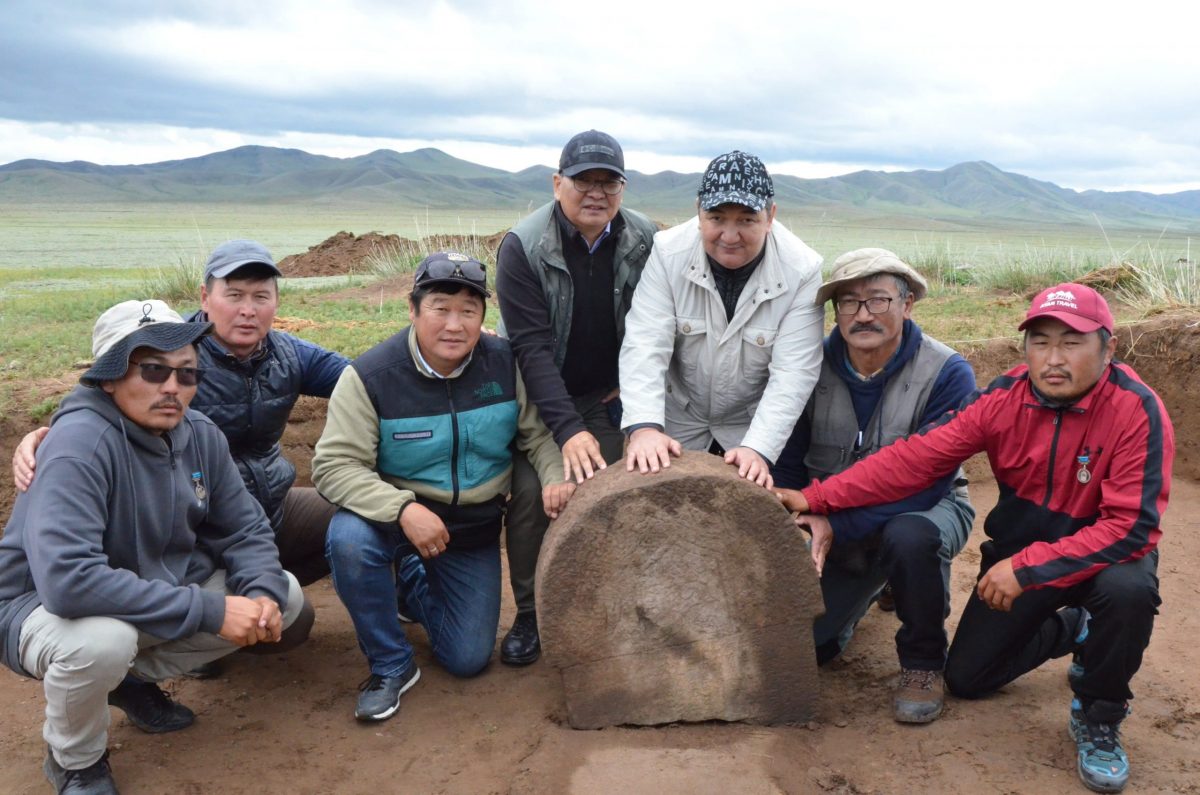
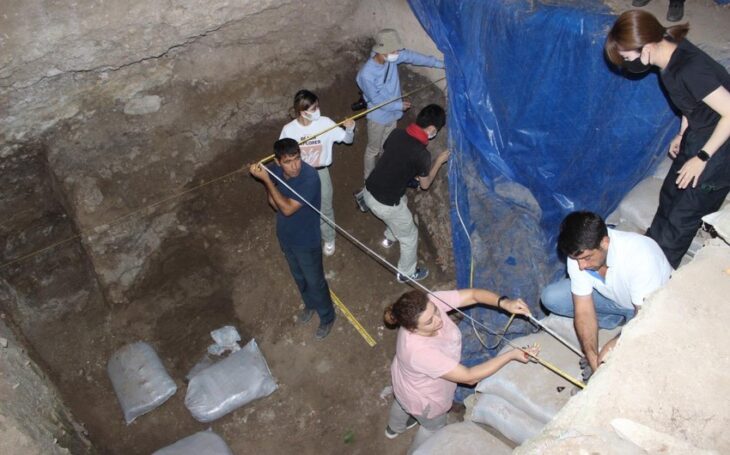
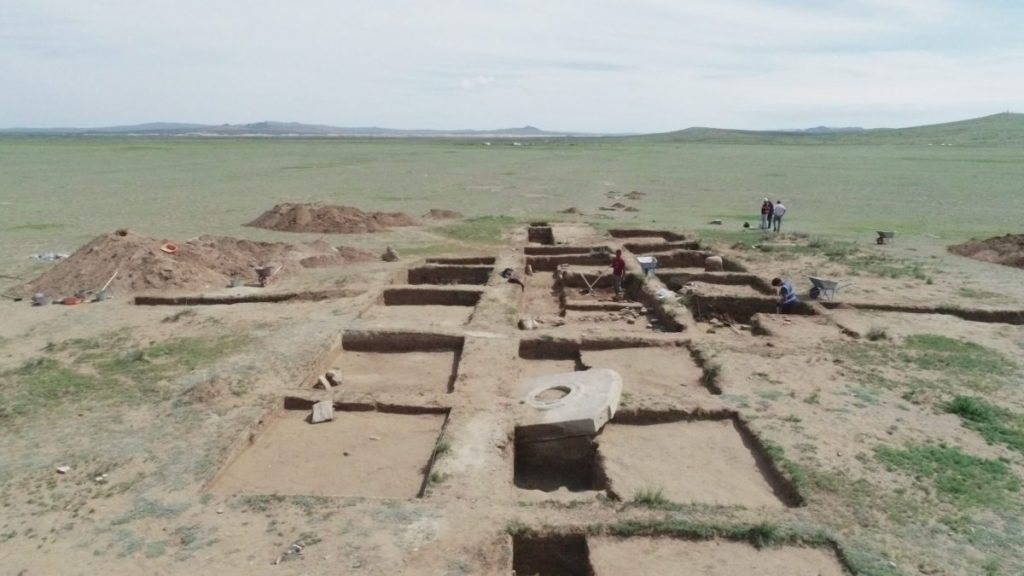
A Turkish inscription of İlteriş Kutlug Kağan was found during the joint scientific archaeological expedition of the International Turkic Academy and the Mongolian Archeology Institute in the Nomgon valley in the Arkhangai region of Mongolia.
Ilteris Kutlug Kagan is the founder of the Eastern Gokturk Khanate in 682.
An important discovery in the field of Turkology has been made at Hangai Jote in Mongolia’s Otuken region: a monument complex and a new inscription of Ilterish Kutlug Kagan.
The inscription found in a joint scientific archaeological expedition of the International Turkic Academy and the Mongolian Archaeological Institute in the Nomgon Valley is written in Turkic and Sogdian languages.

The discovery was announced by International Turkic Academy President Darhan Kidırali on his social media account on Tuesday. The Turkic Academy held a special press conference in Ulan Bator regarding the discovery.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
At the press conference, Darhan Kidirali said, “Today I want to share the good news with you. As a result of this year’s expedition, a monument complex and inscription dedicated to Ilteris Kutlug Kagan, the father of Kultegin and Bilge Kagan, who revived the Khanate, was found. I would like to point out that it is the oldest written monument where the name “Turkish” is mentioned for the first time in a valuable relic of the Turkish period,” he said.
However, G. Eregzen, Director of the Archeology History Institute of the Mongolian Academy of Sciences, reported on the results of the scientific archaeological expedition in the Nomgon Plain.
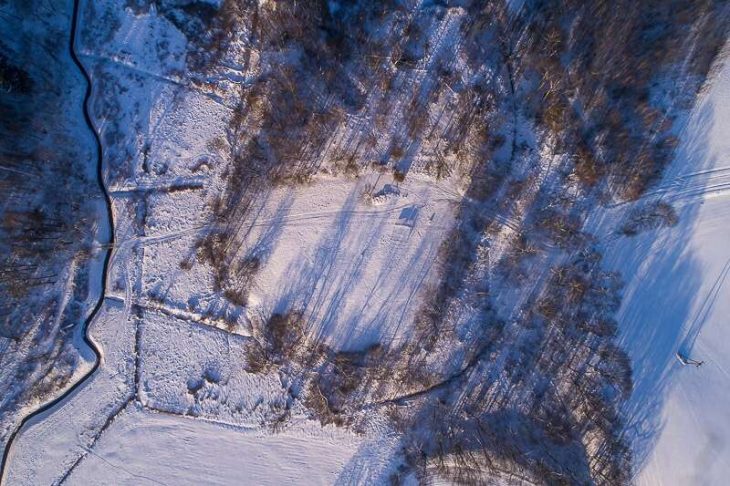
The total area of the complex is 49×41.5 m. A ditch was dug around the complex, which is located in an oval shape from west to east, and a castle was built by piling up soil from there.
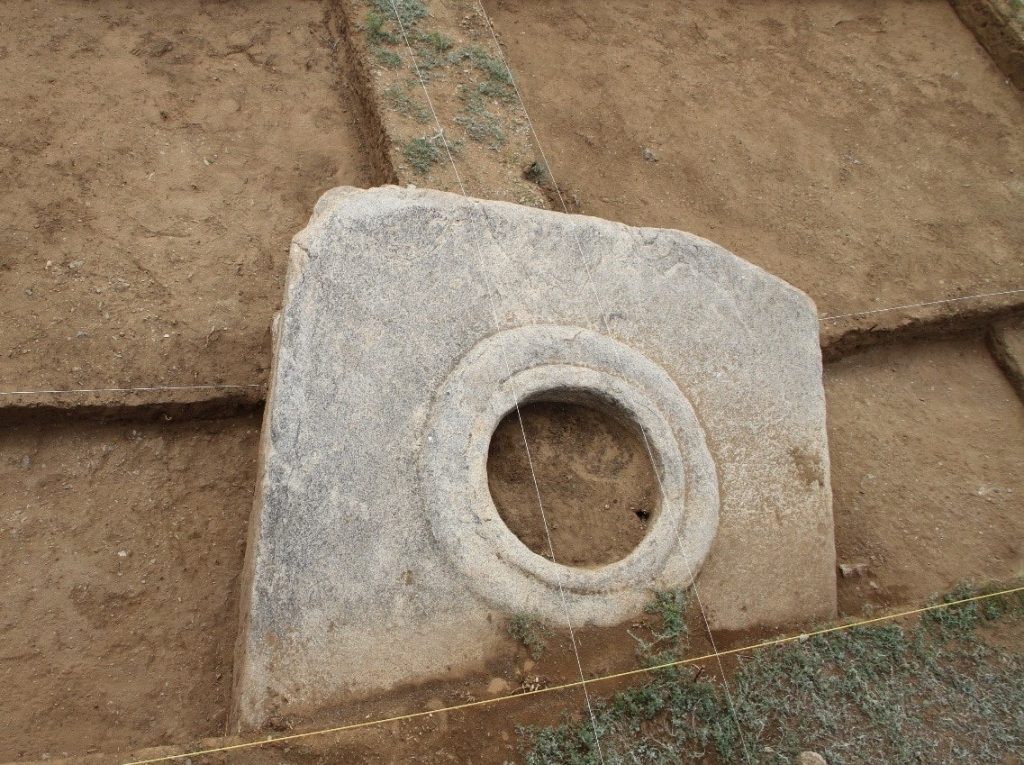

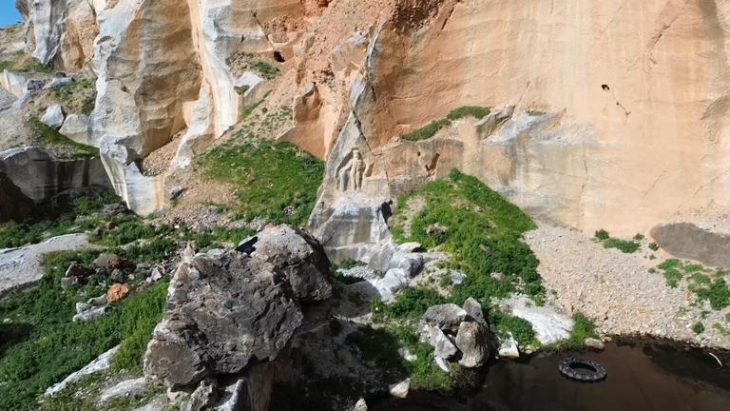
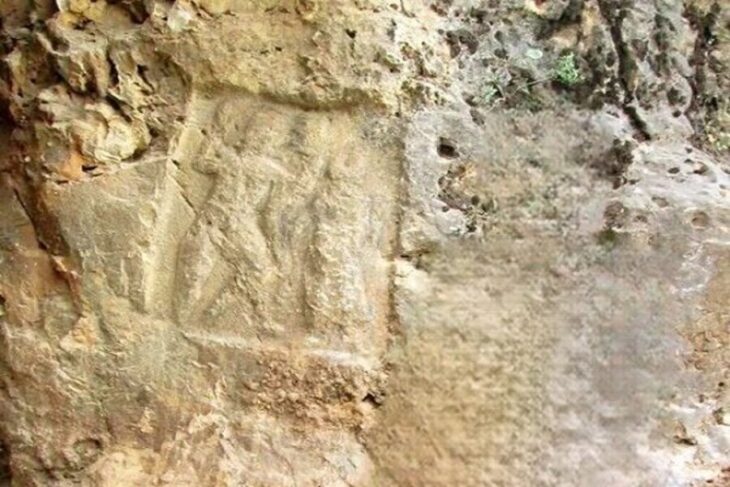
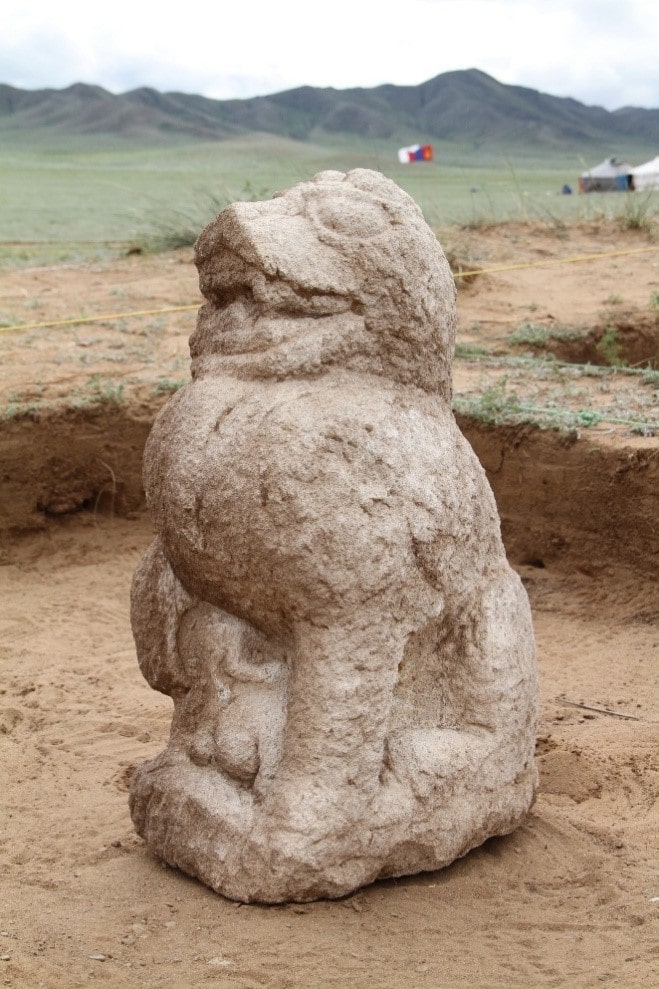
On the west side of the complex, there is a stone cube with a hole (altar) in the middle, stone human figures, a lion statue with two cubs, and two sheep statues. There are 51 balbal stone (Kurgan stelae) protrusions to the east of the gate of the complex. Of these, the “tauteke” symbol belonging to the Ashina family was identified from five balbals.
At the same time, the excavation of clay pavement and brick remains laid on the path shows that there was a baruk (place of worship) inside the complex.
The upper part of the inscription monument and the turtle stand was found in front of the Baruk. The old Turkish Bitik inscription consisting of 12 lines was engraved on both sides of the valuable object, and the old Sogdian script was engraved on the third side.

Scientists participating in the expedition identified words from the text of the monument, such as “Tanrı” (God), “Turk”, “Kutlyk”, and “Tumen”. Based on the information obtained from the inscription text, it was concluded that the Nomgon complex was dedicated to Ilterish Kutlug Kagan, the father of Kultegin and Bilge Kagan, who revived the Khaganate. In addition, Bitiktaş is considered to be the oldest written monument of the Turkish period, where the name “Turk” was mentioned for the first time.
In general, the Nomgon ritual complex is similar to the Bilge Kagan and Kultegin ritual complexes in all its features. On the top of the Nomgon inscribed monument, two dragon-shaped wolf heads are depicted with the body facing down. It is known that such Khagan attributes – a dragon-shaped, wolf-headed symbol – were carved on the top of Taşpar Kağan, Bilge, Kültegin, and other monuments. The Nomgon inscription is considered an important monument at the state level, as are the Orkhon monuments.
The Academy will also develop a scientific collection dedicated to the results of the Nomgon scientific expedition and present it in the capitals of the Turkic states.

Historically significant
The Orkhon inscriptions, which were found in the late 19th century, are memorial installations — an important source for the understanding of the origin of the Turks, their history, culture and their relations with other Turkic tribes.
Turkic inscriptions with runic letters are the oldest known written Turkic works. In addition, the inscriptions were written in the first known Turkic alphabet.
They were erected in honour of two Turkic princes, Kul Tigin and Bilge Kagan. The Kul Tigin inscription was erected by his brother Bilge Kagan, and the Bilge Kagan inscription was erected by his son. The third inscription was erected in the name of Bilge Tonyukuk, a political figure. These three inscriptions make up the Orkhon inscriptions.
The monument complex and inscription found at Hangai Jote is of Kul Tigin and Bilge Kagan’s father, Ilterish Kutlug Kagan.