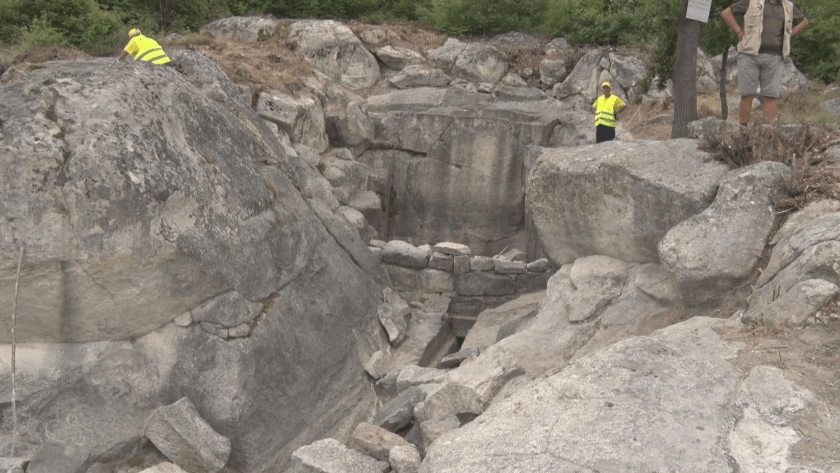
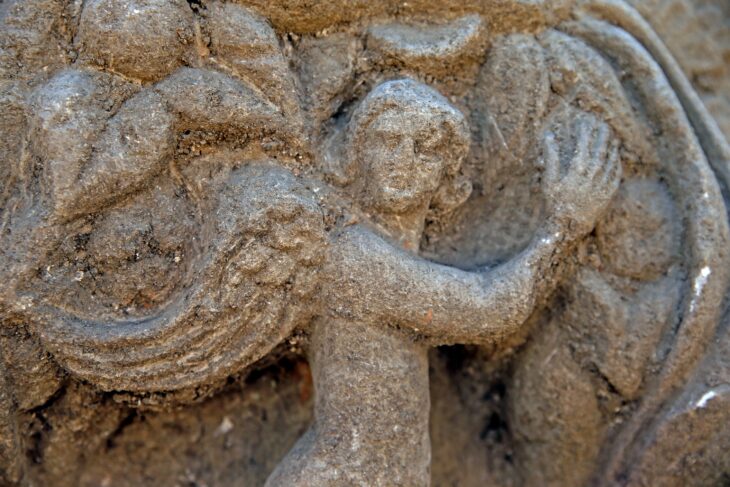
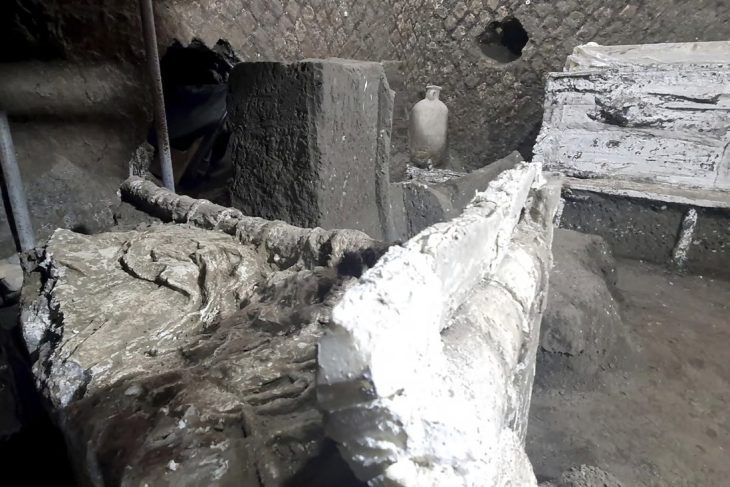
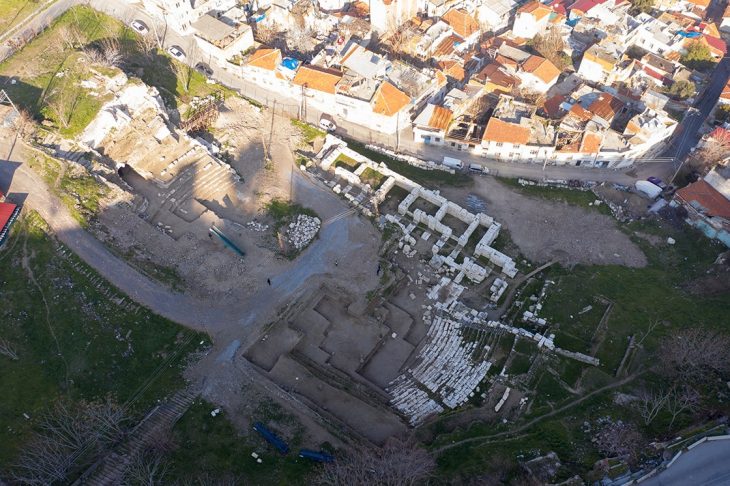
New researchs uncovered a huge monumental sanctuary of water (Nymphaeum) above the reservoir in the southern quarter of Perperikon. Professor Nikolay Ovcharov, head of the excavation of the archaeological complex, told reporters that it is a Nymphaeum from 2-3 centuries.
Perperikon, an archaeological complex located at an altitude of 470 meters near the city of Kardzhali, Bulgaria, in the Eastern Rhodopes, is considered one of the oldest megalithic monuments.
Until now, it was believed that there was only a water reservoir on the site. Recent excavations show that there was a sanctuary with a beautiful wall and columns from the Roman period.
Nymphaeums were sanctuaries for water nymphs. It was an elaborately decorated public drinking fountain – a semicircular monumental Classical fountain house. It often had niches filled with sculpture. The nymphaeum served as a sanctuary, a reservoir, and an assembly chamber where weddings were held.
Professor Nikolay Ovcharov said that the area, which is one of the longest-studied areas of Perperikon, has so far only been considered a reservoir with a drinking water volume of close to half a million liters and a depth of about 5 meters.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

It was the new discoveries during the current restoration project of the site that led archaeologists to conclude that the water temple existed.
It turned out that this cistern, unlike the cistern on the Acropolis, which was completely cut into the rocks, here was cut on only three sides. On the east side, it has a beautiful, very well-made square wall, which, as it turned out, was actually the facade of this facility. In the excavations, we found parts of cornices, pedestals of columns, bases of columns, and perhaps also of statues, explained Prof. Ovcharov.
In his statement, Ovcharov emphasized the importance of urban nymphaeums, especially during the siege periods, and pointed out that such examples exist in Asia Minor, but similar artifacts of glorification and deification of water are rare in Bulgaria.
Archaeological excavations in Perperikon have been going on for 2 years only with the support of the Municipality of Kardzhali due to the lack of state support, and the work will continue until mid-September.
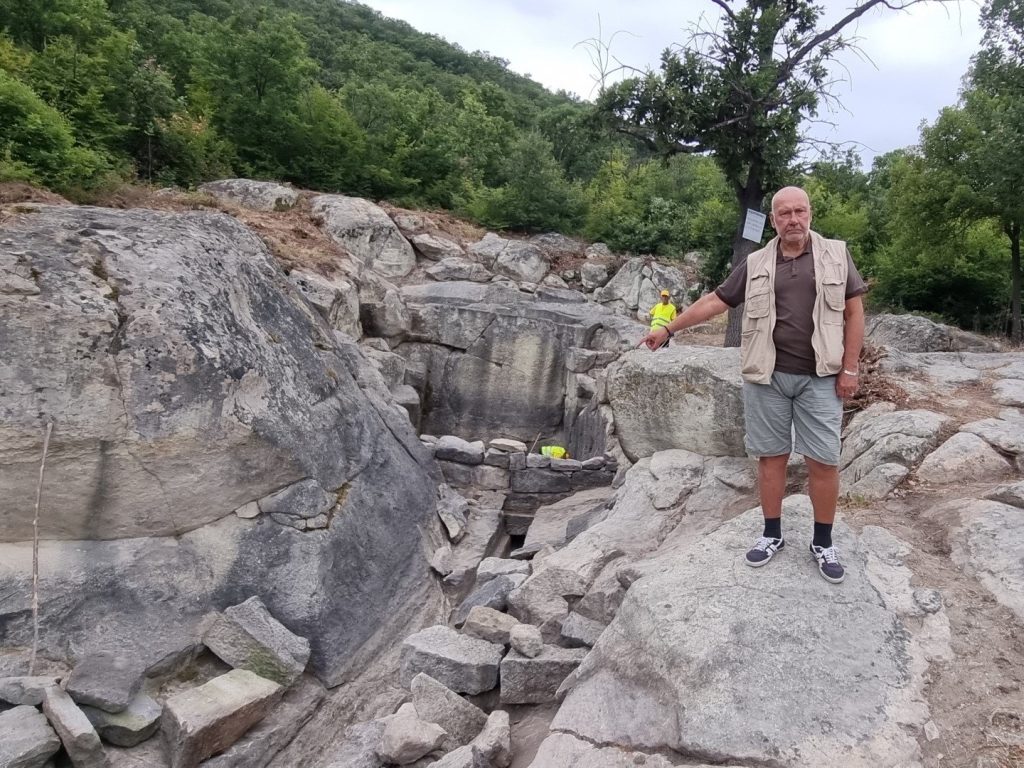

The ancient Thracian city of Perperikon is located in the Eastern Rhodope mountains, southern Bulgaria, 15 km northeast of the present-day town of Kardzhali, on a 470 m high rocky hill, which is thought to have been a sacred place.
Perperikon has its roots from the Chalcolithic period over 8000 thousand years ago but reached its heyday during late Antiquity, when it became a city center within the Thracian province of the Roman Empire.
Google Translate was used to translate articles from Standartnews.
Cover Photo: BTA