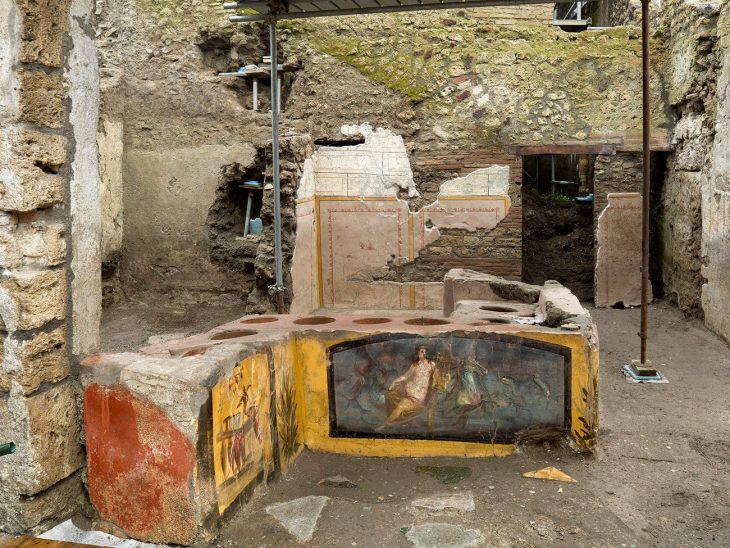
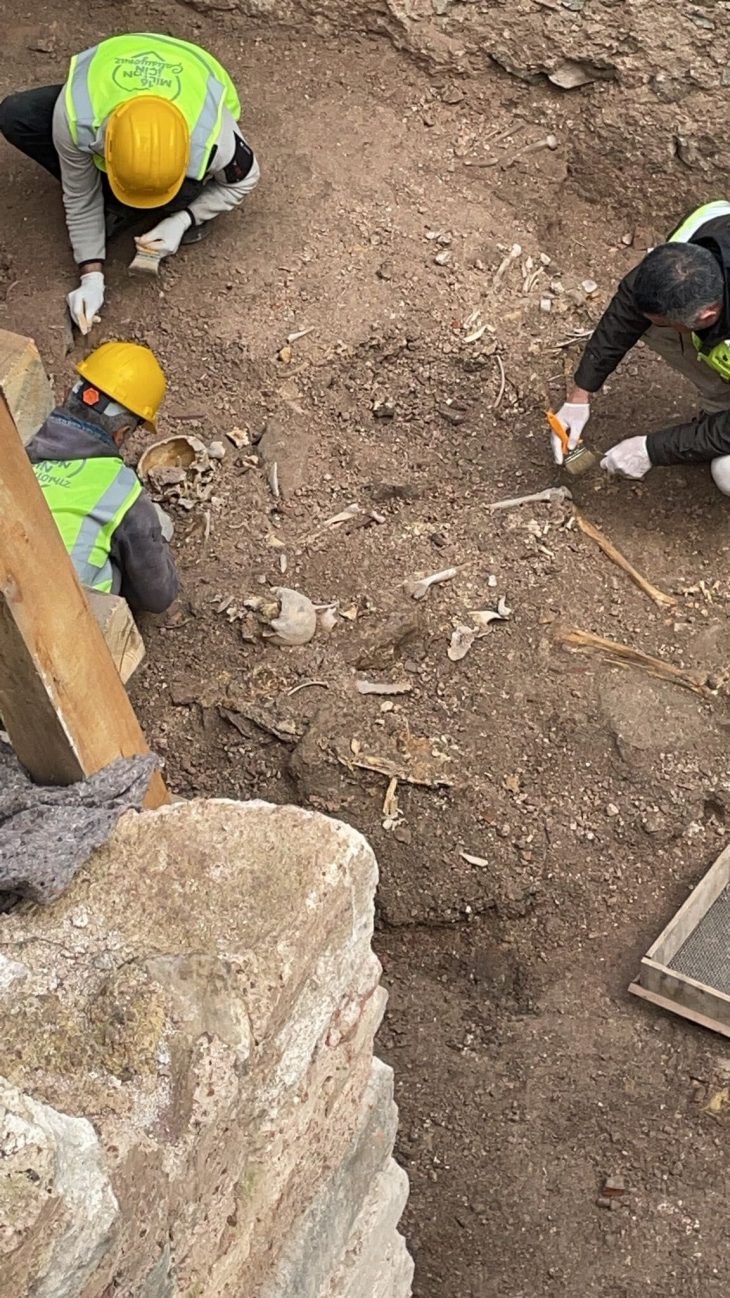
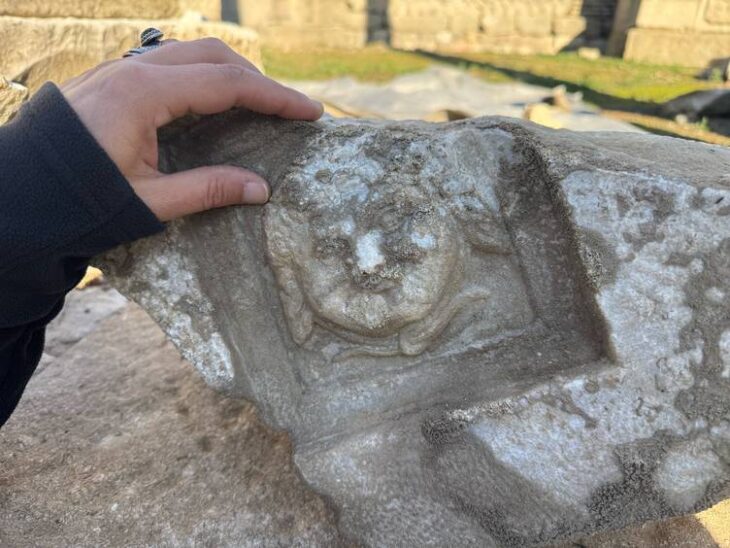
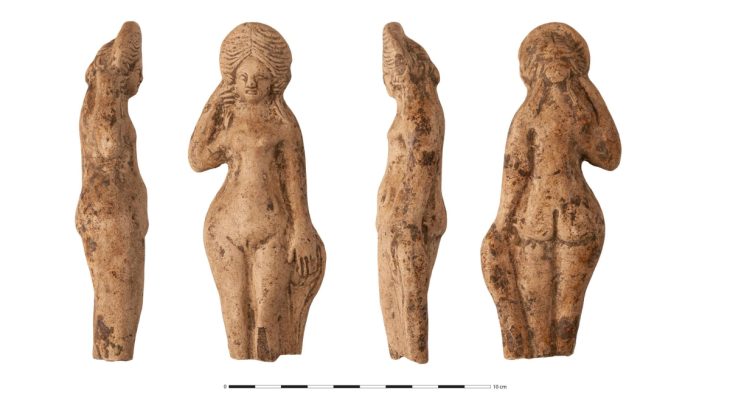
Hypatia of Alexandria was one of the few women in ancient Greek academia. Most of all people remember Hypatia of Alexandria, a martyr of intellectuals and a tragic heroine, for two reasons: her philosophical, mathematical, and astronomical sciences and the fact that she was brutally murdered for them.
She taught philosophy and astronomy at the Neoplatonic school in Alexandria. According to information available on Wikipedia, Middle Ages Hypatia was co-opted as a symbol of Christian virtue and scholars believe she was part of the basis for the legend of Saint Catherine of Alexandria.
Most historians estimate that Hypatia was born in Theon, a mathematician, and philosopher around 350 AD, who encouraged her education from an early age. She did not follow her father’s teachings, and soon found other ways to understand what she was interested in. Outside of mathematics, she was particularly attracted to astronomy and built an astrolabe, which is a tool for inspecting and measuring celestial bodies in the night sky.
He also established himself as a member of the Neoplatonic school of philosophy and dressed in the robes of the academic elite (something only men could do at the time, although this did not deter Hypatia in the least), he was heading downtown. of the city and tell anyone who would listen to her thoughts on Plato.
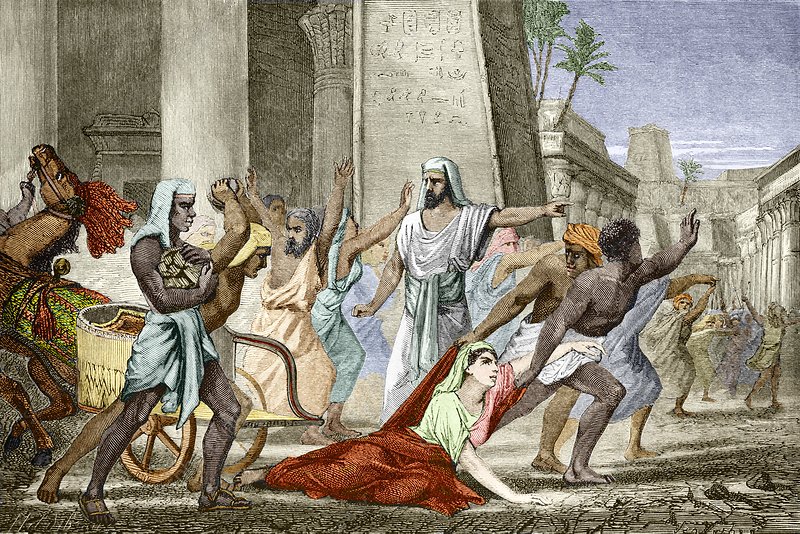
She never married and, by all accounts, she was assumed to be a virgin until her death. Ancient Greek society valued celibacy as a virtue and, as such, men and women accepted and respected Hypatia in large part because she appeared to be almost asexual. This made her much less threatening, despite the intensity of her mind and her growing list of school accomplishments.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Hypatia practiced paganism when Christianity was still in its infancy. Still, new religions began to grow, and because of fear of persecution, many pagans converted to Christianity.
Hypatia didn’t; instead, she continued to practice paganism and did not try to cover it up. Although she was once supported by the Alexander government, her resistance made her the target of a powerful Christian circle. But once the Christians incited violence in the city, this support disappeared, and the government’s efforts to protect her ceased.
Cyril, one of Alexandria’s most famous bishops, led the charge to overturn Hypatia. Cyril failed to attack the government directly, so he decided to cancel one of his most powerful assets.
Therefore, the bishop ordered a group of monks to kidnap Hypatia and continue to drag her into the street while torturing her. The monks burned Hypatia and scraped off her skin with oyster shells. Then they took her to the church, where she stripped naked, beat her with bricks, and tore her limbs from her body.
Cyril justified his actions by saying that Hypatia represented the pagan worship that Christianity fought against. Unfortunately for Cyril and the others, by killing Hypatia, they immortalized her.
She was killed in 415 AD.
















