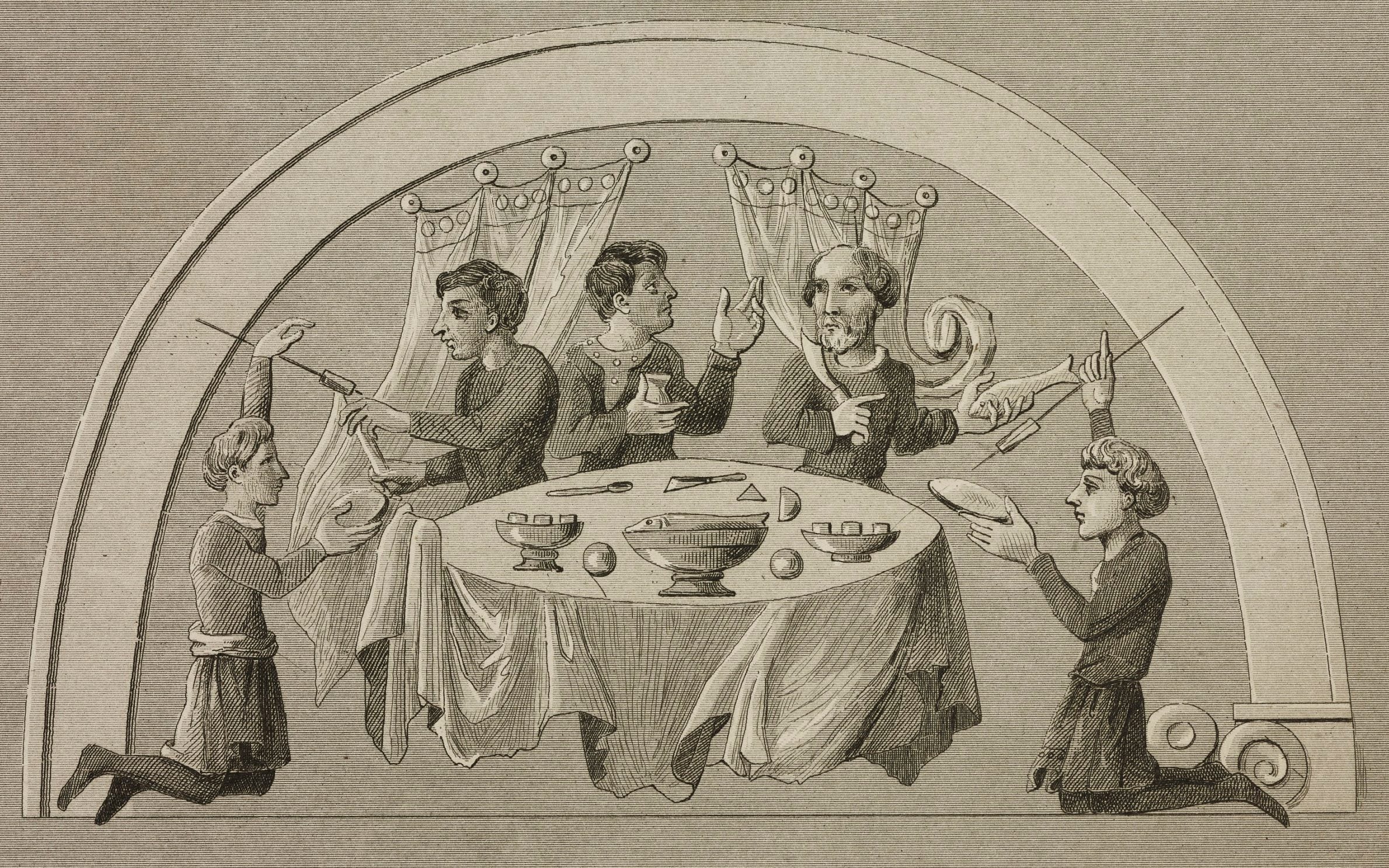
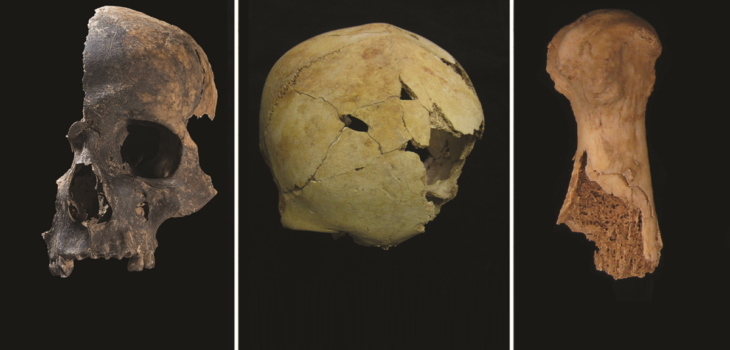
Very few people in England ate large amounts of meat before the Vikings settled, and there is no evidence that elites ate more meat than other people, a major new bioarchaeological study suggests. Its sister study also argues that peasants occasionally hosted lavish meat feasts for their rulers. The findings overturn major assumptions about early medieval English history.
Picture medieval England and royal feasts involving copious amounts of meat immediately spring to mind. Historians have long assumed that royals and nobles ate far more meat than the rest of the population and that free peasants were forced to hand over food to sustain their rulers throughout the year in an exploitative system known as feorm or food-rent.
But a pair of Cambridge co-authored studies published today in the journal Anglo-Saxon England present a very different picture, one which could transform our understanding of early medieval kingship and society.
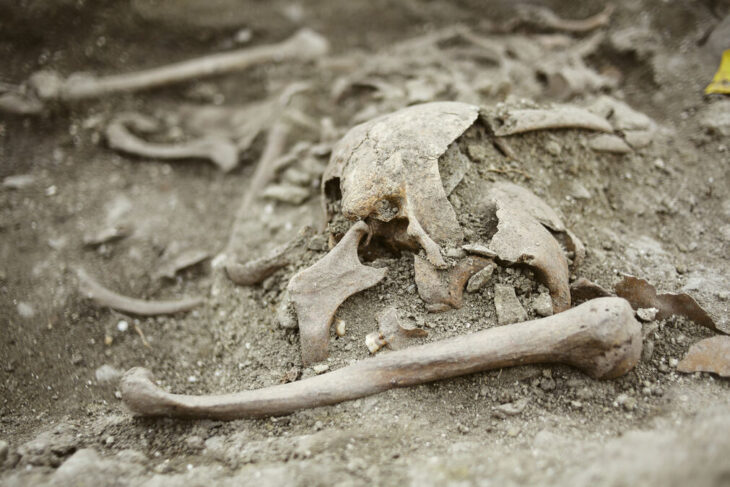
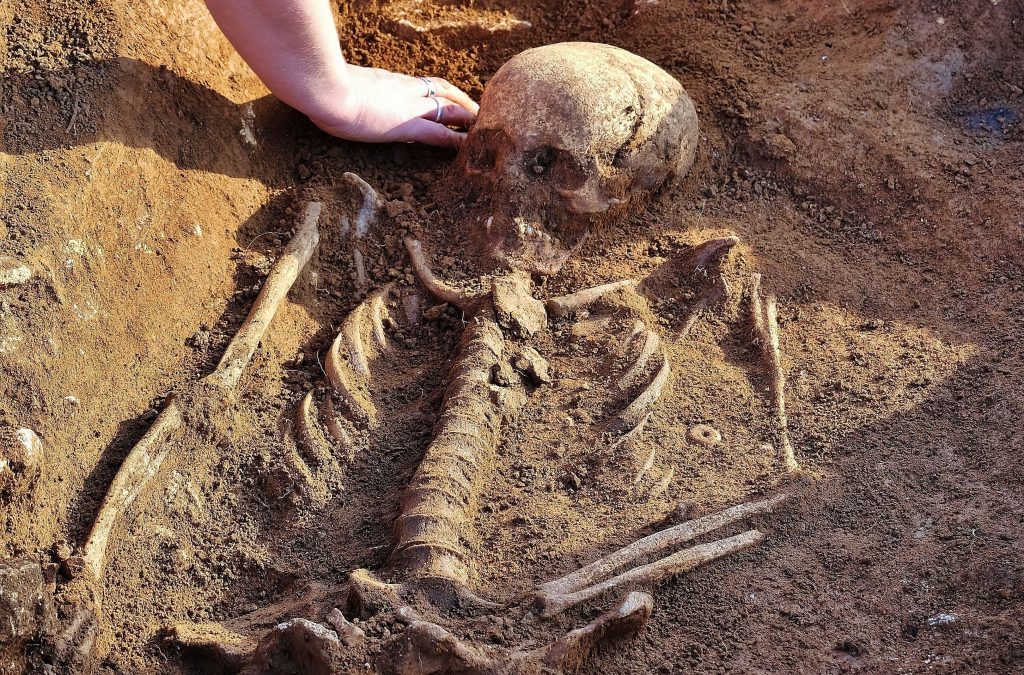
While completing a Ph.D. at the University of Cambridge, bioarchaeologist Sam Leggett gave a presentation which intrigued historian Tom Lambert (Sidney Sussex College). Now at the University of Edinburgh, Dr. Leggett had analyzed chemical signatures of diets preserved in the bones of 2,023 people buried in England from the 5th—to 11th centuries. She then cross-referenced these isotopic findings with evidence for social statuses such as grave goods, body position, and grave orientation. Leggett’s research revealed no correlation between social status and high protein diets.
That surprised Tom Lambert because so many medieval texts and historical studies suggest that Anglo-Saxon elites did eat large quantities of meat. The pair started to work together to find out what was really going on.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

They began by deciphering a food list compiled during the reign of King Ine of Wessex (c. 688-726) to estimate how much food it records and what its calorie content might have been. They estimated that the supplies amounted to 1.24 million kcal, over half of which came from animal protein. The list included 300 bread rolls so the researchers worked on the basis that one bun was served to each diner to calculate overall portions. Each guest would have received 4,140 kcal from 500g of mutton; 500g of beef; another 500g of salmon, eel and poultry; plus cheese, honey and ale.
The researchers studied ten other comparable food lists from southern England and discovered a remarkably similar pattern: a modest amount of bread, a huge amount of meat, a decent but not excessive quantity of ale, and no mention of vegetables (although some probably were served).
Lambert says: “The scale and proportions of these food lists strongly suggests that they were provisions for occasional grand feasts, and not general food supplies sustaining royal households on a daily basis. These were not blueprints for everyday elite diets as historians have assumed.”
“I’ve been to plenty of barbecues where friends have cooked ludicrous amounts of meat so we shouldn’t be too surprised. The guests probably ate the best bits and then leftovers might have been stewed up for later.”

Leggett says: “I’ve found no evidence of people eating anything like this much animal protein on a regular basis. If they were, we would find isotopic evidence of excess protein and signs of diseases like gout from the bones. But we’re just not finding that.”
“The isotopic evidence suggests that diets in this period were much more similar across social groups than we’ve been led to believe. We should imagine a wide range of people livening up bread with small quantities of meat and cheese, or eating pottages of leeks and whole grains with a little meat thrown in.”
The researchers believe that even royals would have eaten a cereal-based diet and that these occasional feasts would have been a treat for them too.
Peasants feeding kings
These feasts would have been lavish outdoor events at which whole oxen were roasted in huge pits, examples of which have been excavated in East Anglia.
Lambert says: “Historians generally assume that medieval feasts were exclusively for elites. But these food lists show that even if you allow for huge appetites, 300 or more people must have attended. That means that a lot of ordinary farmers must have been there, and this has big political implications.”
Kings in this period—including Rædwald, the early seventh-century East Anglian king perhaps buried at Sutton Hoo—are thought to have received renders of food, known in Old English as feorm or food-rent, from the free peasants of their kingdoms. It is often assumed that these were the primary source of food for royal households and that kings’ own lands played a minor supporting role at best. As kingdoms expanded, it has also been assumed that food-rent was redirected by royal grants to sustain a broader elite, making them even more influential over time.

But Lambert studied the use of the word feorm in different contexts, including aristocratic wills, and concludes that the term referred to a single feast and not this primitive form of tax. This is significant because food-rent required no personal involvement from a king or lord and no show of respect to the peasants who were duty-bound to provide it. When kings and lords attended communal feasts in person, however, the dynamics would have been very different.
Lambert says: “We’re looking at kings traveling to massive barbecues hosted by free peasants, people who owned their own farms and sometimes slaves to work on them. You could compare it to a modern presidential campaign dinner in the US. This was a crucial form of political engagement.”
This rethinking could have far-reaching implications for medieval studies and English political history more generally. Food renders have informed theories about the beginnings of English kingship and land-based patronage politics, and are central to ongoing debates about what led to the subjection of England’s once-free peasantry.
Leggett and Lambert are now eagerly awaiting the publication of isotopic data from the Winchester Mortuary Chests which are thought to contain the remains of Egbert, Canute, and other Anglo-Saxon royals. These results should provide unprecedented insights into the period’s most elite eating habits.
More information: SAM LEGGETT et al, Food and Power in Early Medieval England: a lack of (isotopic) enrichment, Anglo-Saxon England (2022). DOI: 10.1017/S0263675122000072
Tom Lambert et al, Food and Power in Early Medieval England: Rethinking Feorm, Anglo-Saxon England (2022). DOI: 10.1017/S0263675122000084