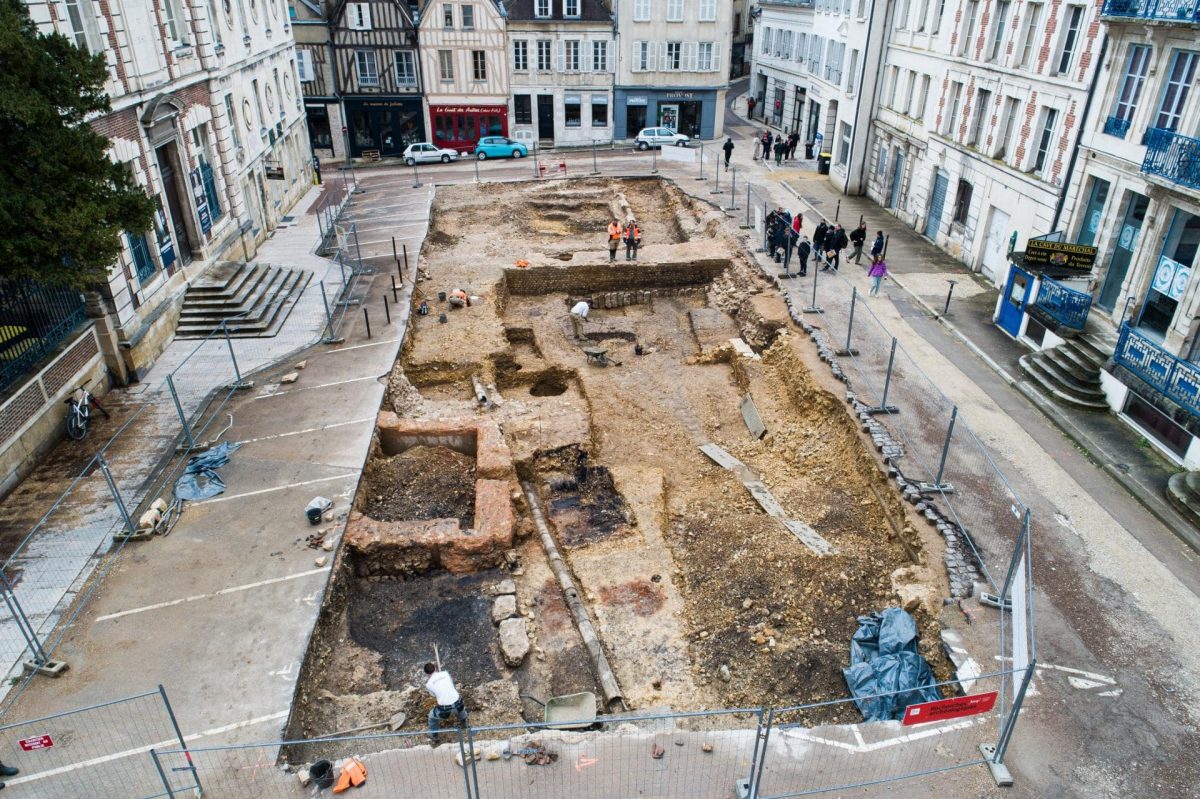
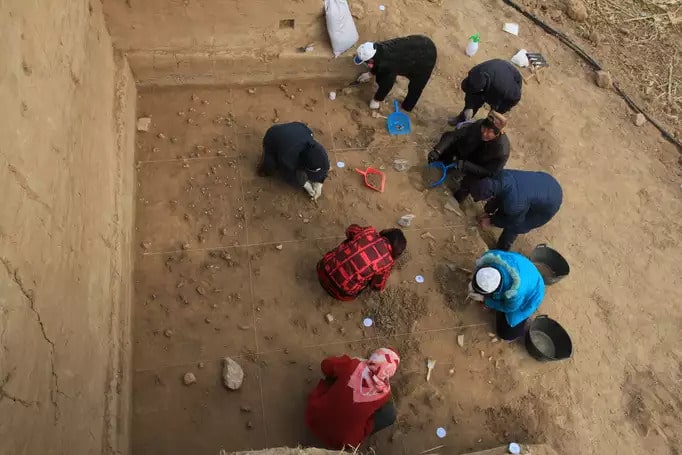
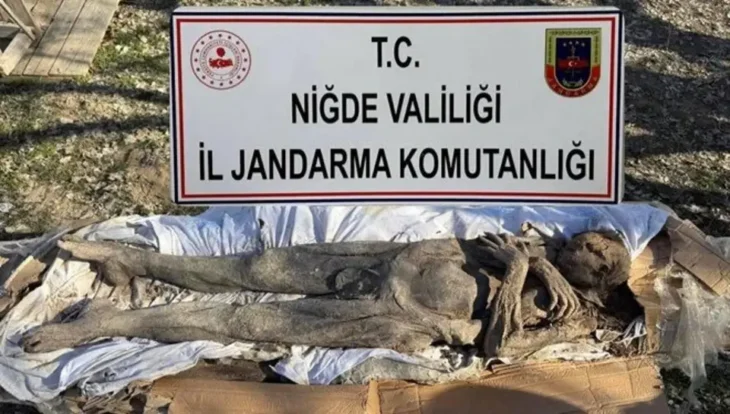
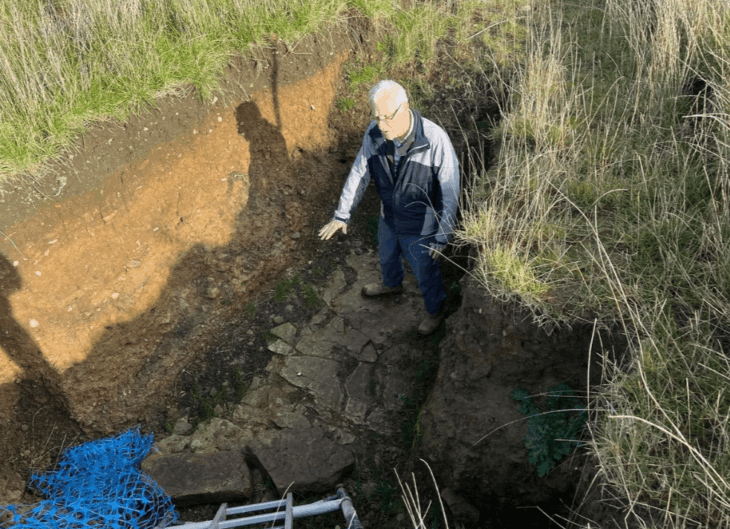
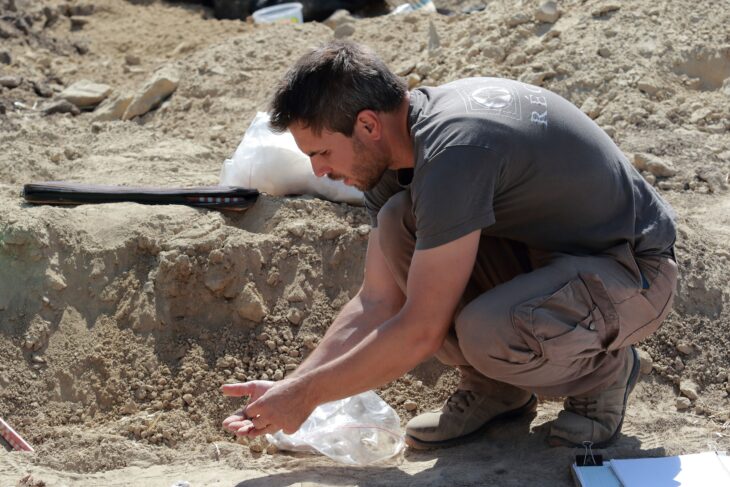
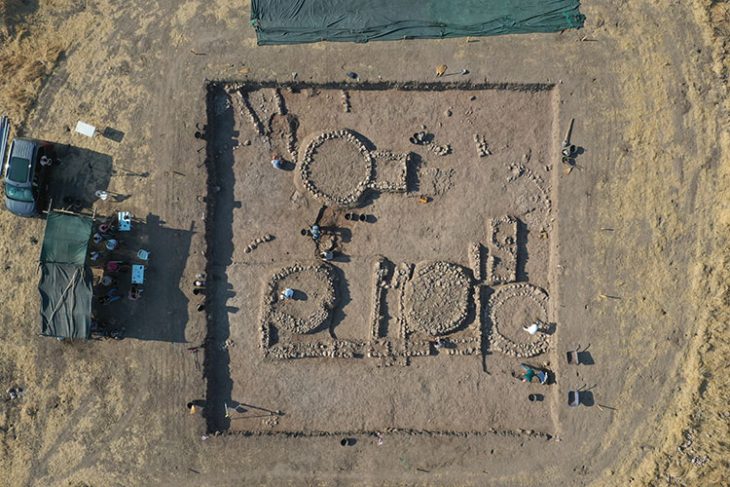A team from INRAP, France’s national archaeology and preservation agency, unearthed a necropolis dedicated to stillborn and very young children during excavations in the historic center of the city Auxerre.
Since February 2024, as prescribed by the Regional Directorate of Cultural Affairs of Bourgogne–Franche-Comté, Inrap archaeologists have been conducting research on Place du Maréchal Leclerc in Auxerre before its landscaping redevelopment.
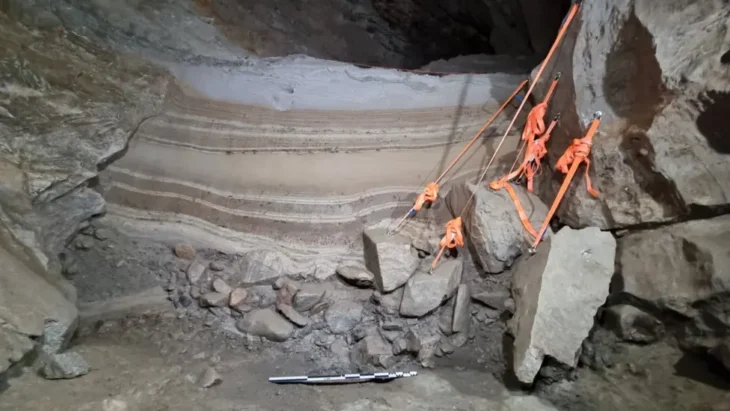
The Gallic Senones people established the fortified town of Autessiodurum on the banks of the Yonne River in 30 B.C. Although it was situated at the crossroads of several crucial roads during Roman rule, it wasn’t until the Roman Empire designated it as a provincial capital in the third century that it attained any real political prominence. In the fourth century, new fortifications surrounded the town. The necropolis was located beneath those ramparts. If this necropolis is part of the Gallo-Roman traditions, it has many characteristics that distinguish it from its contemporaries.
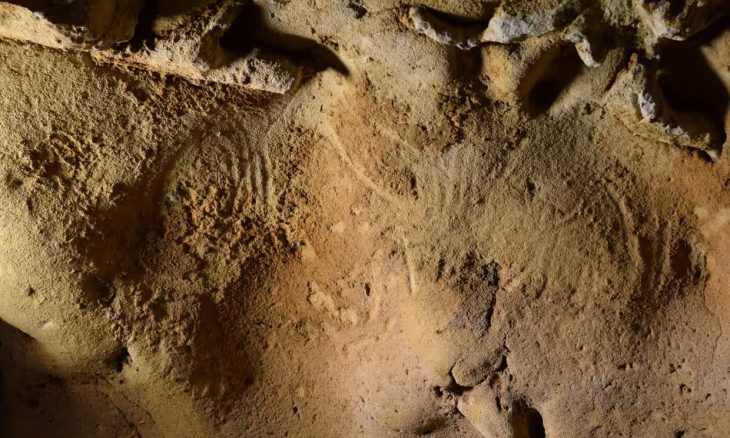
According to ancient rules, the necropolis are located outside the cities. On the periphery of these funeral areas, spaces can be dedicated to very young children (stillbirths and individuals aged a few months) whose mortality rate is high at this time. The excavation carried out in Auxerre explores one of these specific areas. Its very good state of conservation offers archaeologists the opportunity to observe the gestures intended for this very singular population.

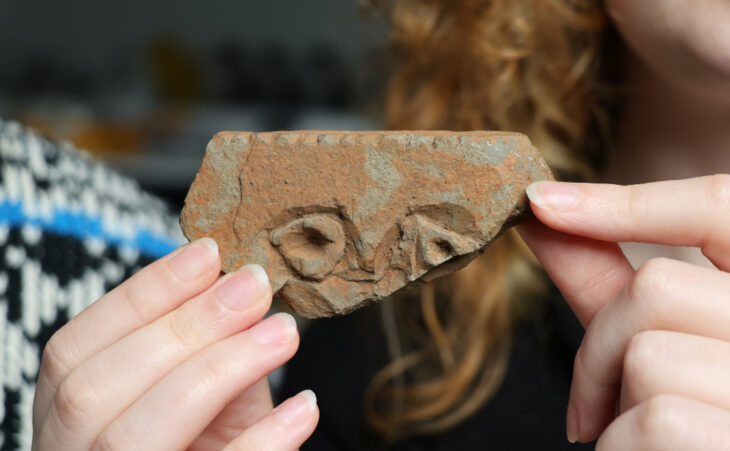
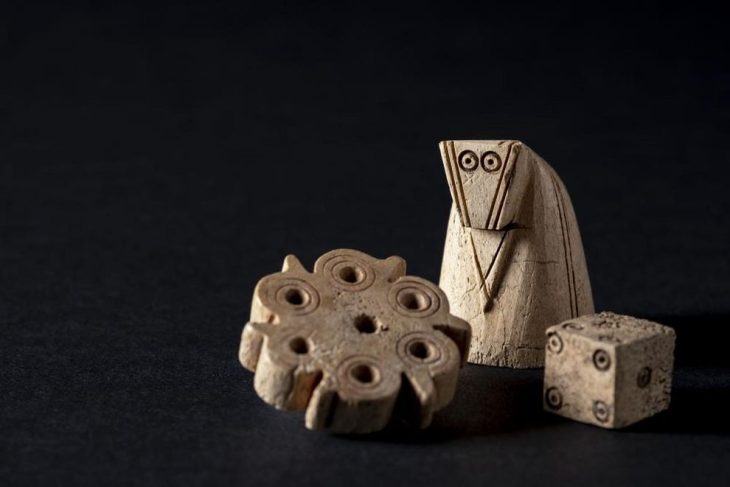
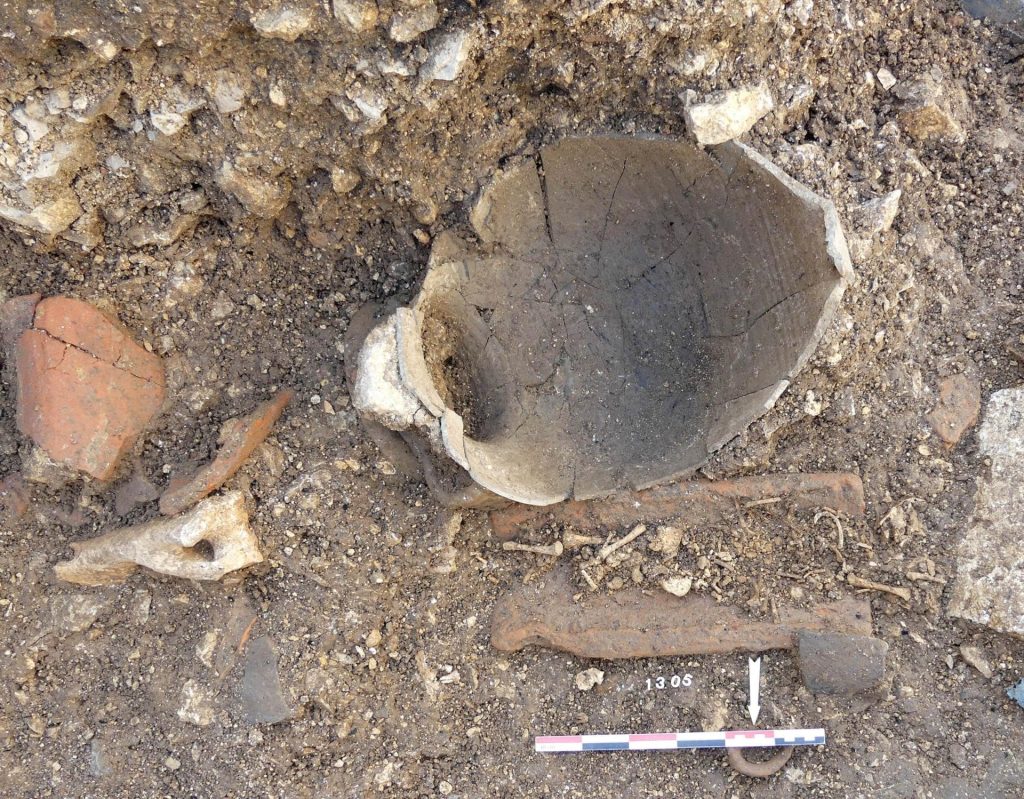
Ceramic tableware is broken near burials on circulation levels, their contents being intended for the dead and the gods. In order to protect these young deceased, objects intended for protection in the afterlife (called «apotropaic» or «prophylactic») accompany them, like a pearl, a currency, a rouelle. A miniature ceramic cup was also placed at the head of a young child.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Various funeral practices
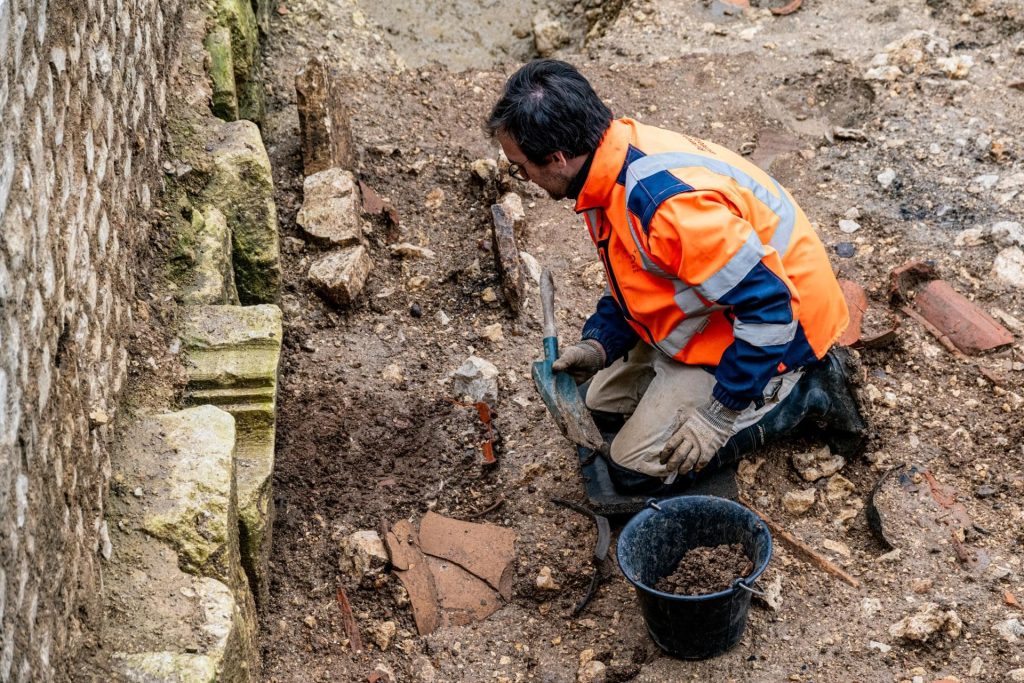
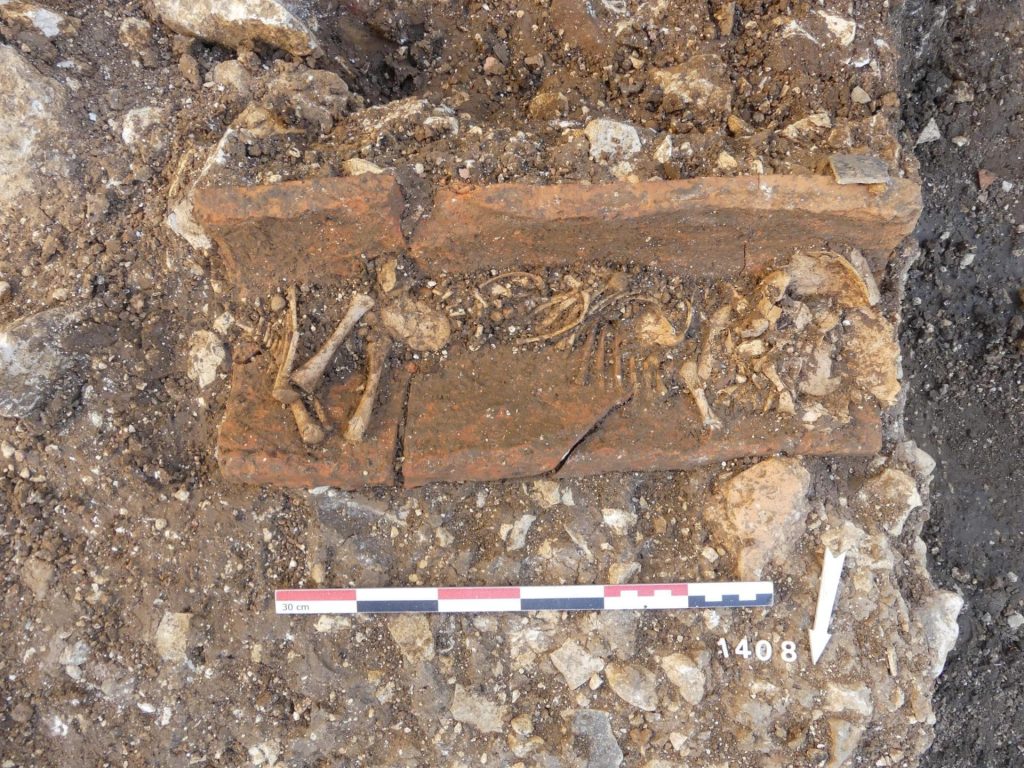
This necropolis testifies to a wide variety of practices on the same funerary space. The majority of the burials are in fetal position although some are on the back. It is the containers of toddlers that show the most diversity: they are arranged in tiles (imbrex), ceramics, wooden coffins, tree bark, stone formwork, textiles and other flexible envelopes. Sometimes the bodies are simply covered with fragments of amphora to protect them.

In one case, a stone engraved with a rosette is reused to mark the tomb. In addition, up to eight stages were observed during the burial of these very young children, proof of the complexity of funeral gestures. These were therefore not rejected, some burials testifying on the contrary to significant attention.
The very high density of graves and their superimposition make it possible to study a very large number of burials and other funeral practices associated with toddlers during the I-III centuries.

Up to five levels of tombs have been observed, which, in the state of research, is unique in the Gallo-Roman world where the integrity of the tomb must be preserved. In Auxerre, however, some tombs destroy others, which may be related to a problem of available space but also to the very status of these very young children, not always perceived as individuals in their own right. The excavation of Auxerre, as recently, that of Narbonne and others, brings a lot of new knowledge and questions about funeral practices associated with very young children and stillborn in Antiquity.
Cover Photo: General view of the excavation site at Place du Maréchal Leclerc in Auxerre. Photo: © Christophe Fouquin, Inrap