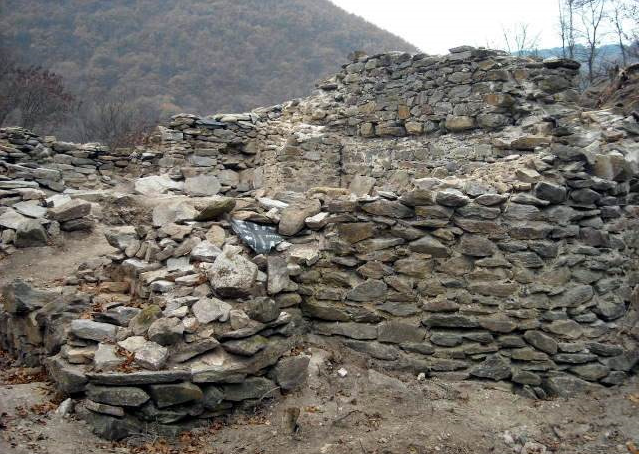
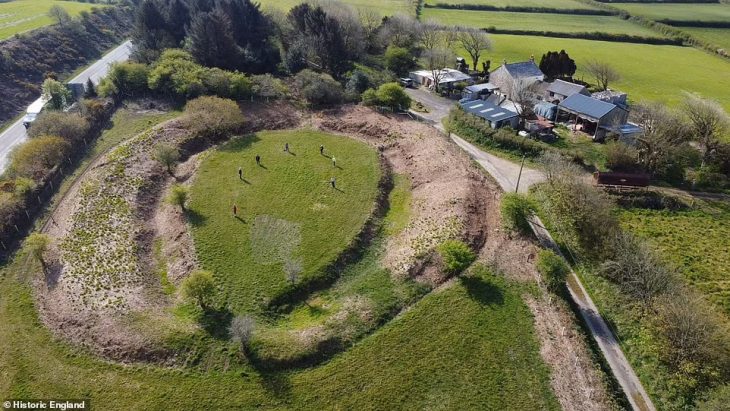
Bulgarian archaeologists have uncovered a triangular stone tower — a rare architectural form in Roman military design — at the Kokalanski Urvich fortress just outside Sofia. Dated to the late 2nd century AD, the structure sheds new light on Roman-era military planning and the early strategic significance of the Sofia region.
The discovery, described as one of the most unique finds in recent decades, was made by Dr. Filip Petrunov and Violina Kiryakova during the final phase of an excavation funded by Sofia Municipality’s “Culture” programme.
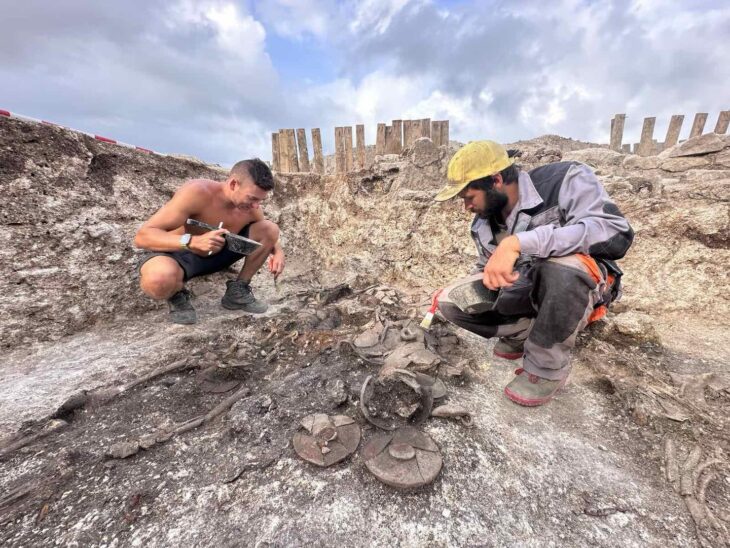
The tower was found 1.7 meters below the surface, embedded in massive stone foundations shaped in a distinct triangular layout — a rare design in Roman military architecture. This configuration immediately caught the attention of experts from the National History Museum, as it suggests a strategically planned defensive structure that predates many known fortifications in the region.
A Hidden Link to Ancient Serdica
What makes this discovery even more extraordinary is its historical alignment with the development of ancient Serdica, the Roman predecessor of modern-day Sofia. Scholars believe the tower was constructed during the same period as Serdica’s urban rise, linking the two sites in a broader narrative of Roman expansion and strategic defense across the Balkans.
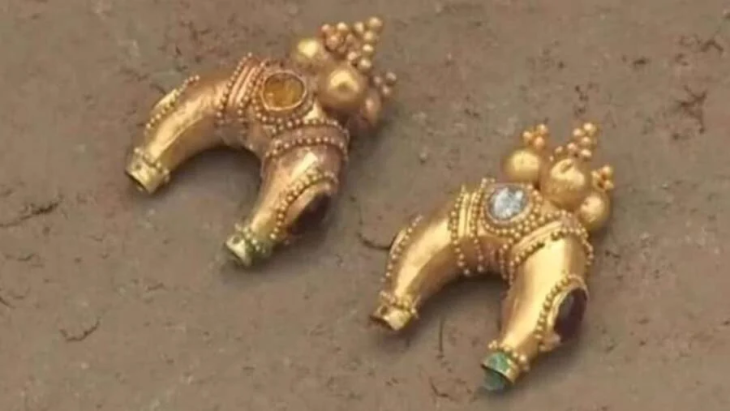
The earliest coins recovered from the site — dating back to the reign of Roman Emperor Caracalla (211–217 AD) — further cement the tower’s 2nd-century origins. According to the excavation team, this is the oldest structure ever found at the Urvich site, revealing that the fortress held a strategic role far earlier than previously thought.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
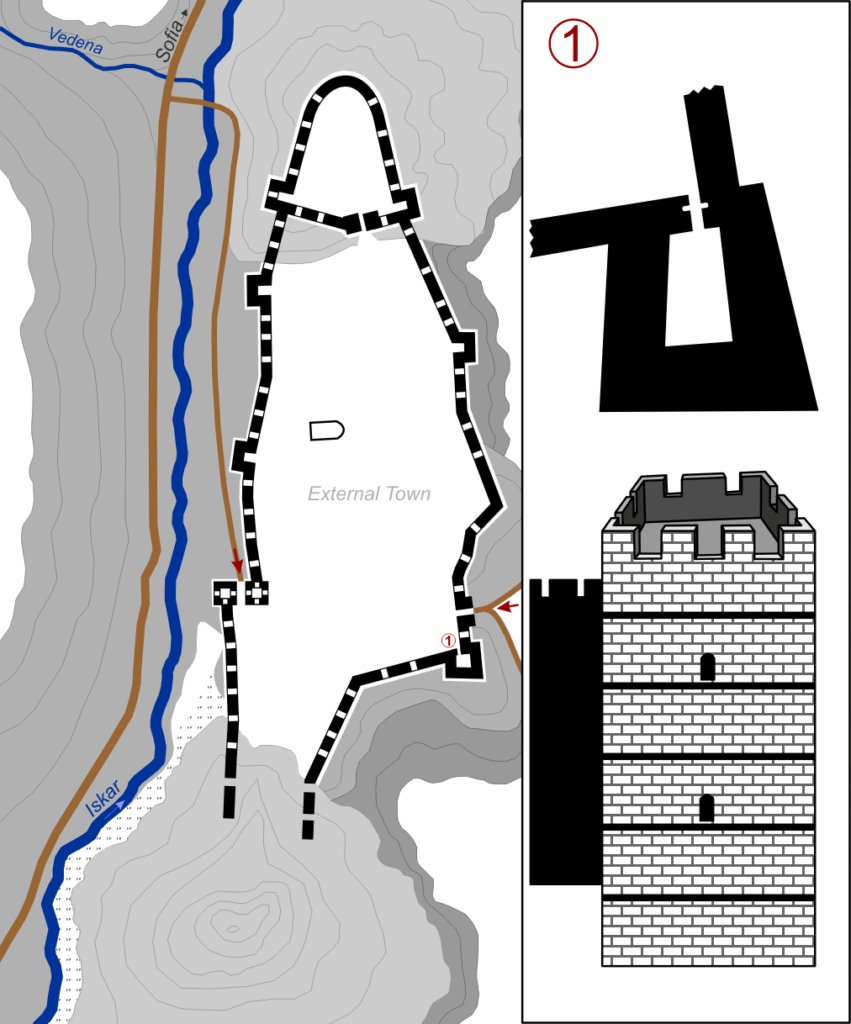
Layered History: From Rome to Byzantium
The tower’s historical relevance doesn’t stop with the Romans. Archaeologists also found signs of continued occupation and reconstruction across centuries, pointing to its multi-period importance. Evidence of later structural reinforcements and fortifications, including Byzantine stonework, suggests that the tower remained a key military outpost well into the medieval era.
Of particular note is a Byzantine coin bearing the image of Emperor Isaac II Angelos (1185–1195 AD). This artifact provides direct evidence of 12th-century reconstruction efforts, implying that the fortress was re-integrated into the defensive network of the Second Bulgarian Empire or late Byzantine territories.
This continuity of use over more than a millennium demonstrates not only the architectural durability of the site but also its enduring geostrategic value in the Balkans.
Public Engagement: Making the Past Accessible
Alongside the excavation work, new informational signage has been installed at the Kokalanski Urvich site to help visitors interpret the area’s most significant archaeological features. The initiative is part of the National History Museum’s project “The House of the Double-Headed Eagle”, which aims to socially integrate historic sites into public life and raise awareness of Bulgaria’s cultural heritage.
This project is a vital step toward cultural tourism development, providing an educational experience for locals and international visitors alike. The triangular tower, with its layered Roman and Byzantine past, now stands not only as an archaeological find but as a living monument to Bulgaria’s rich historical continuum.
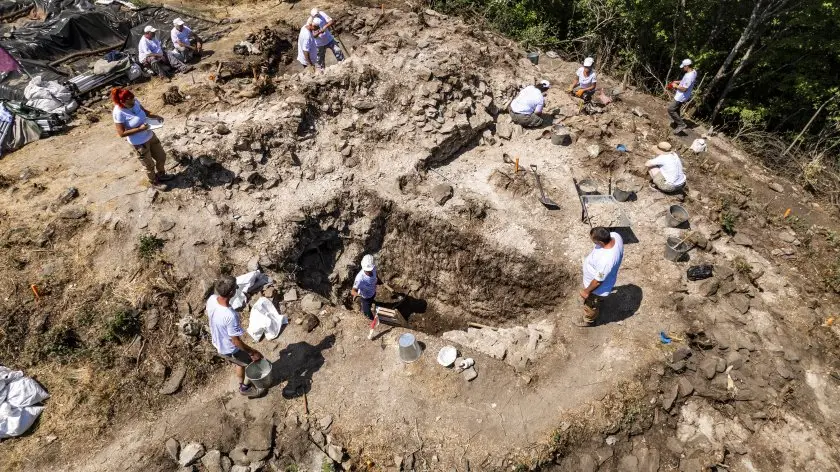

Connecting the Dots: The Serdica Triangle and Kokalanski Urvich
The triangular design of the newly uncovered tower has drawn comparisons to the Serdica Triangle in central Sofia, where Roman ruins lie beneath the modern capital’s government buildings. While the Serdica Triangle represents urban civic planning, the Urvich tower appears to be its military counterpart, reinforcing the strategic web that supported Roman Serdica’s rise.
By connecting these two “triangles,” historians are piecing together a broader vision of Roman infrastructure, defense, and governance in ancient Thrace.
A Triangular Key to Bulgaria’s Past
The discovery of the triangular tower at Kokalanski Urvich is more than just an archaeological event — it’s a window into a layered, dynamic history that spans empires and centuries. As excavation efforts continue and public engagement grows, this site may well become a cornerstone of Bulgaria’s historical tourism and academic research landscape.
Cover Image Credit: Kokalanski Urvich fortress near Sofia. Wikipedia Commons