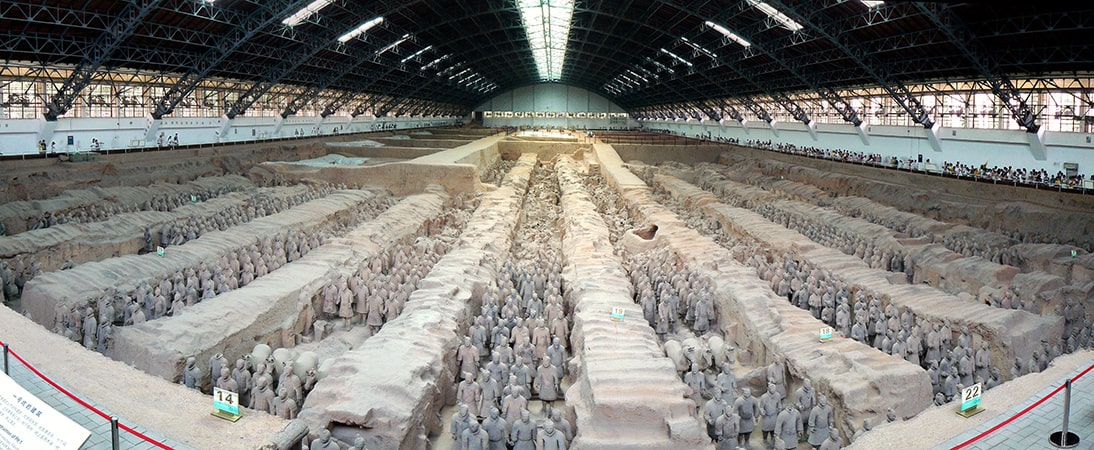
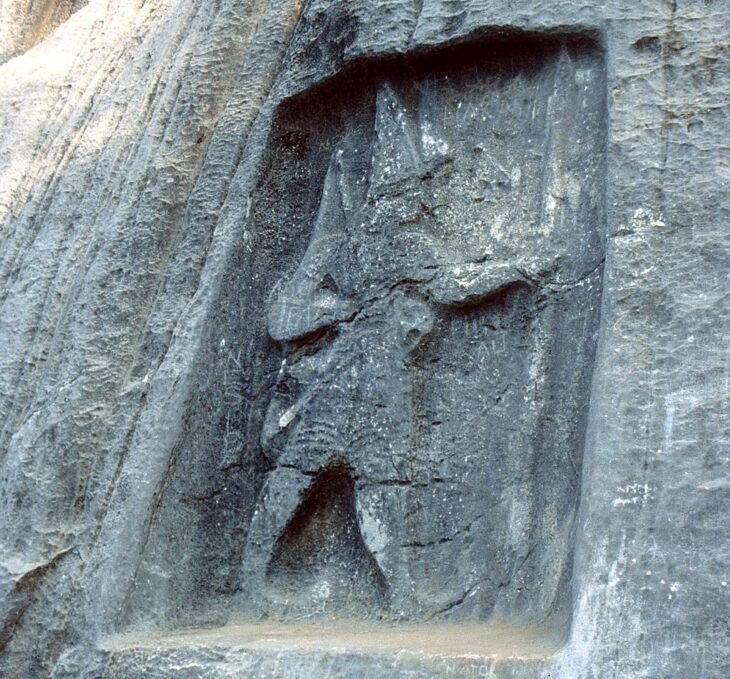
Qin Shi Huang was the first emperor of China, and his tomb is renowned for being guarded by an army of 6,000 life-sized terracotta warriors.
Although Qin Shi Huang (259–210 BCE) accomplished much in this life, his ultimate goal was to defeat death. He constructed a massive underground city, complete with armor and weaponry, to protect himself from death. The army was composed of life-sized terracotta warriors, infantrymen, horses, chariots, and all the other equipment needed for combat.
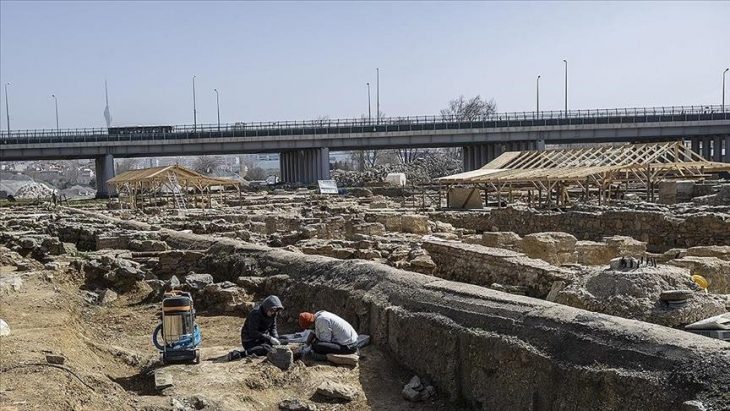
Qin Shi Huang’s tomb is the world’s largest mausoleum, covering 22 square miles, and much of it has yet to be excavated due to concerns about damage from seismic activity, the elements, and looters. A 2010 excavation focused on the tomb’s foundations, uncovering a massive palace with 18 courtyard-style homes arranged around a central building. It is a quarter the size of Beijing’s Forbidden City and is regarded as its conceptual progenitor, though this one was designed for the emperor to live in after his death.
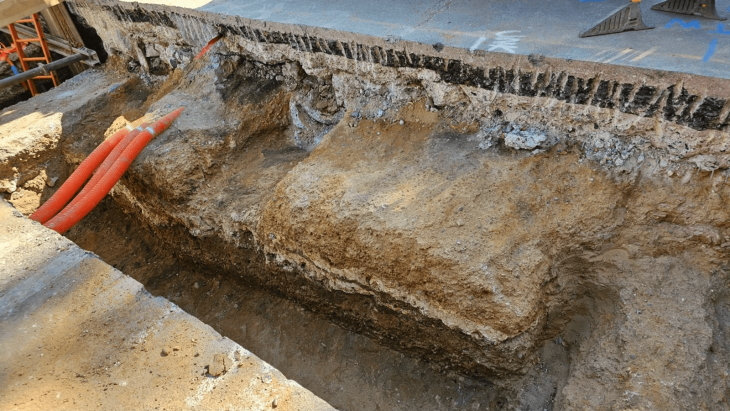
Now, a massive 16-tonne coffin hidden with treasures has been found inside a tomb that could belong to the son of China’s first emperor.
For nearly 2,000 years, the myth of Prince Gao – son to the first emperor of China, Qin Shi Huang – has been carried down the generations, carved into legend in the surviving epic saga of historian Sima Qian, himself writing around 85 BCE.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
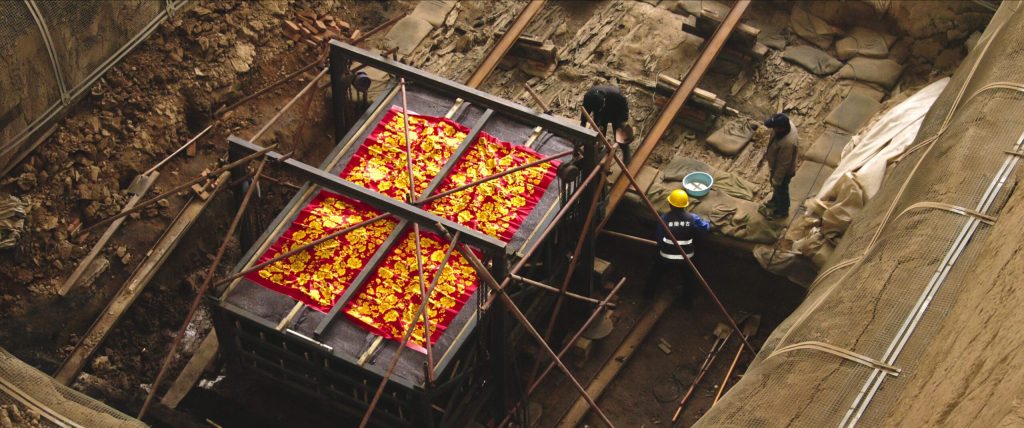

According to Sima Qian (also known as the Shiji), after Qin Shi Huang’s death, his youngest son Hu Hai took the throne after killing all his competitors. Prince Gao told his brother that he regretted not voluntarily following his father into the afterlife, and asked that he be killed and buried in the great mausoleum. Hu Hai was glad to oblige.
Prince Gao’s tale might be wholly made up. Although the Shiji is a chronicle, it treats legend and tradition as fact, much like Livy’s Ab urbe condita. For instance, the mausoleum is said to have “100 rivers of mercury” flowing through it by the Shiji. Perhaps the 100 rivers story was exaggerated, but it was not entirely fabricated, as soil testing revealed mercury levels 100 times higher than usual.
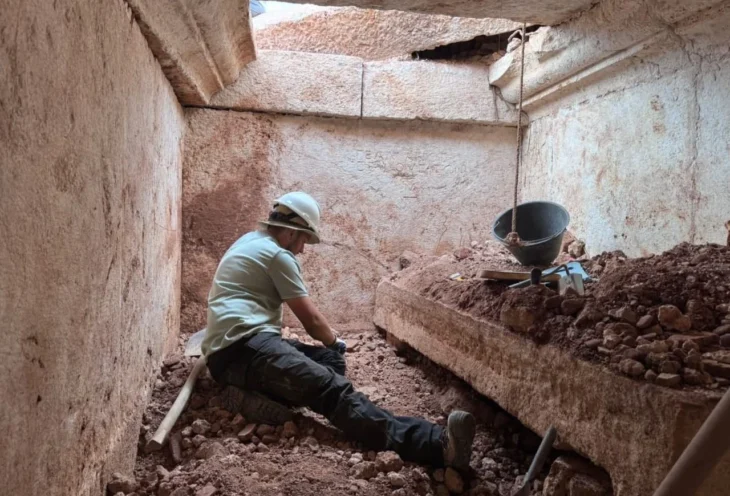
The discovery of a 16-tonne coffin in a large burial chamber near the mausoleum of Qin Shi Huang and his terracotta warriors may now bring the myth to life.
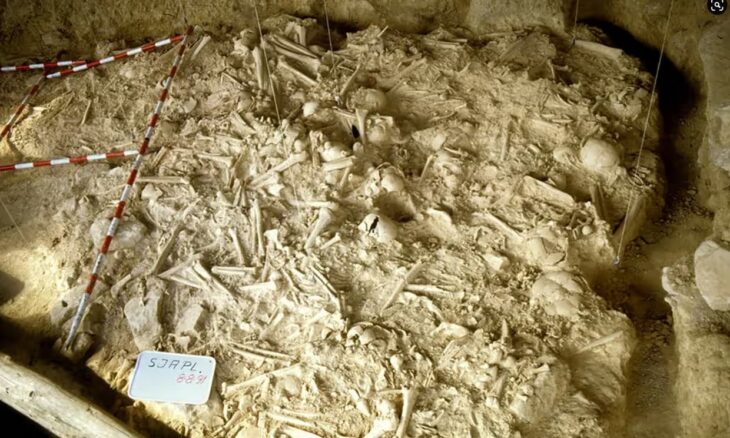
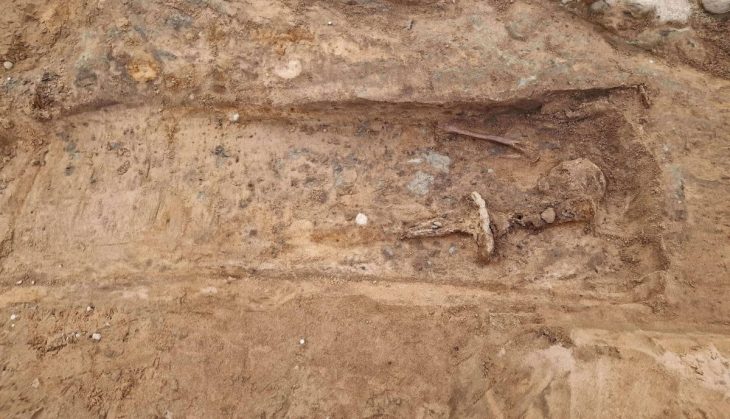
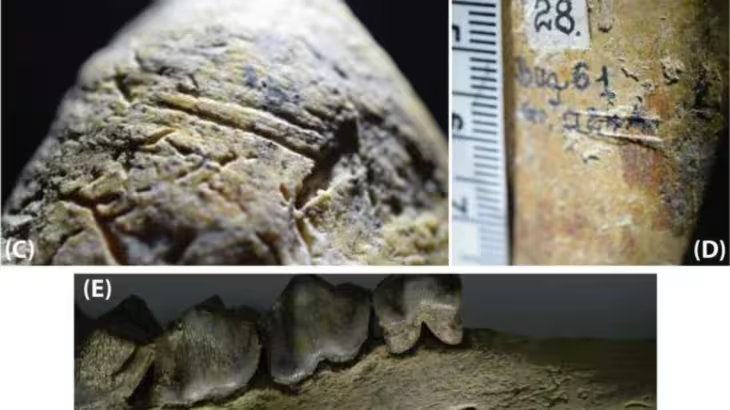
The coffin was found to contain very rich funerary deposits, including weapons, armor, jade, a pair of gold and silver camels, a set of cooking utensils, and 6,000 bronze coins. With such a grand burial, the deceased must have been, even one of the sons of the Qin Emperor or a warrior of high rank.
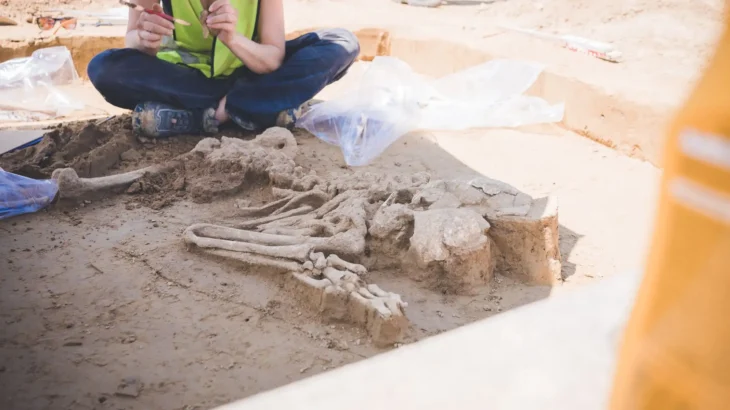
In 2011 excavation also unearthed nine tombs. Their large coffins were left in place in keeping with the Chinese government’s hands-off policy as regards the mausoleum and its contents. Archaeologists returned this year to recover the coffin after it was threatened by heavy rain. It was excavated and removed for further study and examination of the contents in a controlled environment.
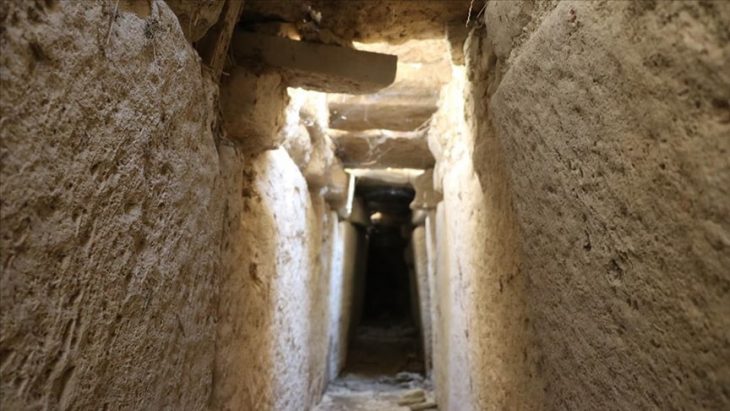
At the bottom of a tomb in central China, 16 meters deep and 109 meters long, a coffin sealed for millennia continues to puzzle archaeologists.
“Every time I go down I still feel amazed,’ said dig leader Jiang Wenxiao, as reported by The Times.
“After the first emperor died, his sons all came to a bad end, so I’m still more inclined to believe that this tomb belongs to a high-ranking nobleman or army chief,” Jiang Wenxiao, the excavation leader, said.
Wenxiao added: “The tomb was so precisely built. So deep, so large in scale. Most ancient tombs have been robbed so we didn’t have much hope for the coffin chamber. But it turned out it hadn’t been robbed. We were amazed.”
A British-Chinese co-production that was given unique access to the mausoleum site and the ongoing excavation was able to film the discovery. The Mysteries of the Terracotta Warriors, which premieres on Netflix on June 12th, will center around the discoveries.
Cover Photo: Terracotta warriors from the mausoleum of the first Qin emperor of China Qin Shi Huang, c. 221-206 B.C.E., Qin Dynasty, painted terracotta, Terracotta Warriors and Horses Museum, Shaanxi, China. Photo: Will Clayton, CC BY 2.0