A group of hobby metal detectorists has discovered two Viking treasures buried a few meters apart near the ruins of the Viking castle Fyrkat in Hobro, northern Denmark.
Treasures both contained many small silver coins and cut-up silver jewelry, which probably served as a means of payment by weight.
The three people who discovered the treasure trove — were Jane Foged-Mønster, Louise Stahlschmidt, and Mette Norre Bækgaard.
Fyrkat is a former Viking ring castle in Denmark that dates back to around 980 AD. Legendary King Harald Bluetooth built several impressive Viking fortresses around 1,000 years ago.
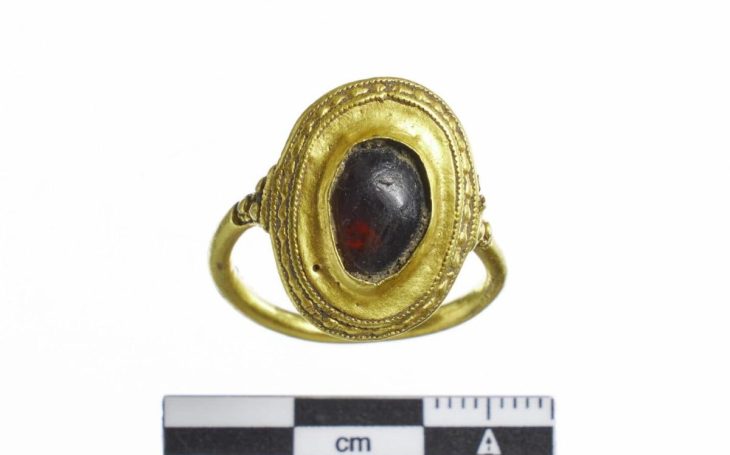
The find — made in autumn last year — dates back to the 900s, when King Harald “Bluetooth” (Blåtand) Gormsson, who united Denmark and Norway. The trove contained over 300 items, including Danish, German, and Arab coins, as well as silver balls, and a ring pin.
Finding Viking treasures is not uncommon in Denmark, but finding two so close to Fyrkat is incredible. The metal detectors who are members of Nordjysk Detektorforening were lucky because due to modern plowing, harrowing, and sowing, the hoards have been disturbed and spread over a larger area.

Archaeologist and museum inspector at North Jutland Museums Torben Trier Christiansen told Danish news site TV2 Nord that “The two silver treasures in themselves represent an absolutely fantastic story, but to find them buried in a settlement just eight kilometers from Harald Bluetooth’s Viking castle Fyrkat is incredibly exciting” that the coins are linked to the king, adding, “We are looking forward to delving into that history.”
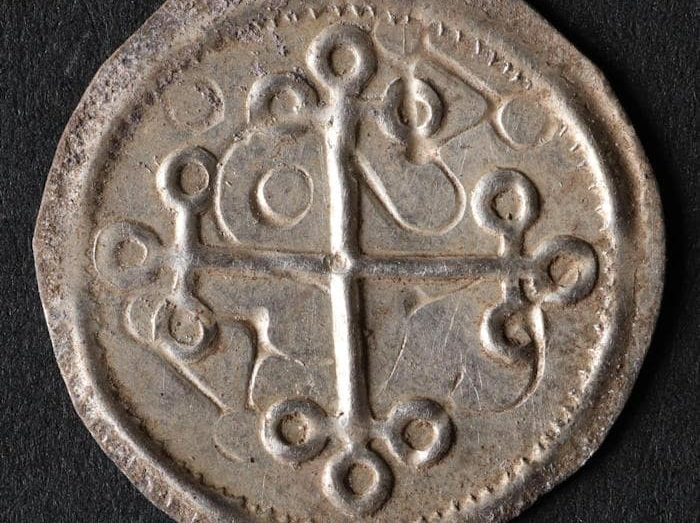
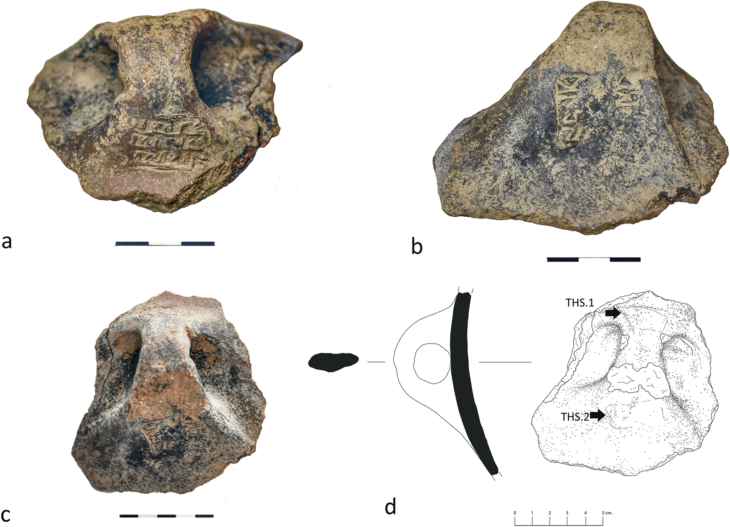
Experts at the nearby Historical Museum of Northern Jutland, where the items are being examined, noted that two of the items found are “particularly interesting”: two ornately braided decorated balls on a small piece of cut silver rod – both clearly once part of the same unusually large silver ring pin.
The museum staff believes that because it is so large and valuable, it was probably taken from a bishop or king and may have come from a member of high society in Ireland, which is more than 1,200 nautical miles away from where the treasure was discovered.
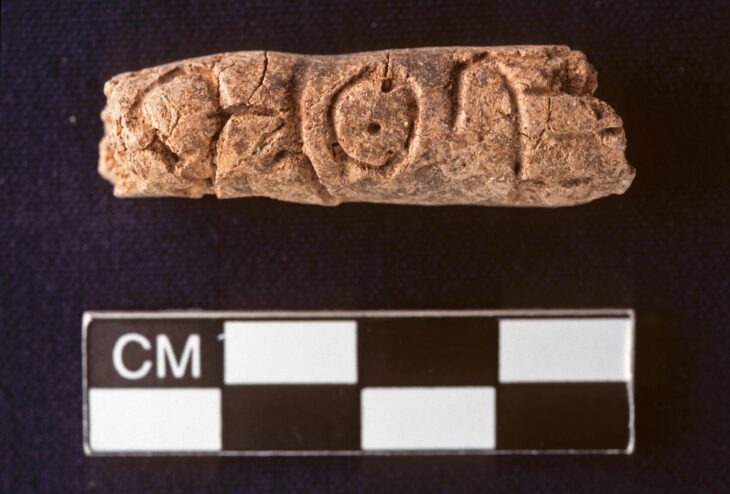
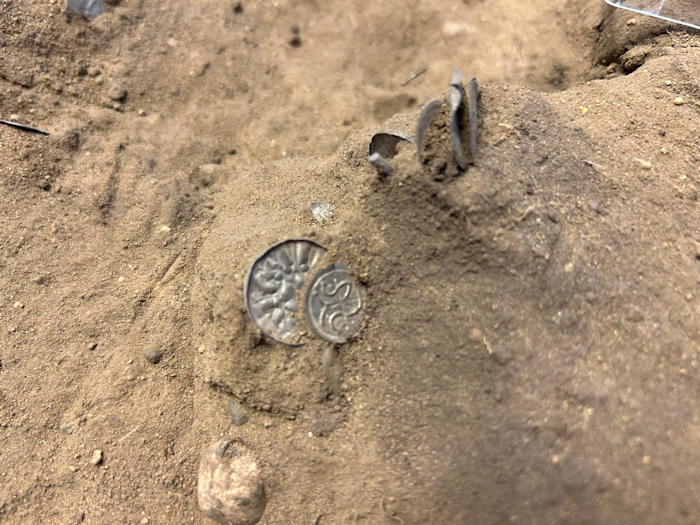
According to the museum’s statement, the coins featured a cross, indicating that they were made late in King Bluetooth’s reign.
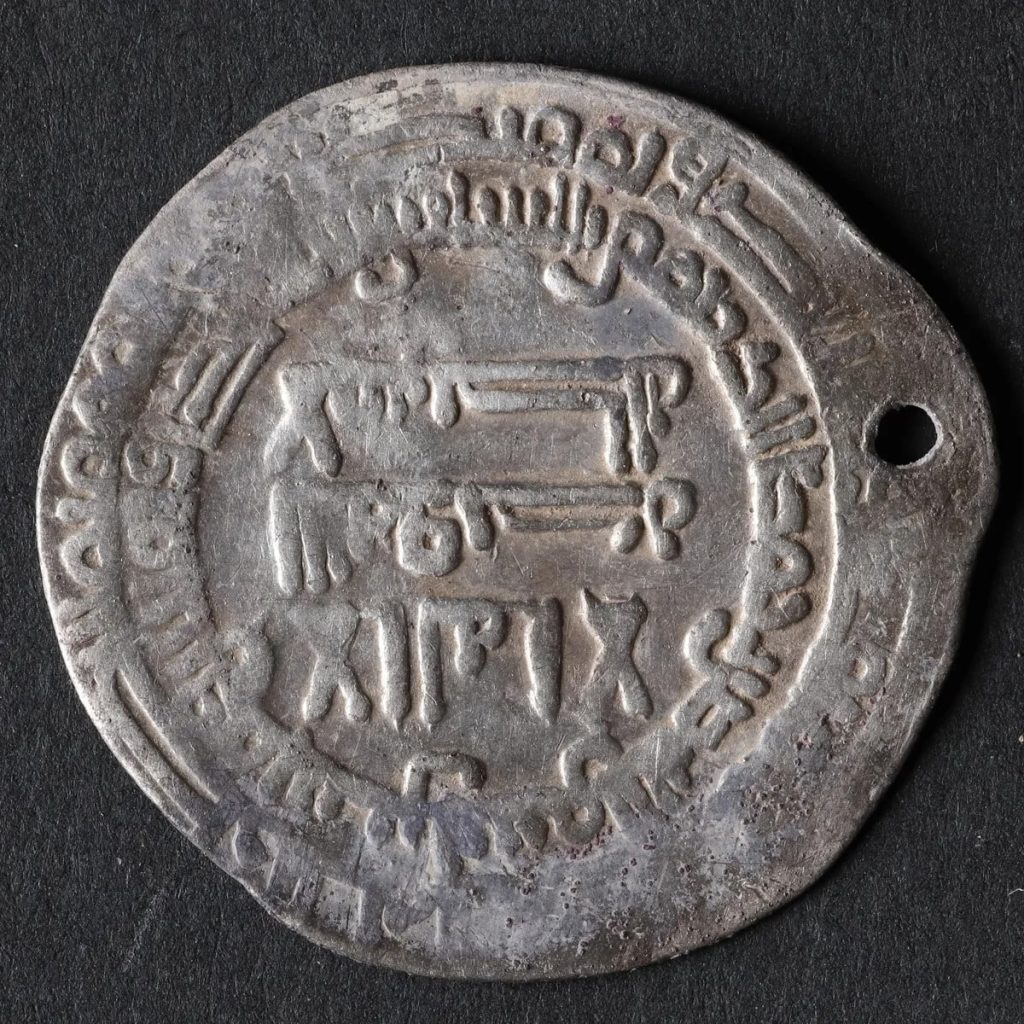

It is believed that King Bluetooth “introduced the cross coins as propaganda in connection with his Christianization of the Danes – i.e. as a further spread of Harald’s message on the great Jelling stone, which was erected around the year 965”
Less than a few decades after the introduction of Harald Bluetooth‘s cross coins into circulation, in the mid-980s, his son Svend Tveskaeg defeated him in a power struggle. Therefore, the artifacts come from this extremely dramatic time in Viking history.
“Perhaps the castles were not given up entirely voluntarily, and perhaps it happened in connection with the final showdown between Harald Blåtand and his son Svend Tveskæg,” suggested Torben Trier Christiansen, an archaeologist and museum inspector at the Museum.
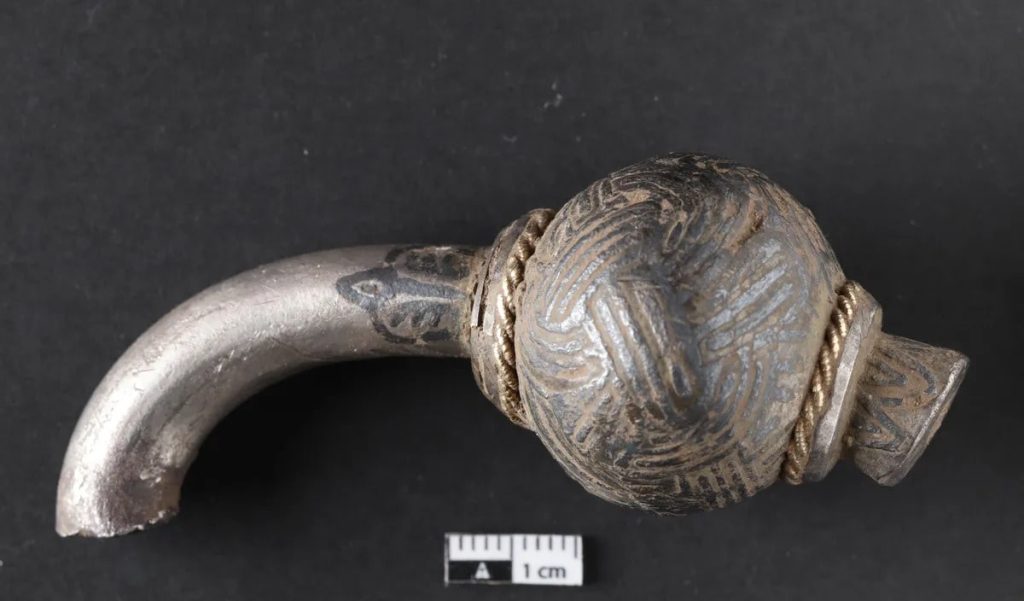

“If there were disturbances at Fyrkat, it makes good sense that the local magnate here at Bramslev would choose to hide his valuables out of the way,” he added.
The Viking hoards were initially buried fairly close to one another. The coins and other silver are thoroughly mixed together as a result of modern disturbances. Which makes it difficult for experts to say for certain which trove any individual item came from.
Cover Photo: The sign of the cross helped scientists to date the coins. Nordjyske Museer