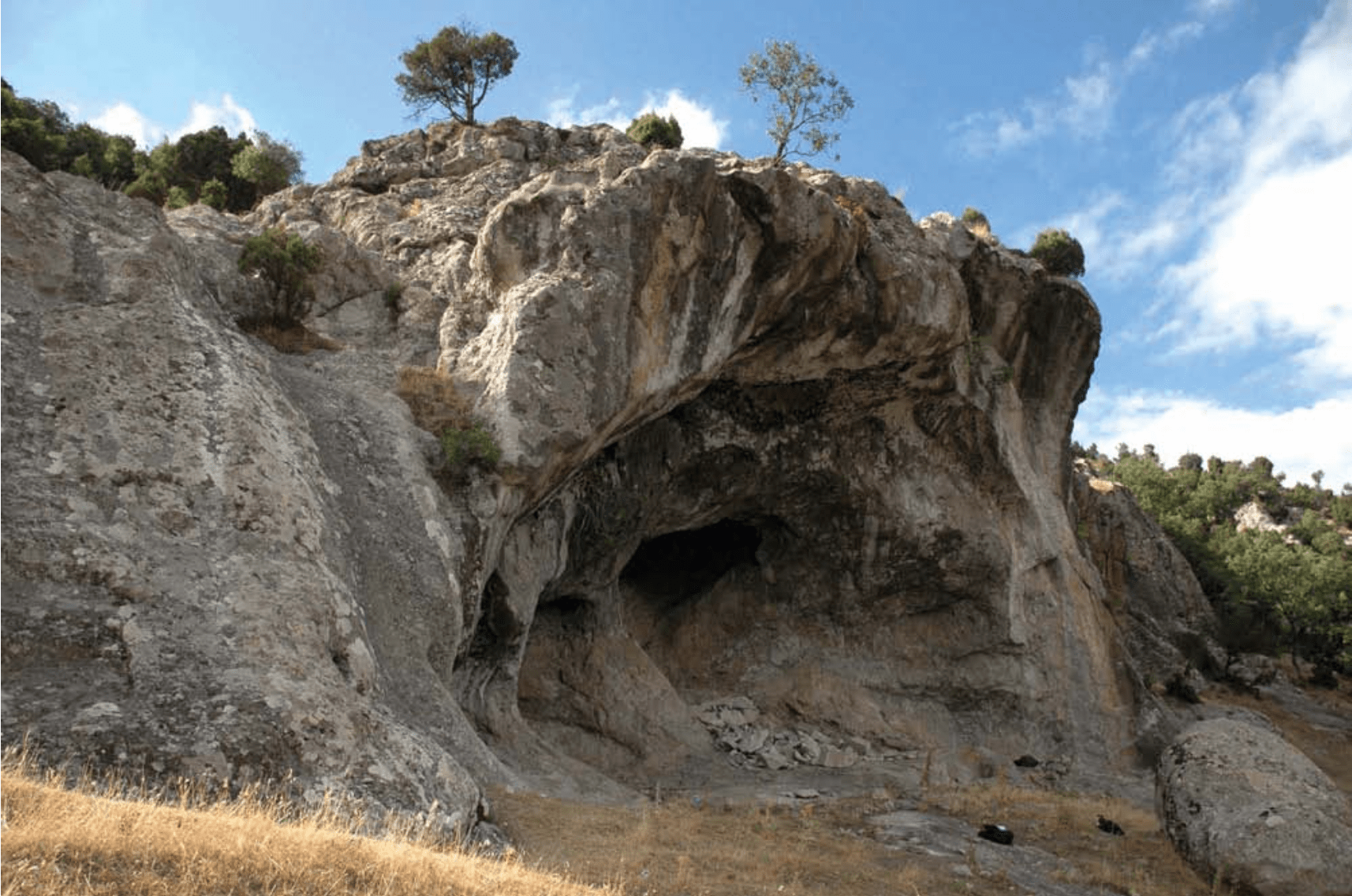
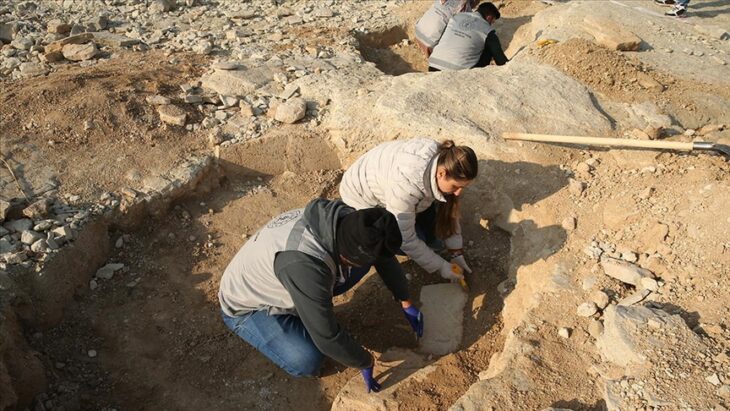
A number of cave paintings dating back some 8,000 years have been found in İnkaya cave in the Marmara province of Balıkesir during a field study conducted by Associate Prof. Dr. Derya Yalçıklı from Çanakkale (18th March) University, in 2015.
During the same studies, another cave located 5 kilometers away from the İnkaya cave was discovered. The discovery of both caves is known as the most important archaeological discovery made in Anatolia in recent years.
The cave paintings discovered in the Baltalıin and İnkaya Caves, which are situated in the Delice neighborhood of the Dursunbey district in the Balıkesir province of Turkey, offer information that sheds light on Neolithic Age life.
One of the remarkable findings showing that people in the Prehistoric Age were undeniably knowledgeable about the phenomenon of childbirth is the scene found among the cave paintings of İnkaya Cave.
The painting depicts a woman becoming pregnant, the pregnancy, and childbirth in an expression that has yet to be matched.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
When Baltalıın and İnkaya caves were analyzed separately, it was revealed they were used for different functions, as the paintings in one of them depicted hunting figures, while the other depicted figures of beliefs. The paintings found in the two caves date back to the Late Neolithic period.
Associate Professor Derya Yalçıklı, who discovered and examined the cave paintings, told Arkeonews in an email, “Social and belief systems in Western Anatolia during the Neolithic and Chalcolithic periods constitute an important question of Anatolian archeology, and examining the wall paintings in Baltalıin and İnkaya caves may provide some important answers.”
The floor and northern wall of the İnkaya Cave were greatly damaged by past treasure hunters using dynamite, however, despite this damage, the cave continues to reflect important information about the Neolithic era.

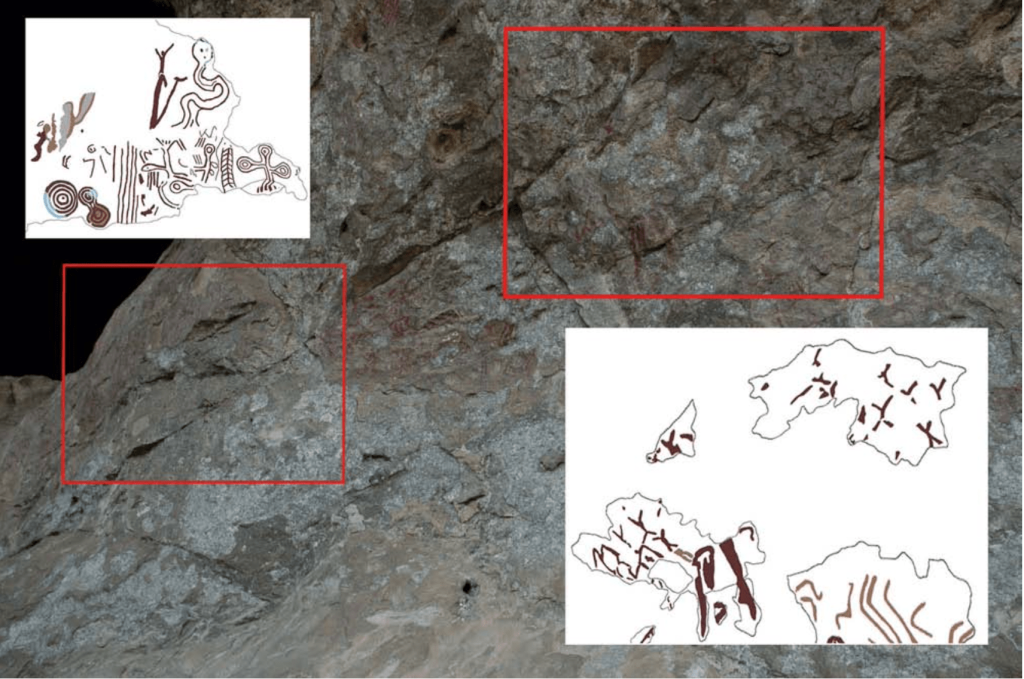
İnkaya Cave is located 2.5 km northwest of Delice neighborhood. The cave, with its karstic quality, consists of a gallery that is 4.5 m deep, 8 m wide, and 4.4 m high. It features two murals located on the northern and southeastern outer edges of the cave entrance. The panel located on the left side (southwest) of the cave entrance measures 1.43×0.87 meters. There are also four people dancing in the main part of the painting on the left side of the entrance.
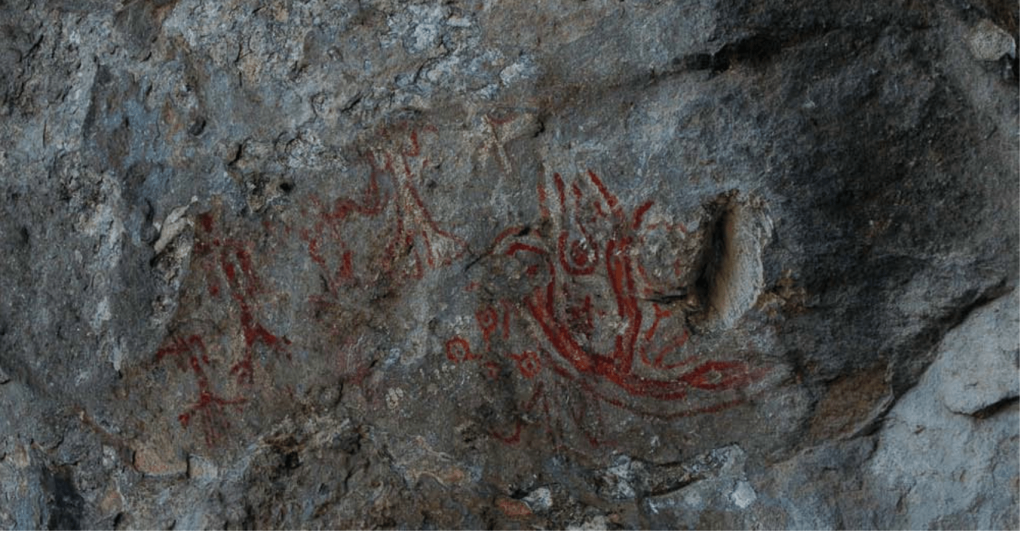
A different depiction of a human wearing fur on the right side of two women and two men is depicted, while on the left side of this painting, there is a depiction of a fetus growing in the womb.
Across from a human wearing fur, a human is depicted with a snake behind. It was believed that the snake represents death in this figure, which was interpreted as “the moment of death” by the experts. The depiction of a human wearing fur and extending his hand forward is believed to be a shaman who is helping human spirits to go to the land of the dead at the moment of death. A portrayal of a dead human without a head offered to the vultures is also depicted.
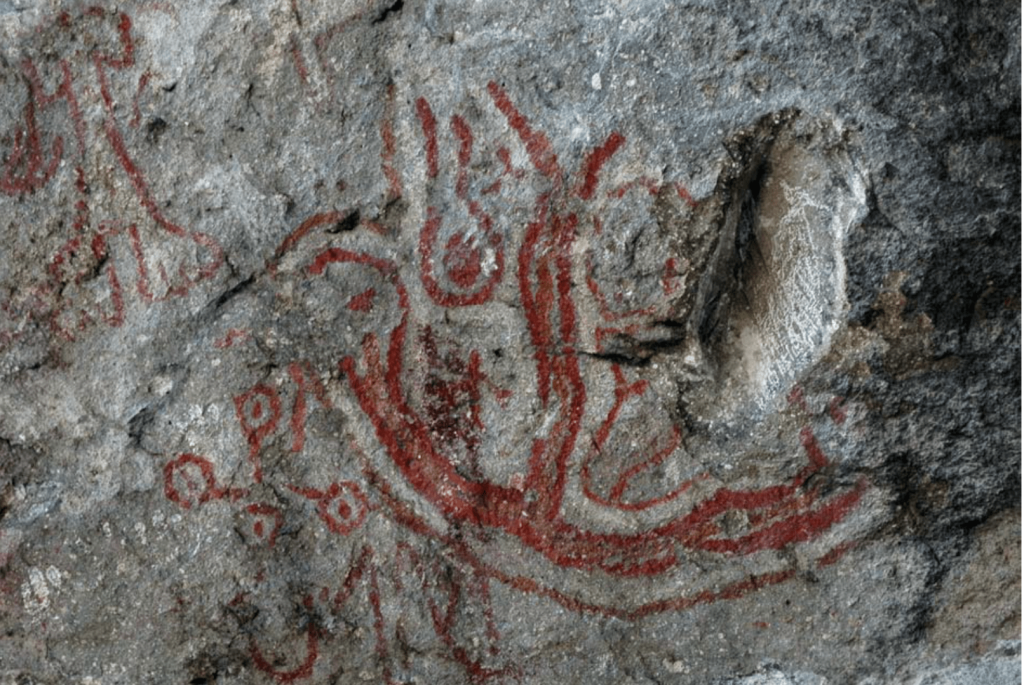

Life and death are the themes of the cave paintings in İnkaya Cave. The panels representing Life are based on the formation of a fetus inside a pregnant woman’s abdomen, its development, and birth, as well as the celebration of a new individual joining the community, with an emphasis on the shaman’s role throughout this process.
In cave paintings, reliefs, and figurines from the Neolithic period in Anatolia, scenes of sexuality, pregnancy, and childbirth are presented to the viewer from various angles. The successful use of the “X-ray” style -The rays pass through the painting and create a negative of the darker areas on film- in the creation of the İnkaya Cave painting in the Neolithic period fills a gap in the history of Anatolian painting and sculpture.
Source article: Associate Prof. Dr. Derya Yalçıklı “Thoughts upon a Neolithic Cave Painting of Childbirth in Anatolia and its implications“.
Cover Photo: İnkaya Cave (Survey Archive). Courtesy of Associate Professor Dr. Derya Yalçıklı