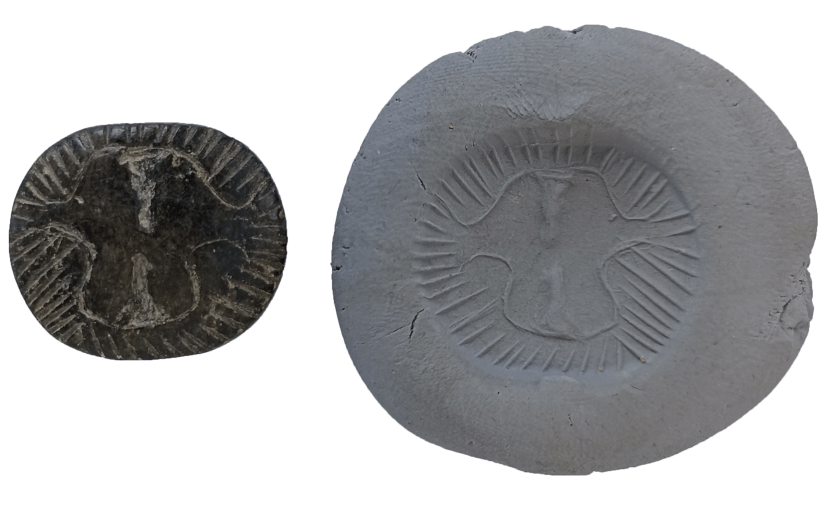
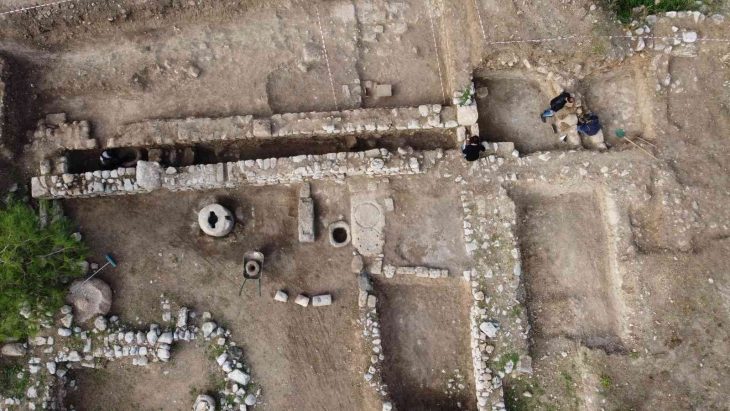
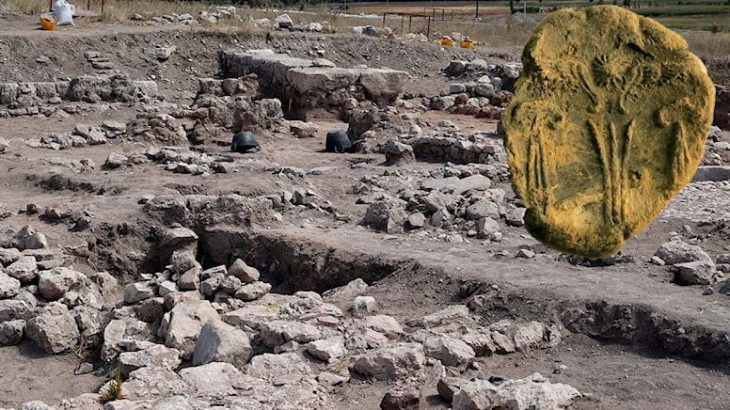
A rare Late Neolithic Seal was discovered during the 2022 excavations of the Domuztepe Mound (Domuztepe Höyük), located on the Narlı Plain in the southern part of Kahramanmaraş province in Turkey’s Mediterranean Region.
Domuztepe, a Late Neolithic settlement (7000-5400 BC), is located in the Türkoğlu district of Kahramanmaraş.
The archaeological digs at the site have been ongoing under the direction of Hacettepe University’s Faculty of Letters and Archaeology Department associate professor Halil Tekin, in collaboration with the Ministry of Culture and Tourism.
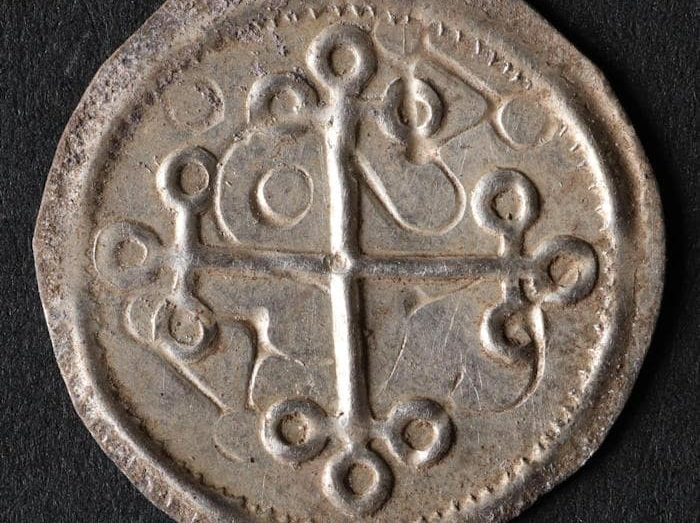
Two animal heads with horns, made with their mouths facing each other with the “mirroring” (antithetic) method, draw attention on the printing surface of the thread-hole button seal made of serpentine in the fill soil of the 2 structure levels of Domuztepe Mound.
The presence of stylized bull head motifs as paint decorations on clay pottery at Domuztepe was detected in the past years. In the mound, which is the largest settlement of the lifestyle known as “Halaf” in traditional Mesopotamian terminology in the Eastern Mediterranean, the bullheads visualized on different materials are mostly accepted as the representative of the species known as domestic cattle (Bos Taurus) in the Near East. On the other hand, it is possible that the species in the samples shaped both as a paint decoration on pottery and by scraping on seal impressions is a water buffalo (bos bubalis). Since archaeozoological studies have not been completed yet, it is premature to say that water buffalo was domesticated in the Eastern Mediterranean, where Domuztepe is located, in the 7th-6th millennium BC.
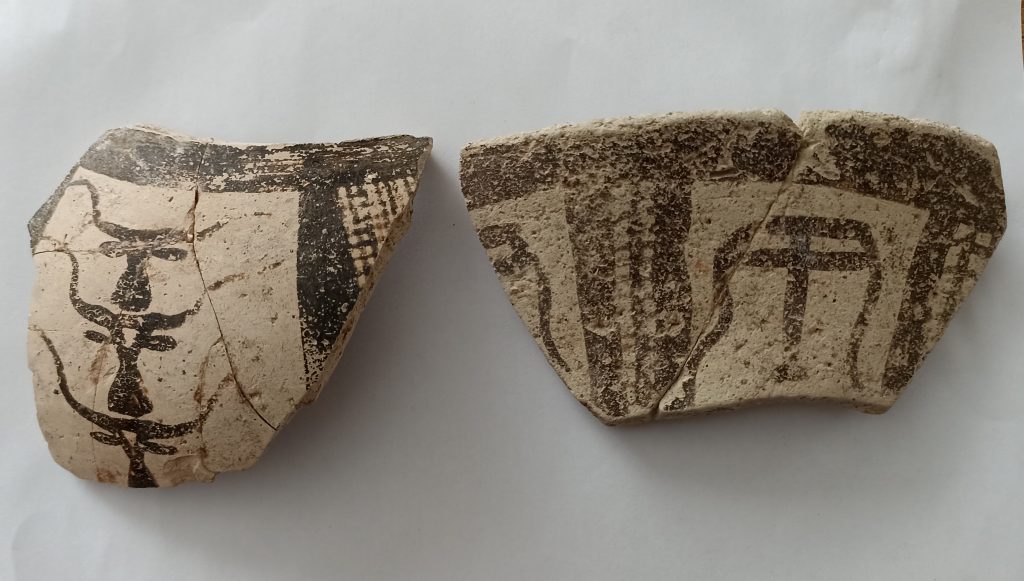

It is also possible that the type observed in the form of paint decorations on the seal stamping surface and on some pottery is not water buffalo but only bullheads were shaped in different styles. Undoubtedly, future analyzes will shed light on this issue. However, it should be noted that such a depiction method is rarely seen in Mesopotamian Late Neolithic seal impressions.
The excavations at Domuztepe between 1995 and 2011 resulted in the recovery of about 180 seals and related items. A total of 130 objects have been classified based on the relationship between the image and the image-bearing surface geometry. This number decreases when the broken or partially finished objects are subtracted from this count. In this context, it has been observed that a total of 15 naturalistically shaped objects carry zoomorphic and anthropomorphic themes, while the remaining 115 items are composed of a limited set of abstract image themes that are difficult make sense of, at a first glance.