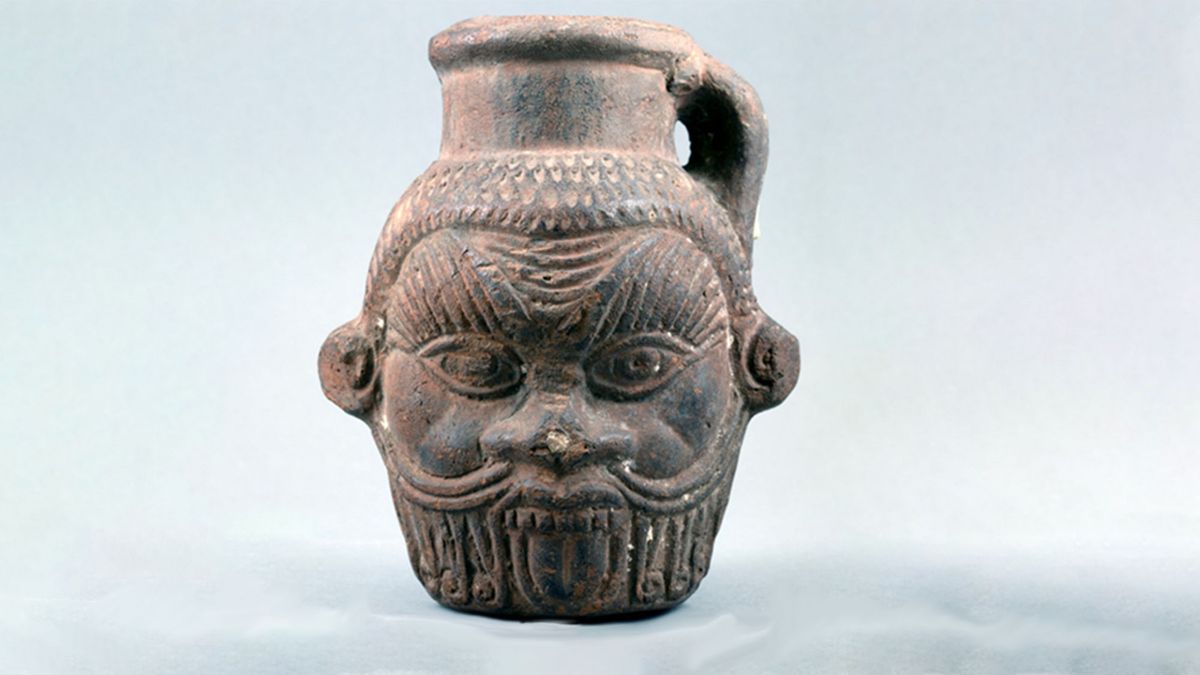
Researchers have identified some of the components of found in an ancient Bes vase dating back to Ptolemaic era Egypt.
The potent mind-altering concoction that was once housed in the second-century BC vase was revealed after a thorough chemical analysis by researchers, who would have consumed it to induce an altered state of consciousness.
According to a paper posted to the pre-print server Research Square, the roughly 2,200-year-old vessel — which is in the shape of the head of the god Bes — contained a number of psychoactive compounds, including fermented fruit, the plant Peganum harmala (also known as Syrian rue), and Nymphaea caerulea (commonly called blue water lilly). Syrian rue, in particular, is known to be hallucinogenic in nature.
“The seeds of [Syrian rue] produce high quantities of the alkaloids harmine and harmaline, which induce dream-like visions,” the researchers wrote.
The ancient cocktail also contained traces of a fermented alcoholic beverage made from fruit, honey, and bodily fluids in addition to these psychotropic or hallucinogenic substances. While the addition of human fluids suggests a magical or ritual purpose, the first two of these ingredients may have been added to make the mixture more palatable or digestible.
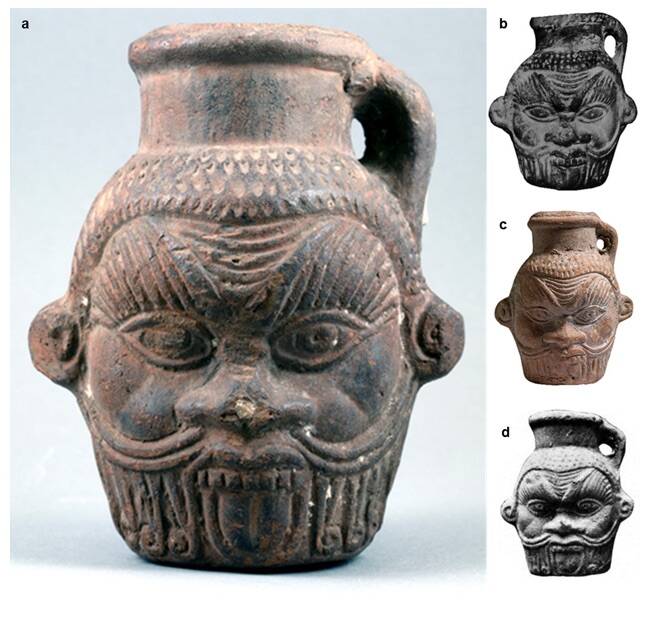

The authors of the study believe that the magic potion contained in the ancient Bes vase was consumed by members of an ancient cult active in Ptolemaic Egypt that worshiped a part-feline/part-human deity known as Bes.
“As the Bes figure was revered as a protective genius, it might be assumed that the liquid drunk from these mugs was considered beneficent,” they said.
Members of the Bes cult appeared to frequently consume magical potions. The researchers involved in this specific study knew where the vase they studied had come from because the ceramic drinking mugs used in the cult were consistently adorned with the head of Bes.
Researchers examined the vessel, which is part of the Tampa Museum of Art collection. They were astounded by what they discovered after using a variety of high-tech techniques to identify the mixture of ingredients in the residues. Apparently, members of the cult would contribute their own fluids to the mix, likely as part of a ritual.
The study offers a fascinating look into the religious practices of this late period of ancient Egyptian history, even though it hasn’t yet been peer-reviewed. Of course, it is unclear what function the vessel’s contents served or what the significance of the object might have been.