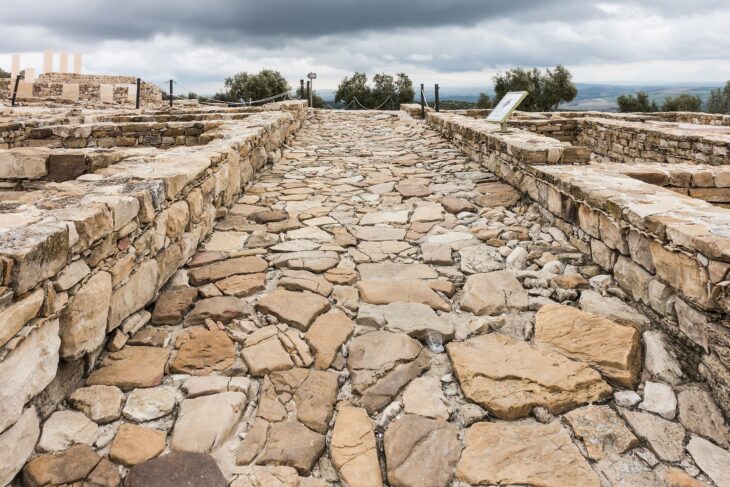
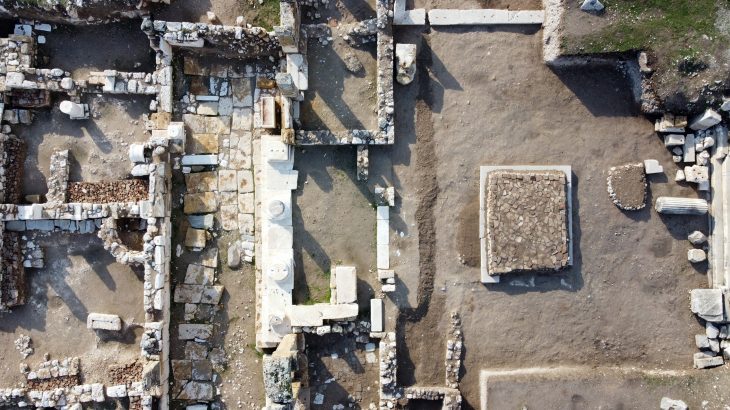
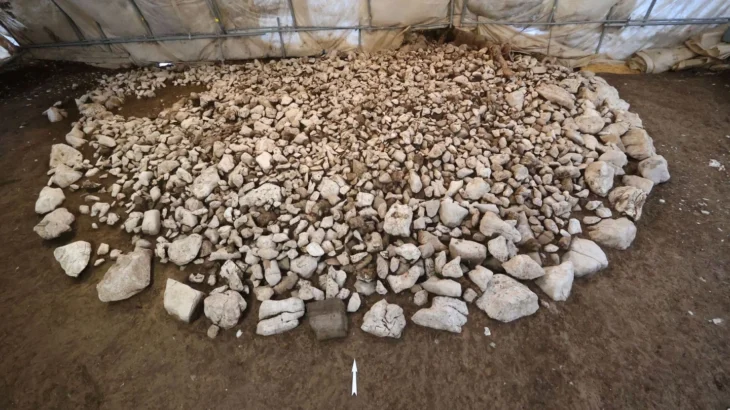
Iranian archaeologists found the ruins of a stoneware workshop estimated to date back to the 3rd millennium BC, during their excavations at Jiroft in Iran’s Kerman Province.
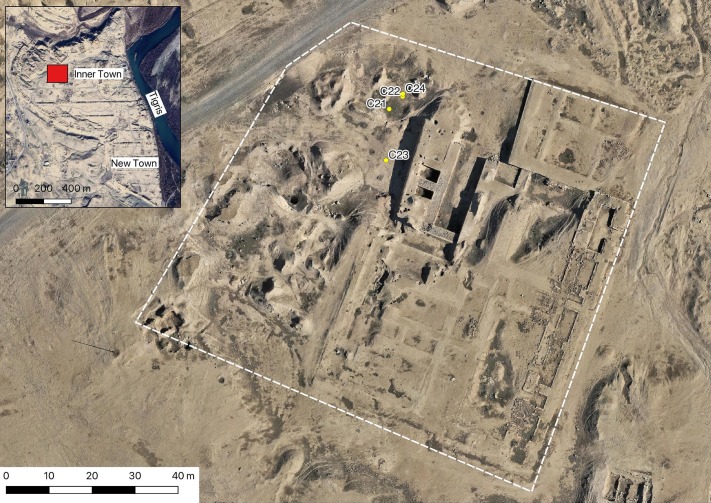
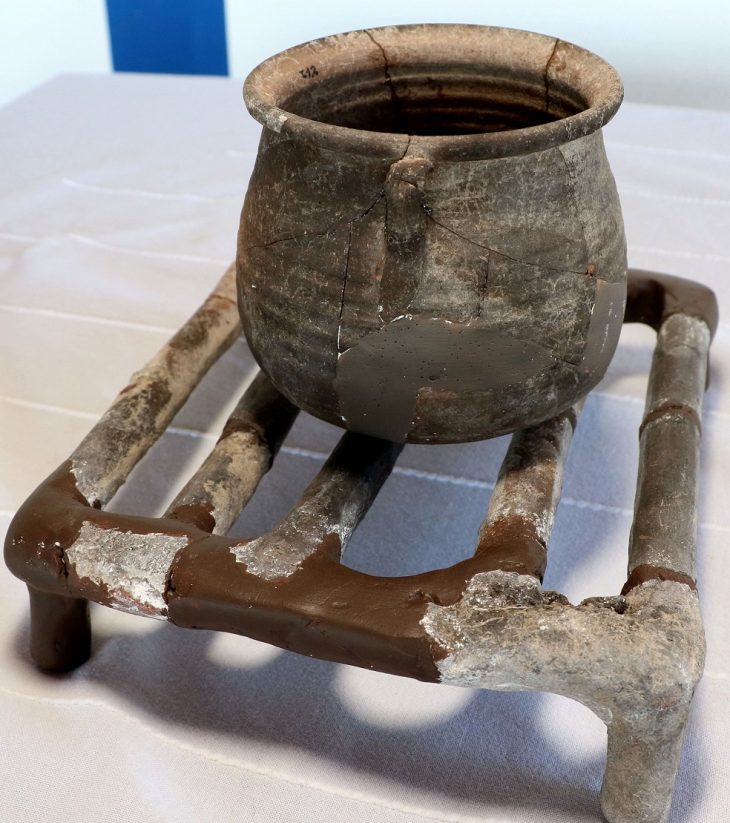
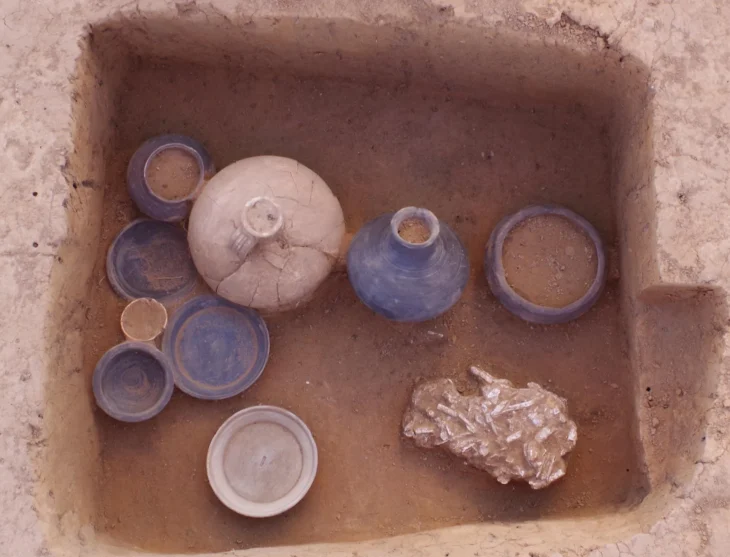
A team of archaeologists from the University of Tehran has discovered a wide variety of stone vessels and stone ornamentations from the site of Hajjiabad-Varamin in Jiroft, IRNA reported.
According to the archaeologists, stone containers and objects that were used or broken by people were not discarded in Jiroft, but their broken pieces were brought to the production workshop to make smaller containers and objects such as beads and pendants.
The Jiroft culture also referred to as the Intercultural style or the Halilrud style is a presumed early Bronze Age (late third millennium BC) archaeological culture that was present in the region of the modern Iranian provinces of Sistan and Baluchestan and Kerman.
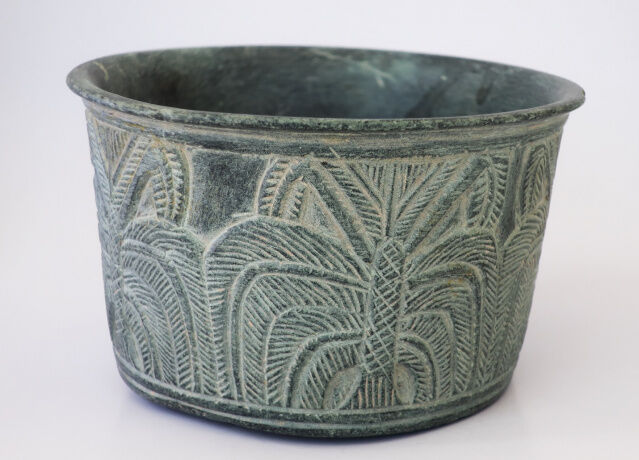

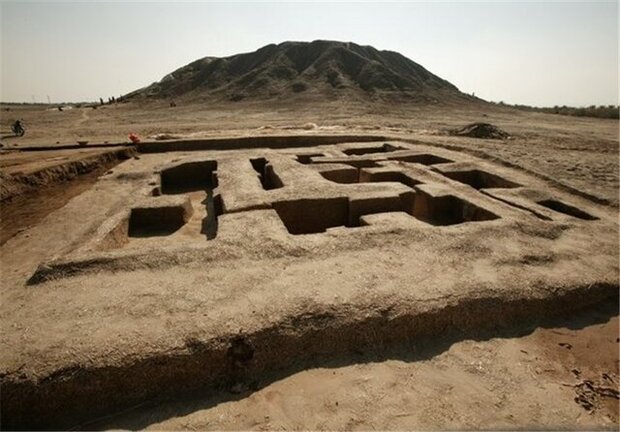
Jiroft historical site covers invaluable items from the third millennium BC and is considered one of the most important historical sites in the world. More than 85 sites have so far been unearthed in a 400 km length of Halil Roud River, leading archeologists to compare the area to that of the Mesopotamian civilization.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The attraction of the sculpted objects discovered in the Halil Rud Valley stems from their highly original decoration. These extraordinary works featured intricate animal figures, both domestic and wild, fighting among themselves or with human figures, with humanity always coming out on top. There were exquisitely rendered bucolic scenes of animals grazing in vast palm groves and architectural replicas of temples or palaces. The motifs adorning the surface of finely sculpted objects, derived from a consistent and meticulous system, reveal a strong and confident aesthetic sensibility.
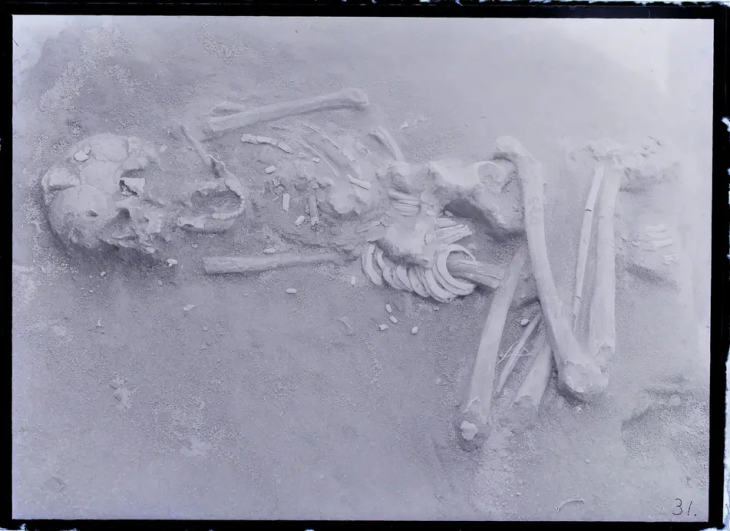
A flood in the Jiroft area in 2000 exposed thousands of ancient graveyards in the area and led to the looting of local looting of artifacts.
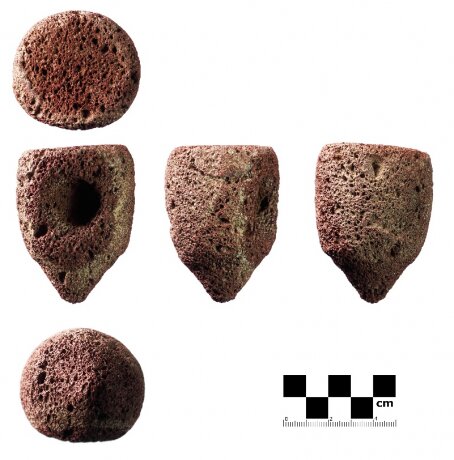

These vessels, which were made of bronze, ceramic, and chlorite stone, had been discovered in small numbers in other contexts in regions of the world contemporaneous with Jiroft but looted artifacts and subsequent excavations revealed that they were present in southern Iran in much greater quantities.
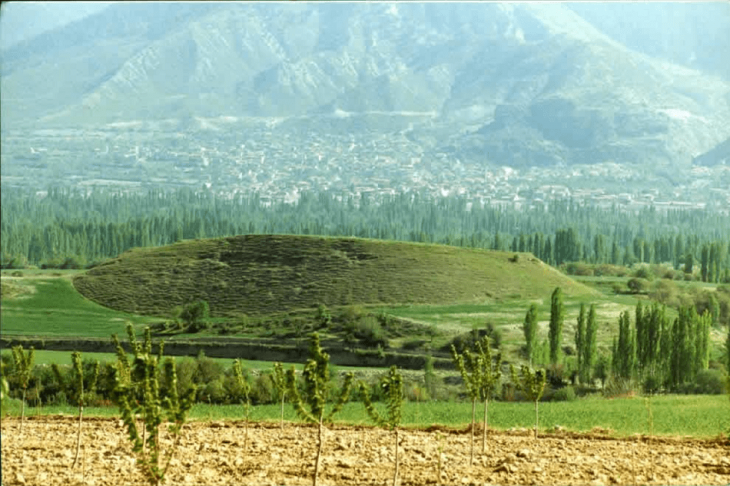
Cover Photo: The image of the Konar Sandal archaeological site south of Jiroft city. Source: Tehran Times