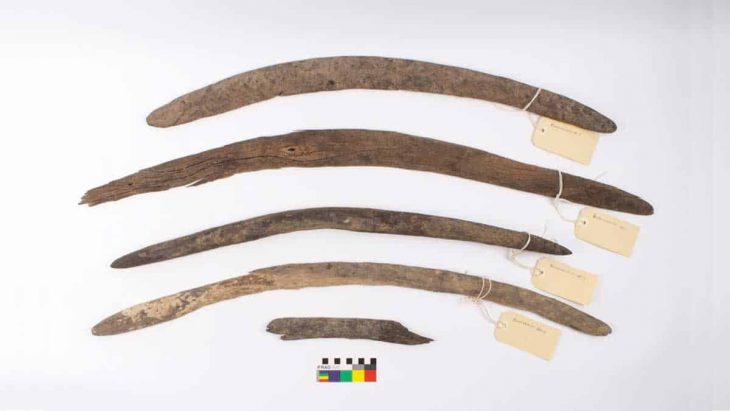
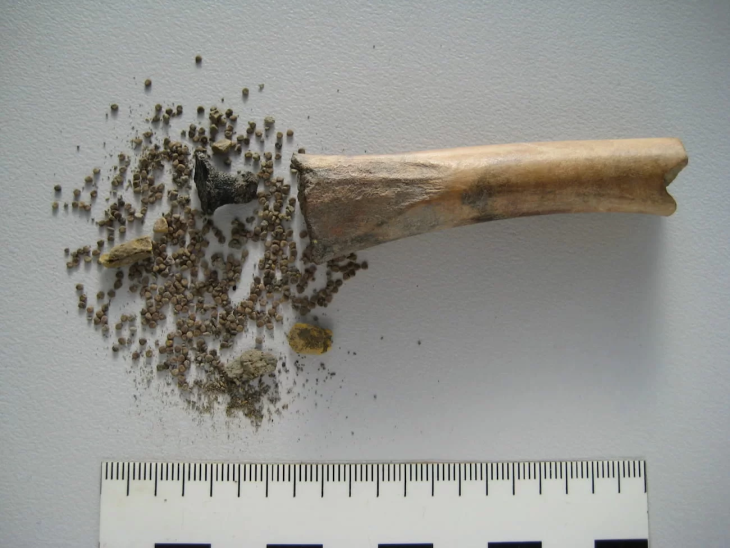
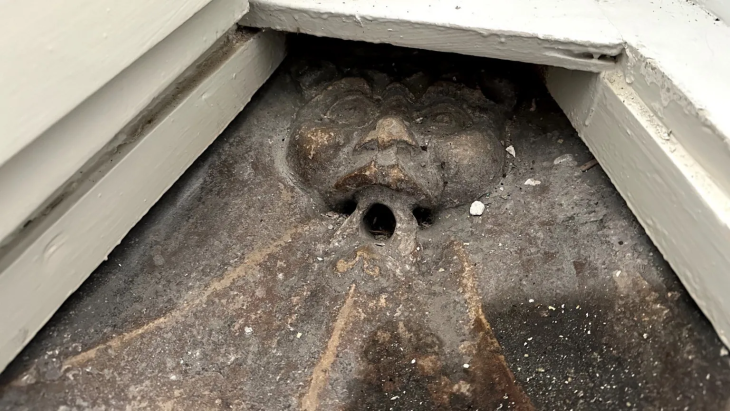
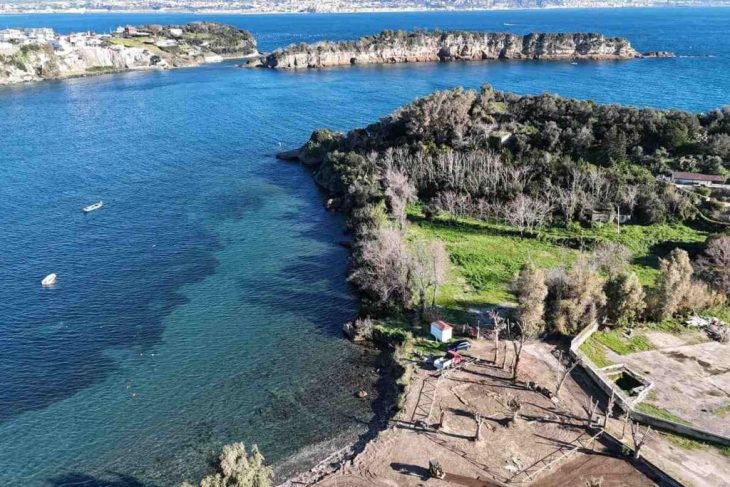
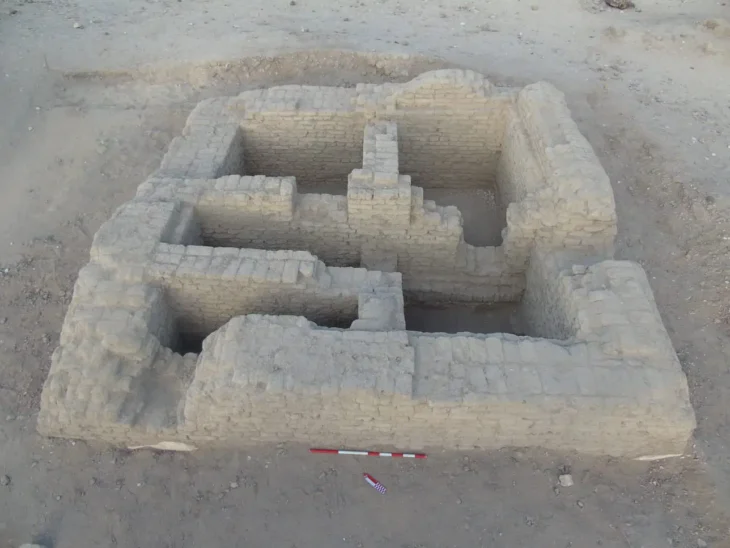
Archaeological excavations at the strategically significant Tell Abu Saifi site in North Sinai have unearthed compelling evidence of Egypt’s long-standing efforts to secure its eastern frontier. An Egyptian archaeological mission from the Supreme Council of Antiquities (SCA) has revealed not only previously known Ptolemaic and Roman-era military fortifications but also the likely remnants of an even older defensive structure, offering a multi-layered perspective on the region’s military importance.
The recent discoveries provide fresh insights into the sophisticated defensive infrastructure employed by ancient Egypt. Notably, the mission identified the distinctive architectural layouts of the eastern gates belonging to both the Ptolemaic and Roman fortresses. Furthermore, a substantial defensive trench, exceeding two meters in depth, was uncovered at the entrance of the Ptolemaic fortress, suggesting an adaptable defense system designed to counter potential threats.
According to Minister of Tourism and Antiquities Sherif Fathy, the findings underscore Tell Abu Saifi’s crucial historical role as both a military stronghold and an industrial center across various periods. “This discovery offers a deeper understanding of the defensive systems established in eastern Egypt and reaffirms Tell Abu Saifi’s historical role as both a military and industrial hub across various eras,” he stated, emphasizing the site’s strategic significance as Egypt’s “eastern gate and its first line of defense.”
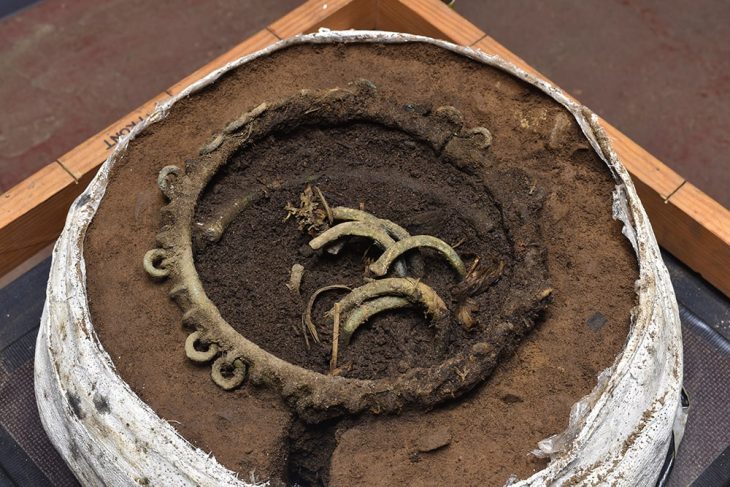
Adding to the understanding of daily life at the site, archaeologists unearthed well-preserved soldiers’ quarters dating back to the Roman era, specifically the reigns of Emperors Diocletian and Maximian. These dwellings offer a rare glimpse into the lives of the cavalry stationed at this vital outpost.
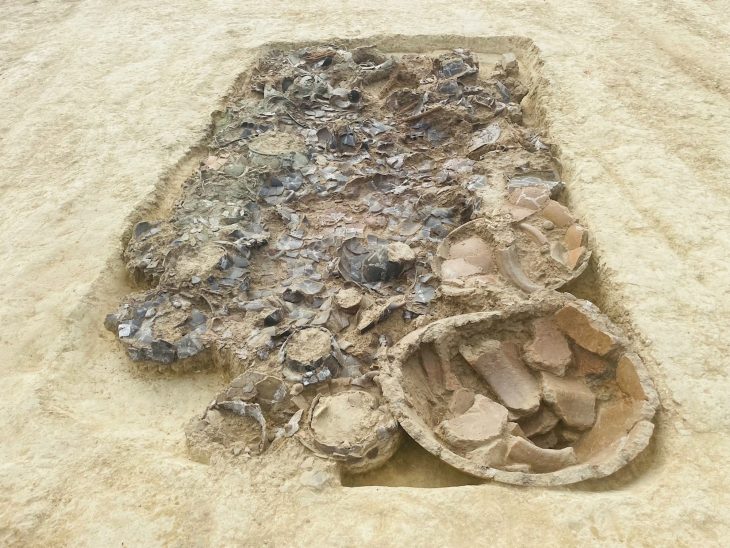
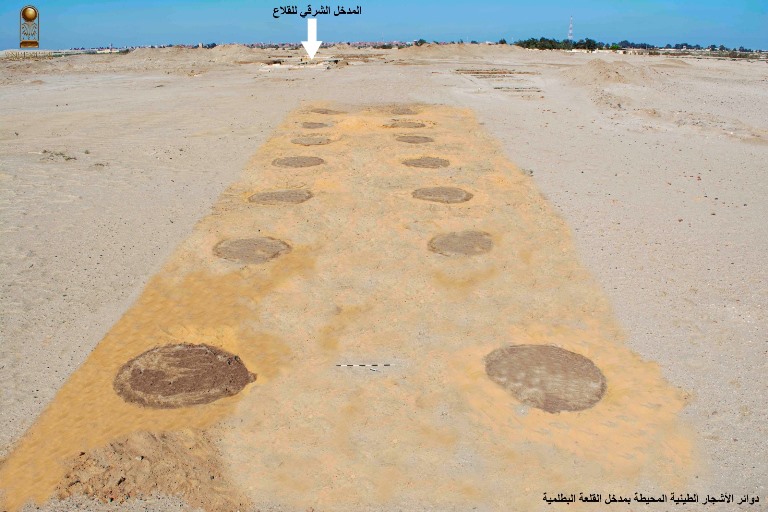
A significant find was a limestone-paved road, stretching over 100 meters in length and 11 meters in width, connecting the eastern gate of the Roman fortress to the site’s interior. Intriguingly, this Roman road was constructed over an earlier limestone road from the Ptolemaic period, indicating continuity and adaptation of infrastructure. Along the sides of this thoroughfare, over 500 clay planting circles were discovered, believed to have once held trees that adorned the entrance to the Ptolemaic fortress, adding a touch of planned landscaping to the military installation.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Perhaps the most intriguing discovery is the potential third, older fortress lying beneath the well-documented Ptolemaic (332-30 B.C.) and Roman (30 B.C.-395 A.D.) fortifications. The archaeological team has identified the four corners of this earlier structure, and current dating efforts are underway to precisely determine its age. However, initial assessments suggest that this newly found fortification predates both the Ptolemaic and Roman eras, indicating that the military significance of the Athar region extends even further back in history.
Hisham Hussein, head of the archaeological mission and Director-General of Sinai Antiquities, also highlighted the discovery of four industrial-scale kilns used for quicklime production. This finding indicates a later transformation of the site into a production center during the Roman period, which likely led to the dismantling of some earlier stone structures for materials.
Mohamed Ismail Khaled, secretary general of the Supreme Council of Antiquities, emphasized the broader implications of these discoveries for understanding Egypt’s eastern border defenses. He reiterated Sinai’s historical significance as Egypt’s “eastern gateway and its first military stronghold.”
The ongoing excavations at Tell Abu Saifi continue to reveal the dynamic history of this crucial site, illustrating its evolution from a primary military defense point to an industrial hub, shaped by shifting geopolitical landscapes and the changing course of the Nile River. The multi-layered fortifications and associated residential and industrial remains offer a rich tapestry of ancient Egyptian military and daily life across centuries.
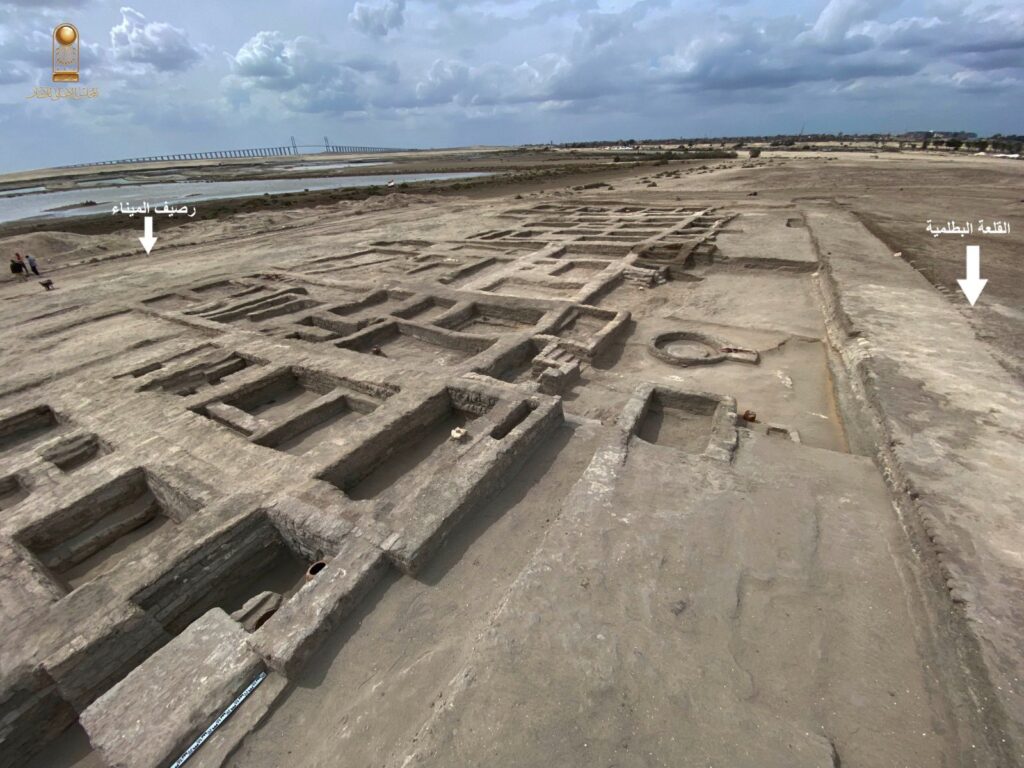

As the excavation continues, the team is working to further explore the overlapping rectangular buildings believed to have served as long-term residential spaces during the Ptolemaic era. The strategic location of Tell Abu Saifi, near the ancient border city of Tharu, has made it a focal point for understanding Egypt’s eastern defenses throughout history.
With ongoing research and exploration, the Tell Abu Saifi site promises to reveal even more about the complexities of ancient Egyptian military and industrial life, reaffirming its importance as a key archaeological site in the study of Egypt’s rich heritage.
Egypt’s Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities
Cover Image Credit: Egypt’s Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities- Facebook