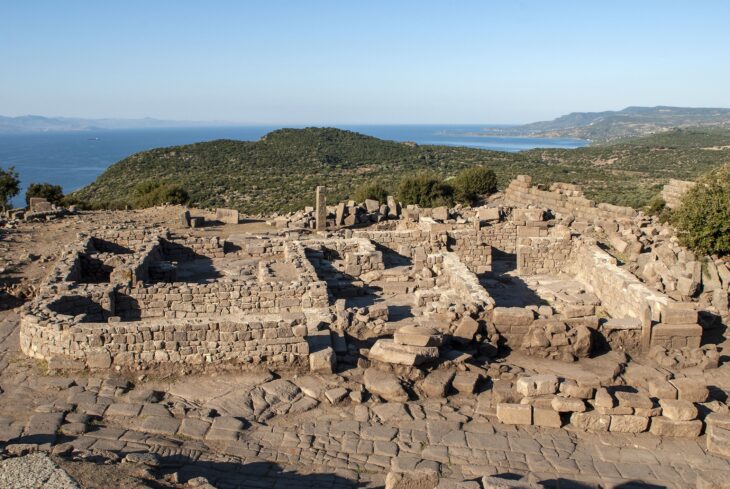
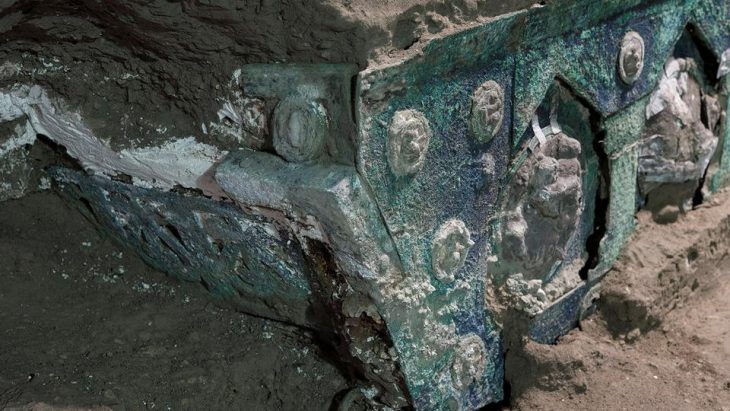
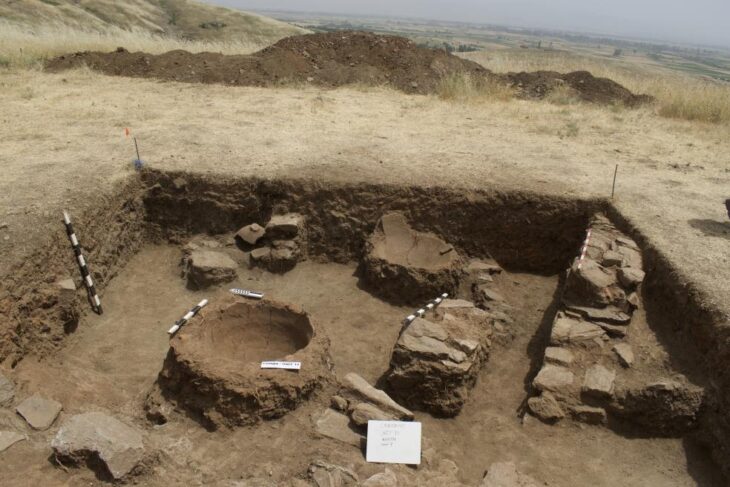
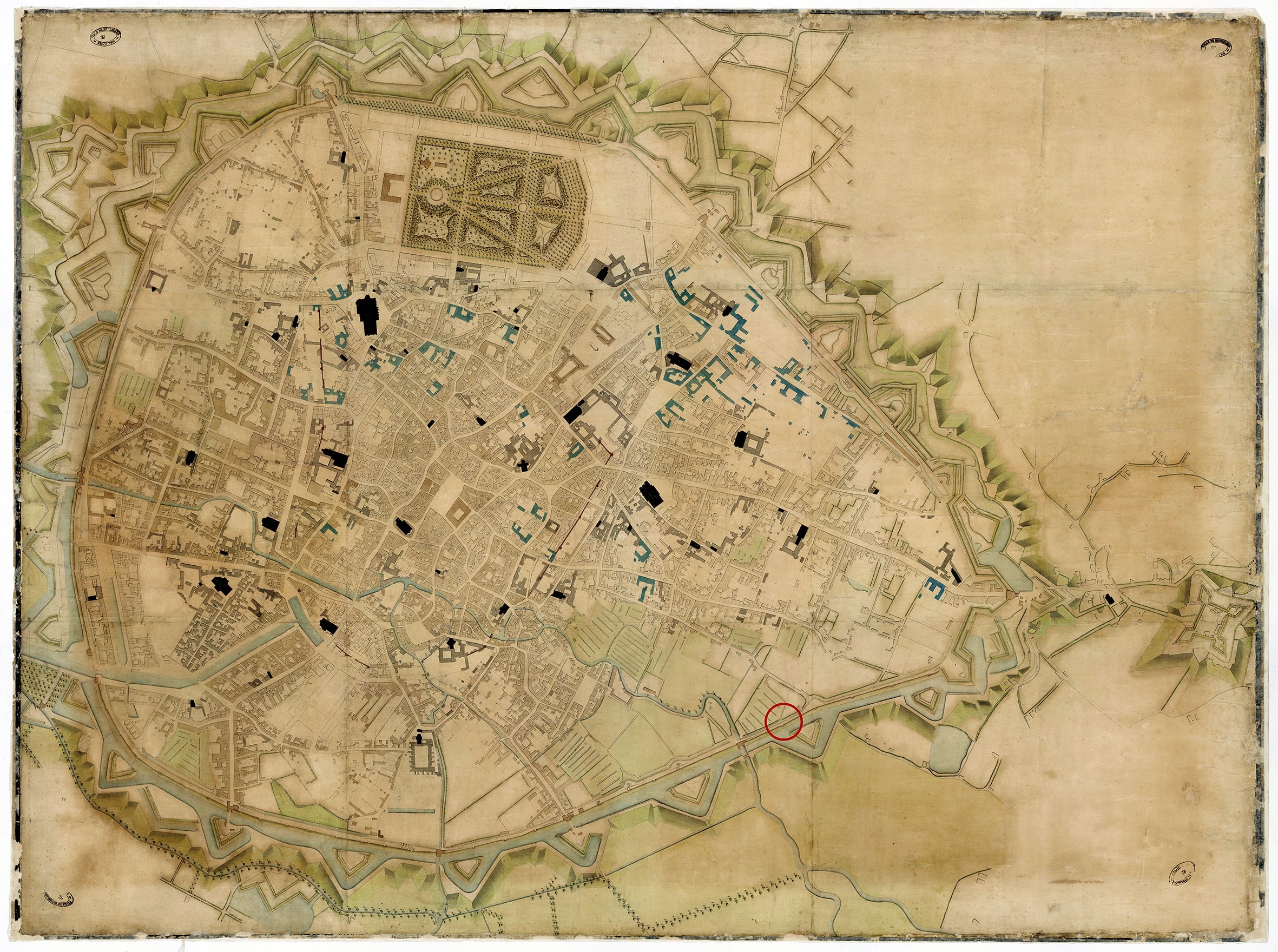
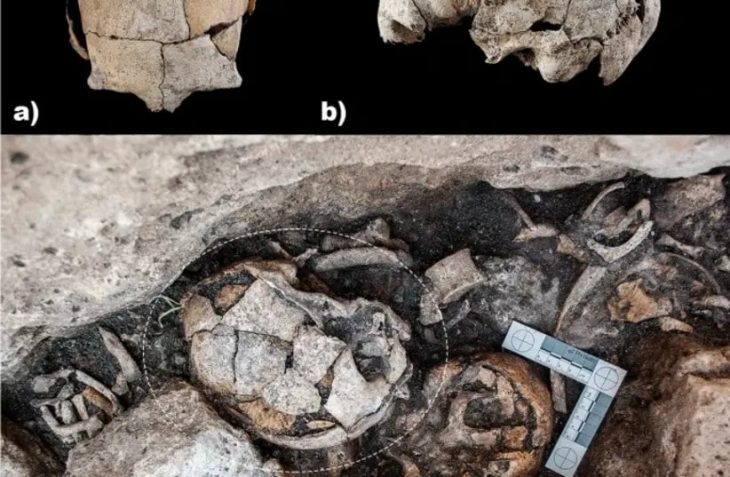
Construction work on the new metro line 3 in Brussels, the Belgian capital, has revealed part of the second rampart wall and one of its semicircular towers.
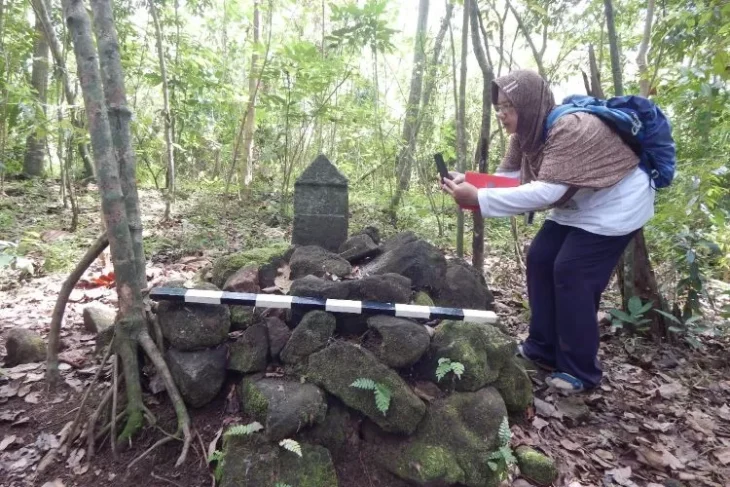
Bruzz reports that as a result of the construction, remnants of Brussels’ second city wall have been uncovered. This is the first time that one of the approximately 70 semicircular towers of the second rampart wall was uncovered.
One of the nearly seventy semicircular constellations has been revealed for the first time. Prior to this discovery, the only archaeological remains of the second city wall were the Porte de Hal and the 17th-century fortress wall discovered during the construction of the Porte de Hal metro.
The archaeologists discovered “two relatively parallel sections of the wall” in addition to the tower. Both discoveries have been stymied largely by recent developments, such as a concrete hatch on the west side and brick ducts running directly through it.
This new discovery, near the Brussels-Midi station, was made last year by archaeologists supervising the works, but the discoveries were only recently reported in the journal Cahiers Bruxellois.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Brussels’ economy and population grew rapidly in the 14th century, forcing the city to expand and construct a second wall. Ludwig van Male (Count of Flanders) and his forces’ difficulties in defending the city in 1356 may have been decisive in laying the foundation stone in 1357.
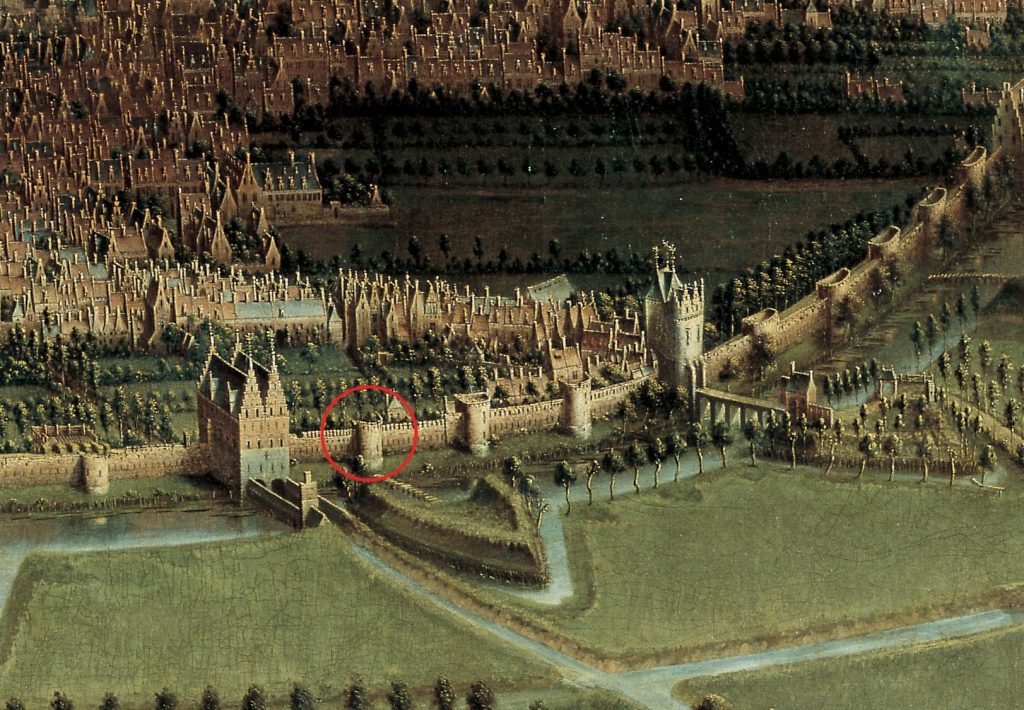
The second Brussels city wall was eight kilometers in circumference: twice as long as the first. The wall had about seventy semi-circular towers, and two round watchtowers, and was pierced with seven gates and two locks.
Although only the Halle Gate remains, many references can still be found in Brussels to the entry gates of yesteryear: the Halle Gate, the Naamse Gate, the Leuven Gate, the Schaarbeekse Gate, the Lakense Gate, the Flemish Gate, and the Anderlechtse Gate and eighth gate, Oeverpoort. Oeverpoort Gate was built in the 16th century.
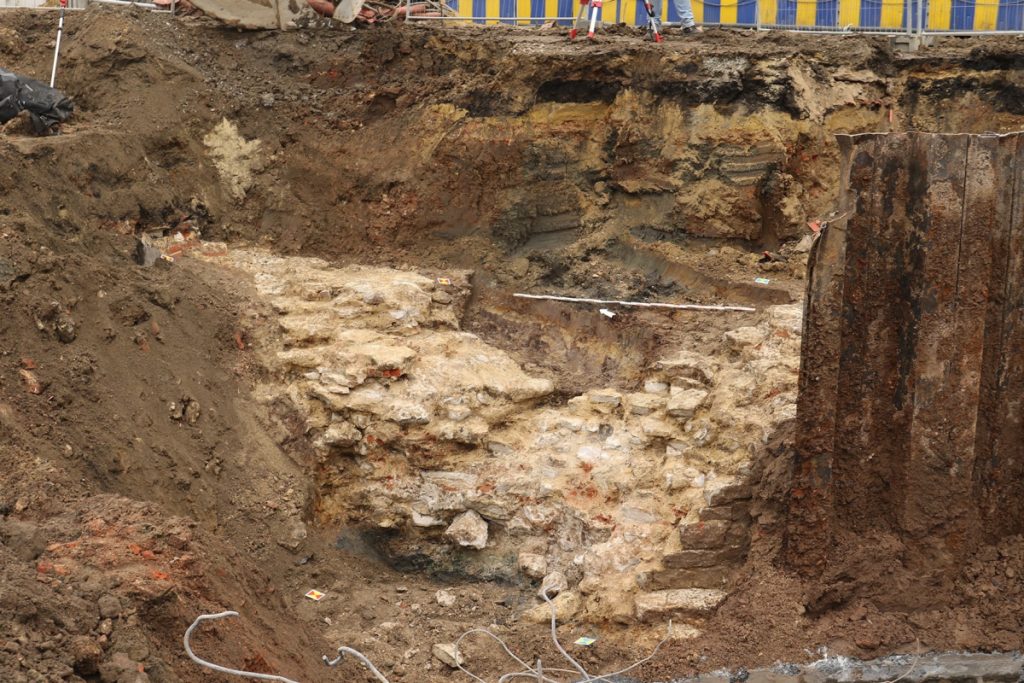

The majority of the entrance gates were destroyed at the end of the 18th century when it was decided that the wall would no longer be used as a military defense. Since it was a prison, only Hallepoort has survived. Since that time, the city wall has changed from a shelter to a walkway with a stunning view of the city.
Similar to Paris, Brussels decided to create space for a wide city avenue so that residents could travel along it on foot or by horseback until the end of the 19th century. Many of the city’s neighborhoods were altered by this choice: new residential areas grew up around the avenue, and the industrial area grew on the north and west sides as a result of the harbor’s presence.
Because work on Metro Line 3 is far from finished, researchers anticipate more archaeological discoveries.