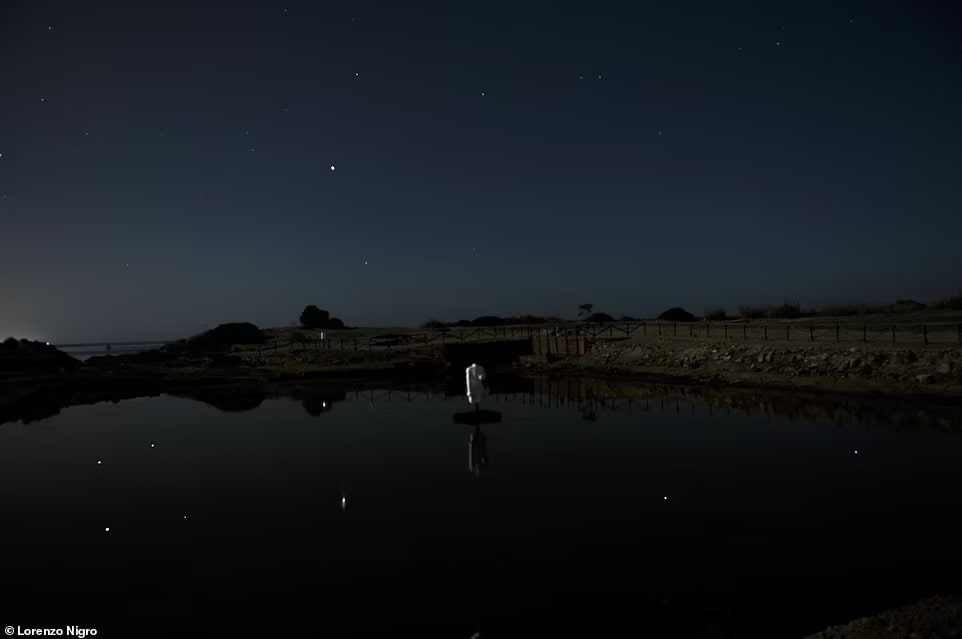
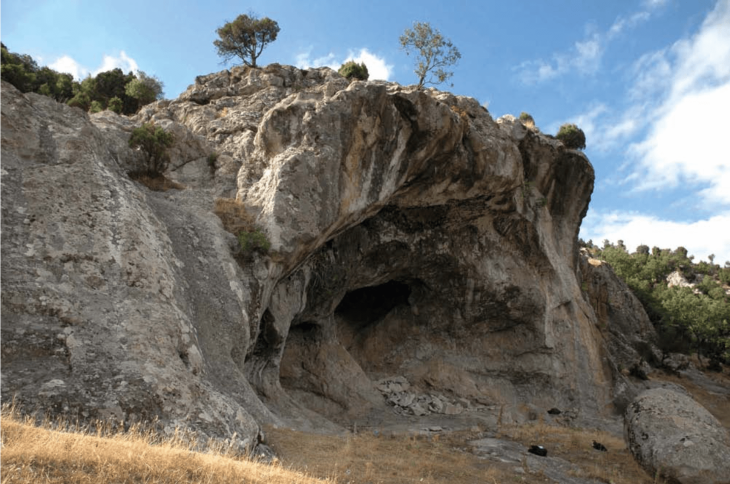
A sacred freshwater pool on western Sicily’s San Pantaleo Island that dates back some 2,500 years was aligned with the stars, archaeologists have revealed.
The pool, which was first unearthed in the 1920s, was found among the ruins of the ancient island city of Motya, which was a bustling Phoenician port back in the first millennium BC. Phoenicia was an ancient maritime state that lived in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily around what today is Lebanon, from around 2500–64 BC. It was originally believed that the feature was a “Kothon” — an artificial harbor — as it bore similarities to one known from the ancient military port of nearby Carthage, but reanalysis has revealed this assumption to be incorrect.
The research was conducted by archaeologist Professor Lorenzo Nigro of the Sapienza University of Rome in collaboration with the Superintendence of Sicily.
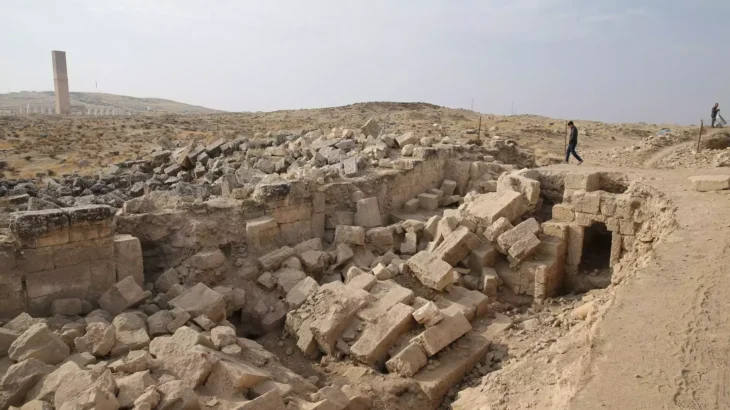
“Kothon” was a harbor but new excavations have drastically changed its interpretation: It was a sacred pool at the center of a huge religious compound,’ said Professor Lorenzo Nigro.
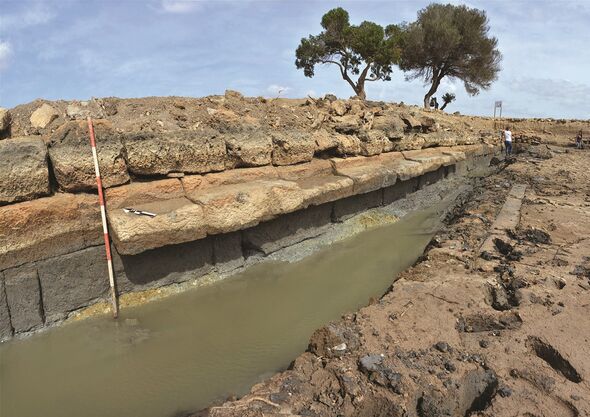

Previous research had found a Temple of Ba’al on the edge of Motya’s Kothon, rather than the expected harbor buildings. This unexpected discovery prompted the reinvestigation of the Kothon starting in 2010. This temple was much to the surprise of the archaeologists who had expected to find harbor buildings instead.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
This prompted a reevaluation of the site, with the excavations that began in 2010 seeing researchers fully drain and excavate the artificial basin.
‘This revealed it could not have served as a harbour, as it was not connected to the sea. Instead, it was fed by natural springs,’ Professor Nigro said.

The water feature, the team said, was longer and wider than a modern Olympic swimming pool, making it one of the largest sacred pools in the whole of the ancient Mediterranean.
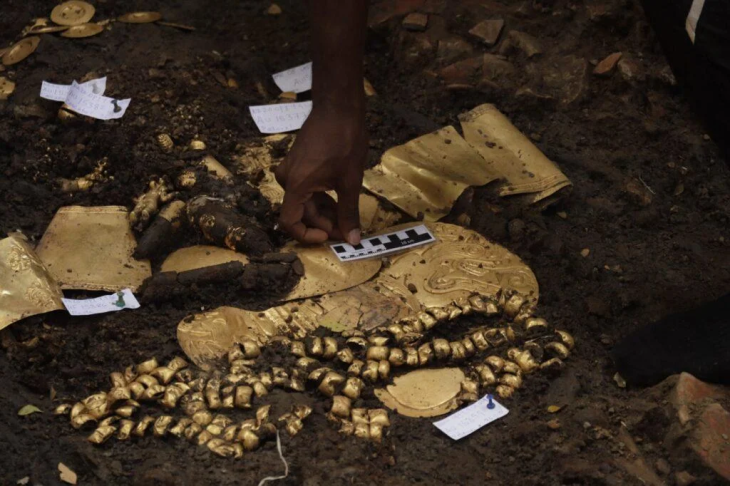
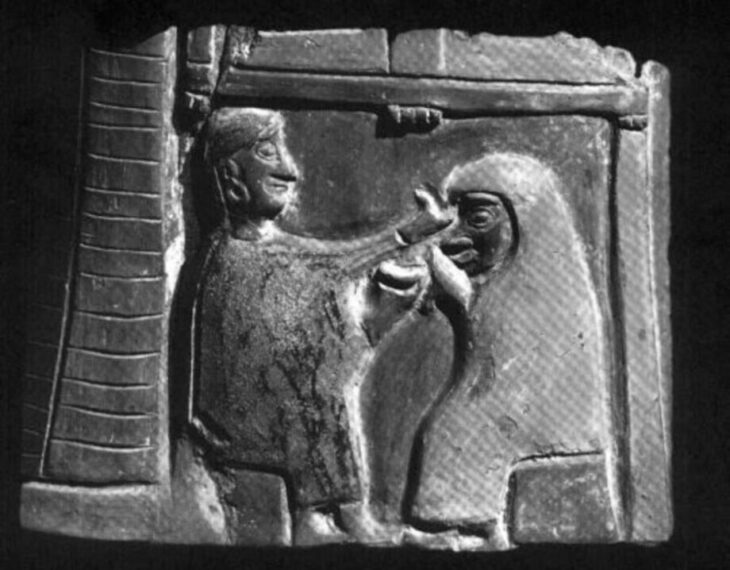
Archaeologists also found additional temples flanking the Kothon, along with stelae, altars, votive offerings, and a pedestal in the center of the lake that once held a statue of Ba’al, often seen as a fertility god.
Ba’al was worshipped widely was known as the Phoenician god of storms and fertilizing rains. As vanquisher of the sea, the deity was regarded by the Canaanites and Phoenicians as the patron of sailors.

Together, the experts said, these features confirm that the “Kothon” was not a harbour, but a sacred pool within one of the pre-Classical Mediterranean’s largest cultic complexes. Mapping the site also revealed it was aligned with the stars.
The new study was published in the journal Antiquity.
Cover Photo: An ancient sacred freshwater pool on western Sicily’s San Pantaleo Island was aligned with the stars (Image: Lorenzo Nigro)