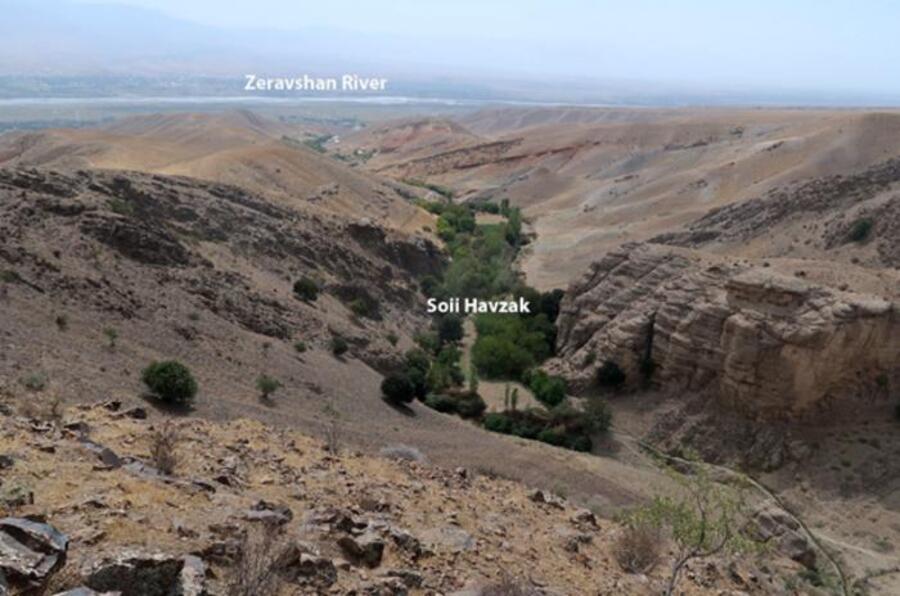
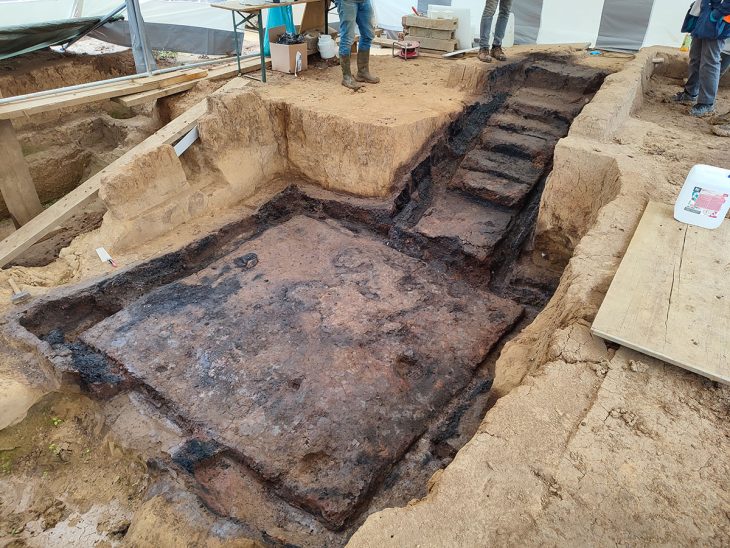
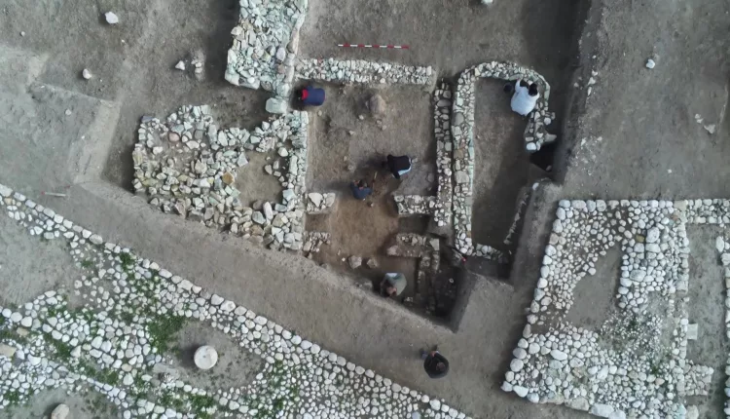
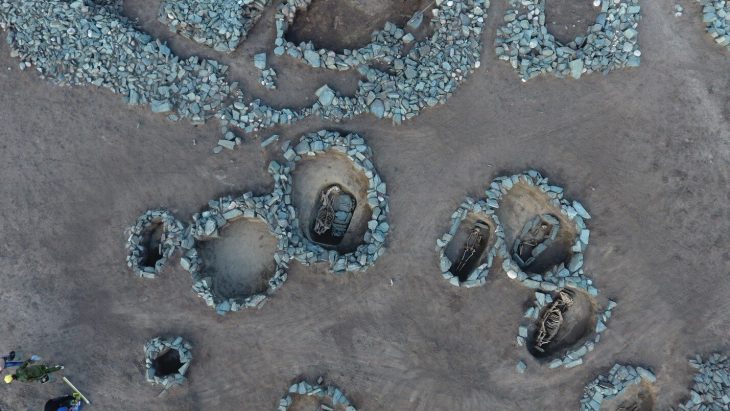
Archaeologists have discovered a multi-layered archaeological site in the Zeravshan Valley of central Tajikistan that reveals early human settlement in the area.
Zeravshan Valley occupied from 150,000 to 20,000 years ago may have alternately hosted all three human species in Eurasia at the time. The findings from the site, known as Soii Havzak, provide crucial evidence that Central Asia played a vital role in early human migration and development.
Led by Prof. Yossi Zaidner of the Institute of Archaeology at Hebrew University and Dr. Sharof Kurbanov from the National Academy of Sciences of Tajikistan, the research, published in Antiquity, revealed a rich array of stone tools, animal bones, and ancient vegetation.
“It turns out that the Zeravshan Valley, known primarily as a Silk Road route in the Middle Ages, was a key route for human expansion long before that—between 20,000 and 150,000 years ago,” explained Prof. Zaidner.
“This region may have served as a migration route for several human species, such as modern Homo sapiens, Neanderthals, or Denisovans, which may have coexisted in this area, and our research aims to uncover who were the humans that inhabited these parts of Central Asia and the nature of their interactions.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
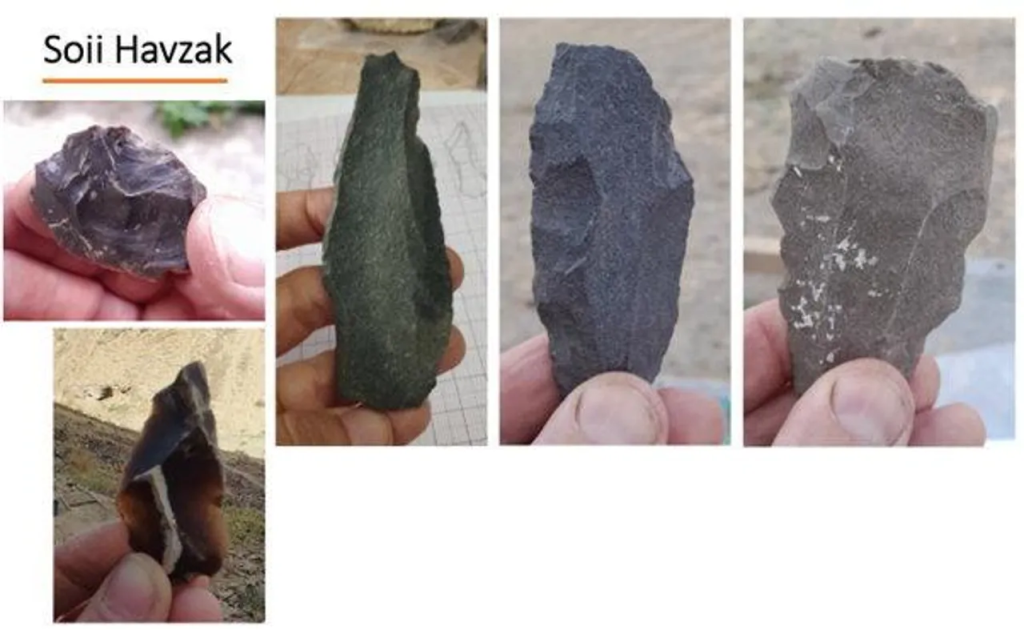

Scientists have long thought that the cold, arid mountainous realms of Tajikistan and central Asia in general didn’t seem so important to the story of human evolution and our migration out of Africa to Eurasia.
It was assumed that Central Asia had been generally unpleasant during the ice age and that reasonable hominins would stay away from hostile areas. But it is not so. Early humans didn’t abandon Central Asia even when the climate turned colder, recent research indicates.
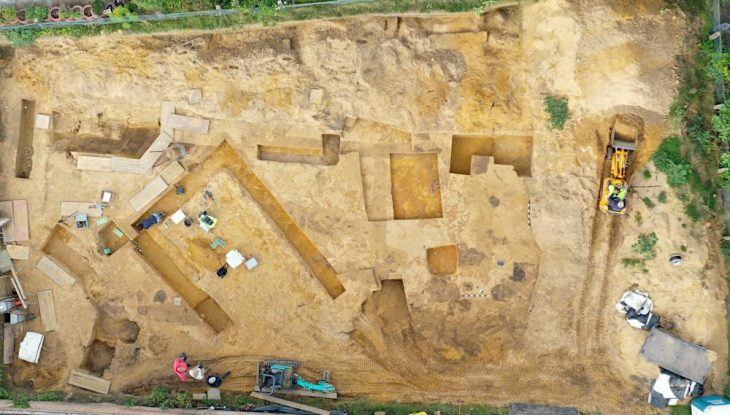
Probably due to a lack of search, the Soii Havzak rock shelter, which is naturally carved into a cliff and is currently approximately 40 meters above ground level, is one of only two stratified sites from deep prehistory found in the Zeravshan Valley. Following the discovery of stone artifacts on the slope beneath the rock shelter, archaeologists dug three trenches.
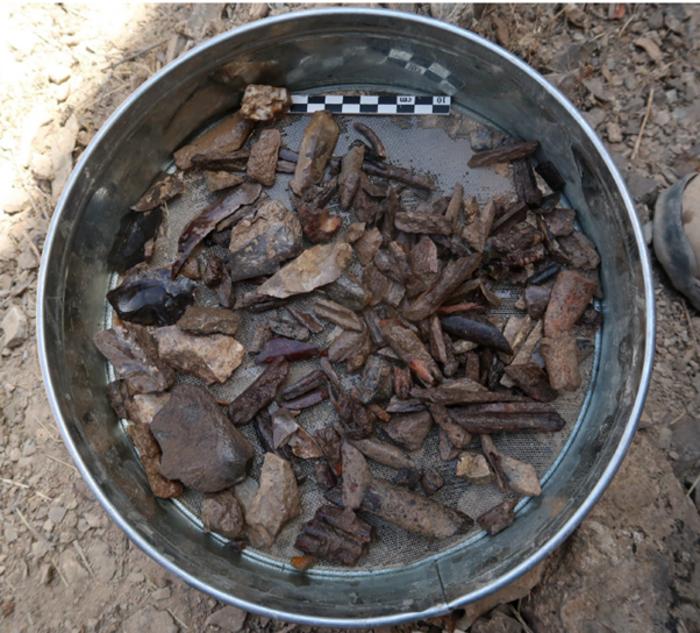

At Soii Havzak, the archaeological team excavated three areas and unearthing layers of human activity. In addition to the possibility of finding human remains that could reveal which species of humans lived in the area, the well-preserved remains provide important hints about the climate and environment of the past.
“The preservation of organic materials, such as burnt wood remains, as well as bones, is remarkable. This allows us to reconstruct the region’s ancient climate and provides hope that further excavations might reveal clues about human biology in the region,” said Prof. Zaidner. “This is crucial for understanding the development of human populations and behavior in Central Asia.”
Understanding how ancient human groups may have interacted with one another is one of the research’s wider implications for the study of human evolution and migration. According to the team, Soii Havzak’s location in Central Asia’s mountainous corridor may have been a crucial turning point for human populations, allowing early humans to disperse over large areas.
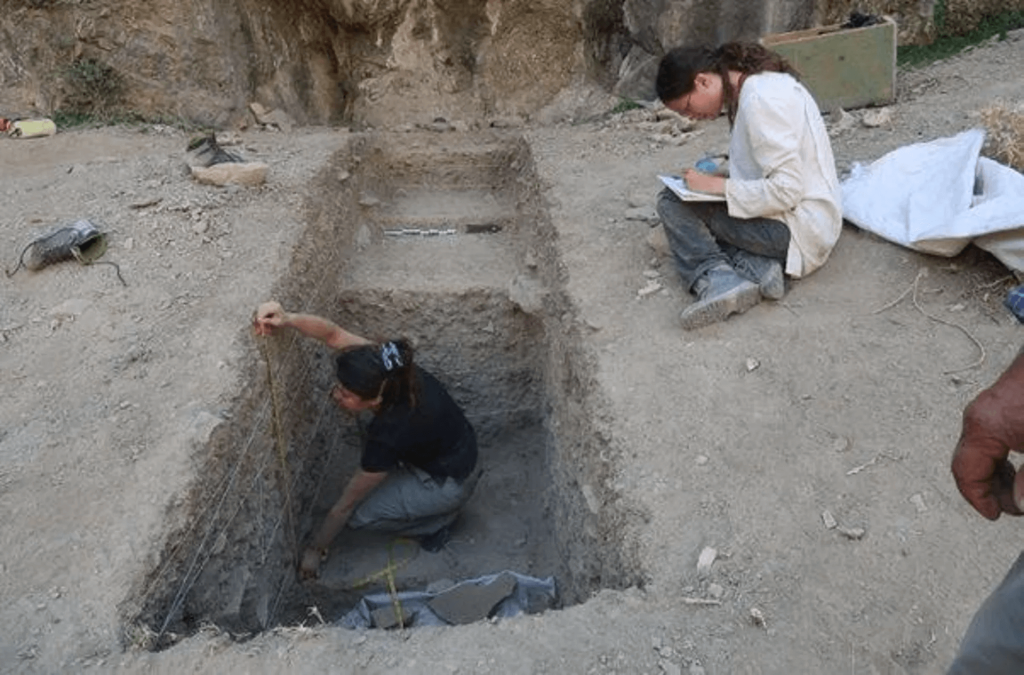

“We hope that ongoing research at this site will reveal new insights into how different human groups—like modern humans, Neanderthals and Denisovans—may have interacted in this region,” said Prof. Zaidner. “This discovery is a significant step toward understanding ancient human history in Central Asia and marks an important collaboration between international scientific teams.”
The excavation at Soii Havzak will continue over the coming years, with further digs planned to explore deeper layers and conduct more in-depth analyses of the findings.
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
Antiquity, DOI: https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2024.149
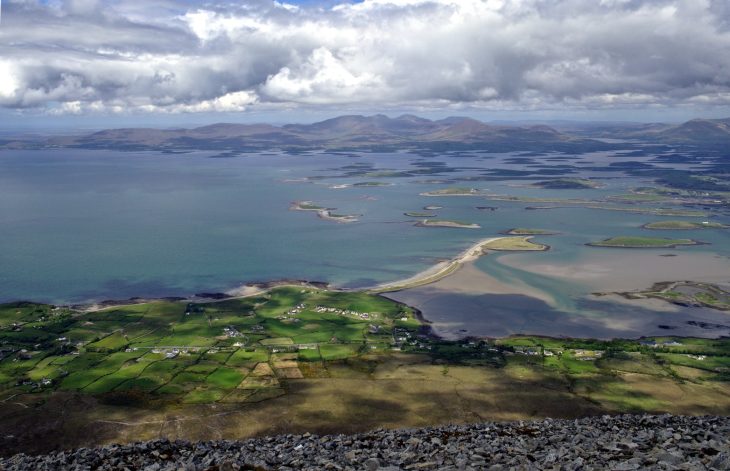
Cover Image Credit: View on Zeravshan River valley from Soii Havzak. Photo: Yossi Zaidner and Team