An essential Gallo-Roman worship complex was unearthed by Inrap (National Institute for Preventive Archaeological Research) archaeologists at Chapelle-des-Fougeretz (Ille-et-Vilaine), near the city of Rennes in northwest France.
The site in the village of Chapelle-des-Fougeretz has been slated for development, triggering a comprehensive preventative archaeology excavation of more than seven hectares of the site.
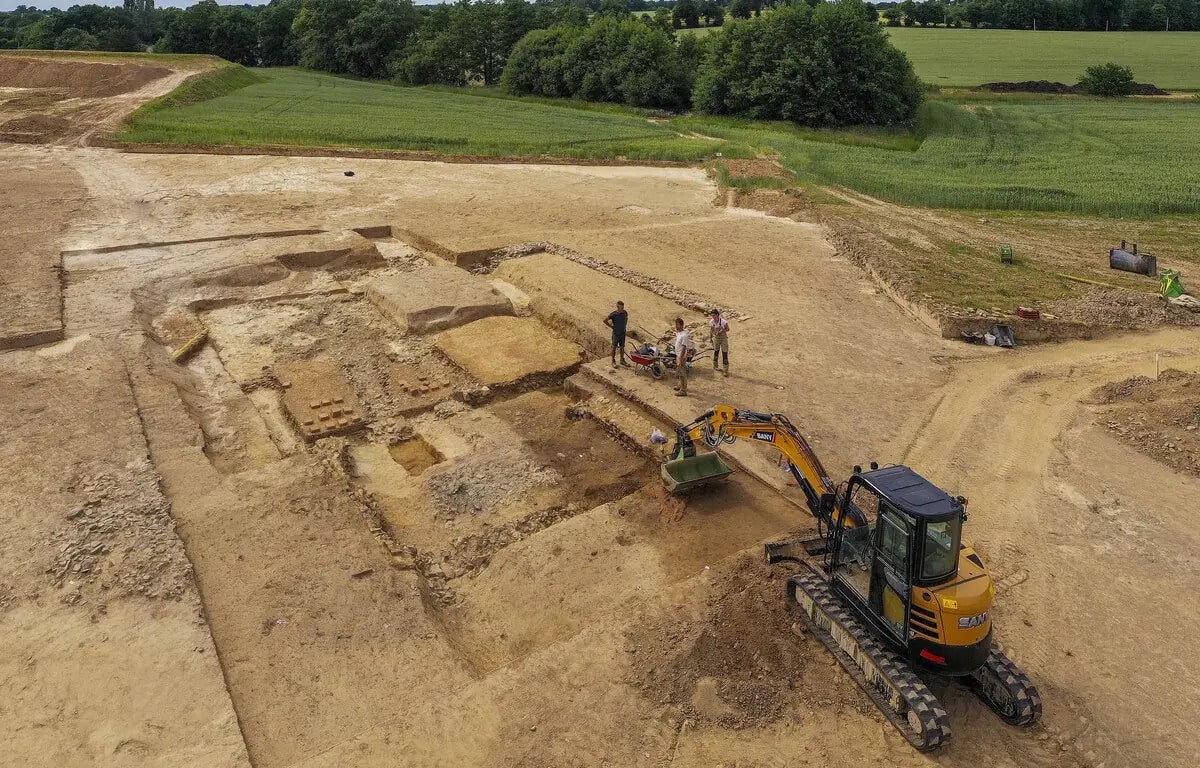
Excavations began in March, and archaeologists have unearthed the remains of a Gallo-Roman worship complex built just after the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC. The sanctuary was originally established in the period following the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC and operated for at least five centuries until the 4th century AD.
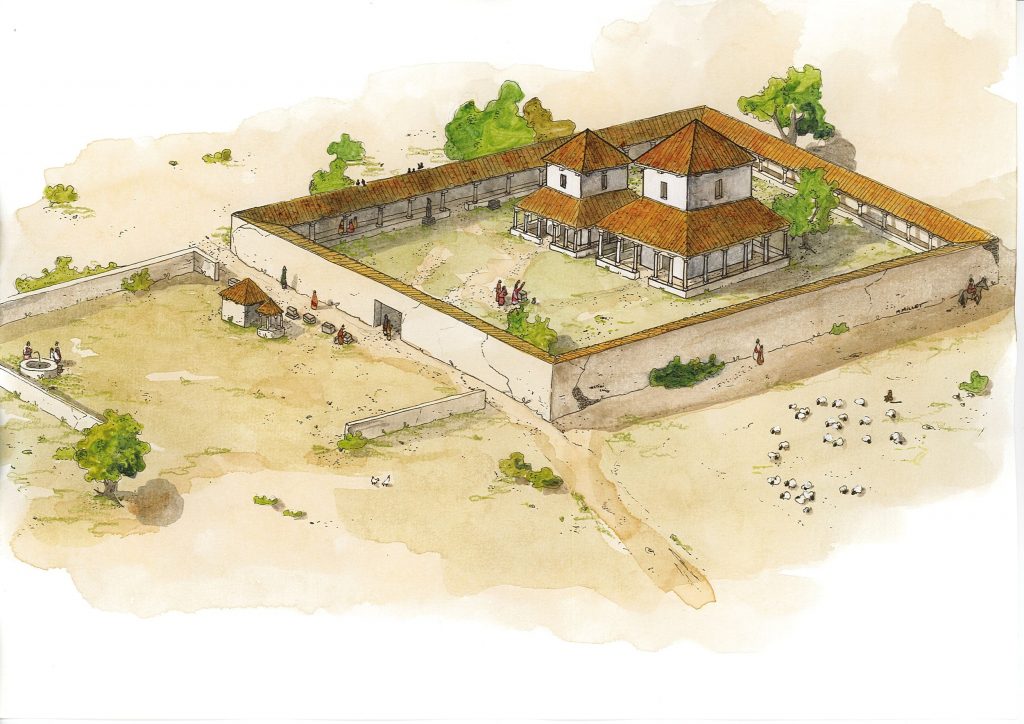

Located only 10 km from Condate, the sanctuary was visible from afar. It faces the Flume valley to the west, the Rennes basin to the east, and the great Roman road connecting Rennes to Corseul to the north. The discovery could shed light on the lifestyles of the time. The discovery may provide insight into how local Celtic populations gradually integrated the Roman religious and social practices of the Riedones.
The worship complex consists of a large sanctuary, bounded on either side by a 60 m columned gallery. Two temples, one larger and one smaller, were built-in typical Romano-Celtic fanum style (ie, a square masonry temple with a central cella inside a square gallery). A cult figure of a deity inhabited the cella. The faithful would offer their prayers and votives in the gallery. The large temple was dedicated to the sanctuary’s primary deity (or deities); the smaller to deities of secondary importance. Welcoming pilgrims to the sanctuary was a forecourt with a well and two small chapel-like structures.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
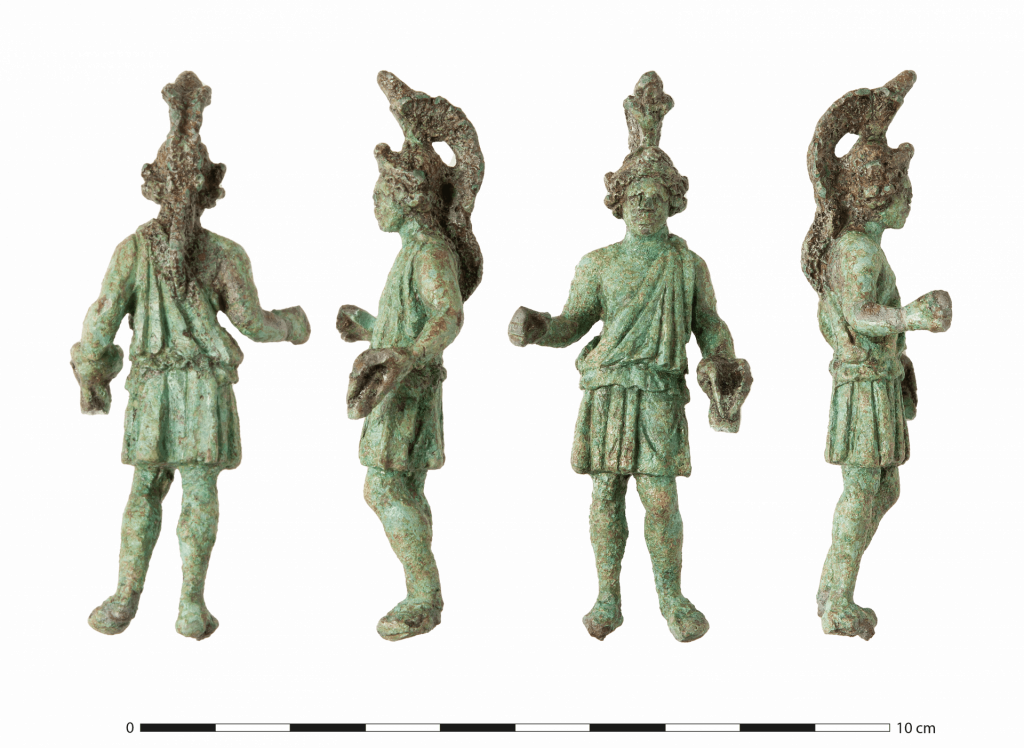

Also, during the excavation of the Chapelle-des-Fougeretz, a small bronze statuette of the god Mars was uncovered, suggesting that at least one of the temples was dedicated to him. In Roman Gaul, God Mars was not the bloodthirsty god of war so much as a benevolent figure and a protective healing deity.
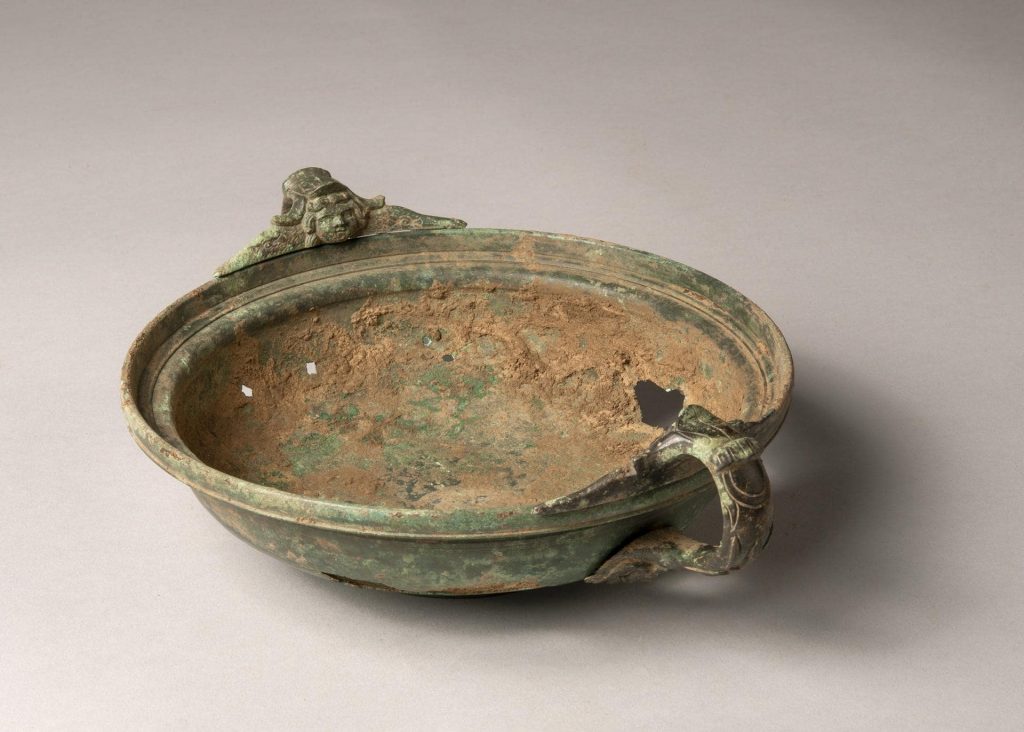
Another sacred object unearthed, a remarkable bronze vessel has a Jupiter-themed decoration (eagle and lightning bolt figures on both handles). The cup was found upside down and intact with its two ornately decorated handles still attached. One side of the handle is carved with the relief of a face of a Cupid. Two wings are engraved on each side of the face. The other end of the handle mounts is decorated with reliefs of eagles in profile. The curved part of the handle between the terminals features stylized thunderbolts. Such a rich offering suggests Jupiter may also have been worshipped at the sanctuary.

In addition to the two temples, habitats have been unearthed as well as 120 m2 baths. Symbols of a Roman way of life, the baths were probably intended for public use and for the faithful of the sanctuary.