Tel Aviv University and Jerusalem’s Hebrew University researchers have unraveled the earliest evidence for the domestication of a fruit tree.
According to the researchers, the first domestication of fruit trees anywhere in the world took place in the Jordan Valley about 7,000 years ago.
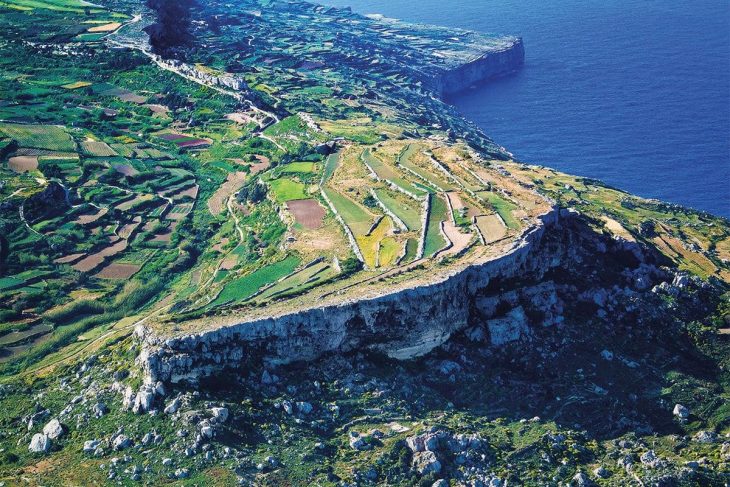
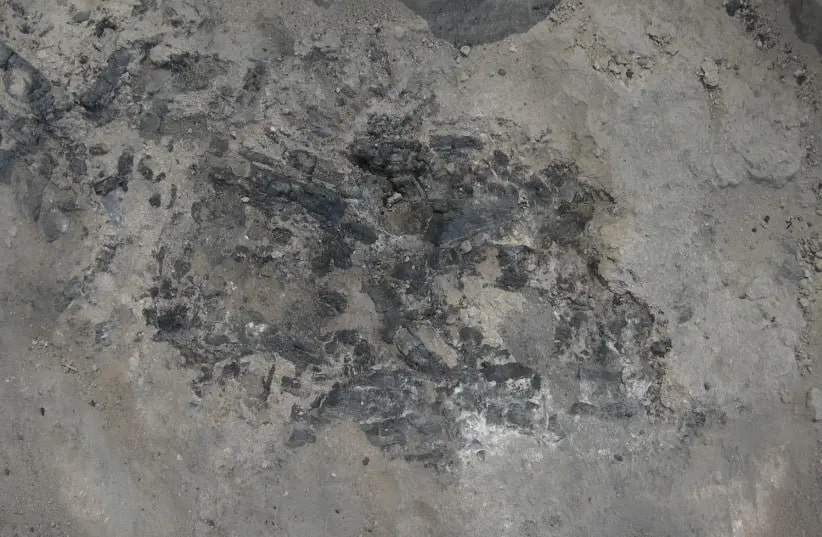
Analyzing remnants of charcoal from the Chalcolithic site of Tel Tsaf in the Jordan Valley, researchers determined they came from olive trees. Since olive trees did not grow naturally in the Jordan Valley, this means the inhabitants of the site must have planted the trees intentionally about 7,000 years ago, said the researchers.
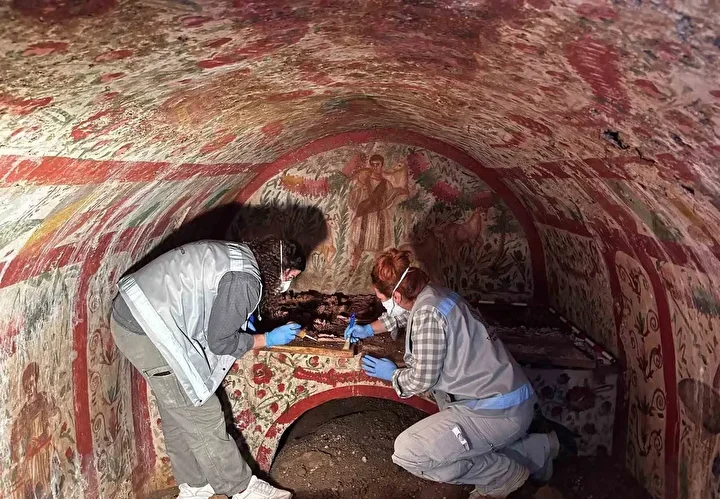
The study was led by Dr. Dafna Langgut of the Jacob M. Alkow Department of Archaeology & Ancient Near Eastern Cultures and the Steinhardt Museum of Natural History at Tel Aviv University. The charcoal remnants were found in the archaeological excavation directed by Professor Yosef Garfinkel of the Institute of Archaeology at the Hebrew University. The findings were published in the journal Scientific Reports.
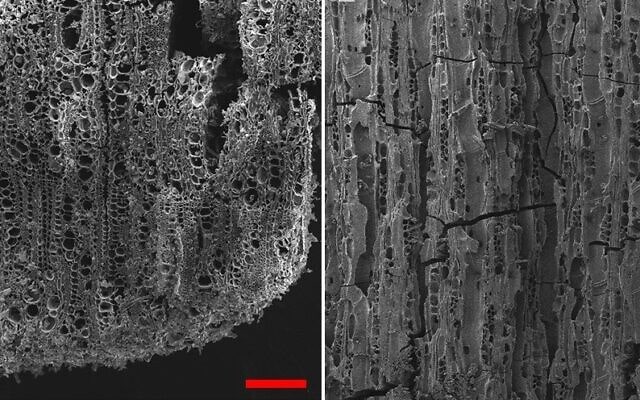
Dr. Dafna Langgut, head of Tel Aviv’s Laboratory of Archaeobotany and Ancient Environments, which specializes in microscopic identification of plant remains, said it was possible to identify trees by their anatomic structure even if they had been burned down to charcoal.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
“Wood was the ‘plastic’ of the ancient world,” said Dr. Dafna Langgut.
“It was used for construction, for making tools and furniture, and as a source of energy. That’s why identifying tree remnants found at archaeological sites, such as charcoal from hearths, is a key to understanding what kinds of trees grew in the natural environment at the time, and when humans began to cultivate fruit trees.”
Langgut’s analysis of the charcoal from Tel Tsaf found locally native trees, but also olive and fig.
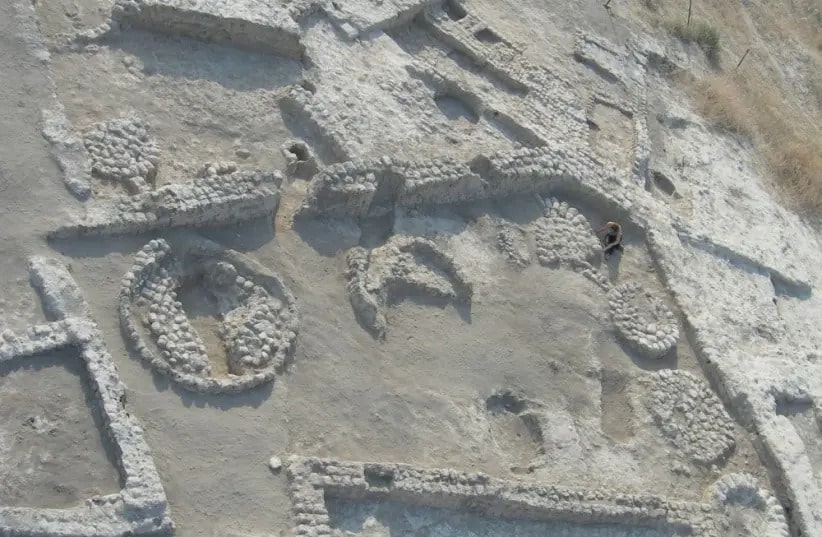

“Olive trees grow in the wild in the land of Israel, but they do not grow in the Jordan Valley,” she said. “This means that someone brought them there intentionally — took the knowledge and the plant itself to a place that is outside of its natural habitat.”
“In archaeobotany, this is considered indisputable proof of domestication, which means that we have here the earliest evidence of the olive’s domestication anywhere in the world.”

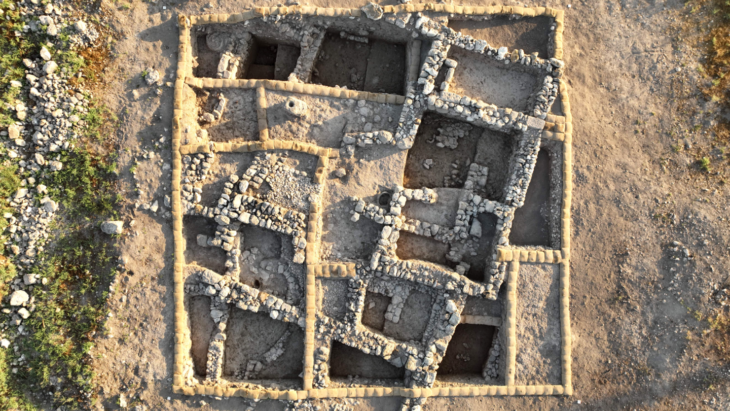
The tree remnants examined by Dr. Langgut were collected by Prof. Yosef Garfinkel of the Hebrew University, who headed the dig at Tel Tsaf Prof. Garfinkel says that “Tel Tsaf was a large prehistoric village in the middle Jordan Valley south of Beit She’an, inhabited between 7,200 and 6,700 years ago. Large houses with courtyards were discovered at the site, each with several granaries for storing crops. Storage capacities were up to 20 times greater than any single family’s calorie consumption, so clearly these were caches for storing great wealth. The wealth of the village was manifested in the production of elaborate pottery, painted with remarkable skill. In addition, we found articles brought from afar: pottery of the Ubaid culture from Mesopotamia, obsidian from Anatolia, a copper awl from the Caucasus, and more.”
According to a joint university press release, Langgut and Garfinkel were not surprised to learn that the residents of Tel Tsaf were the first in the world to intentionally grow olive and fig trees, because growing fruit trees is a sign of wealth, and this site is known to have been exceptionally wealthy.
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-10743-6
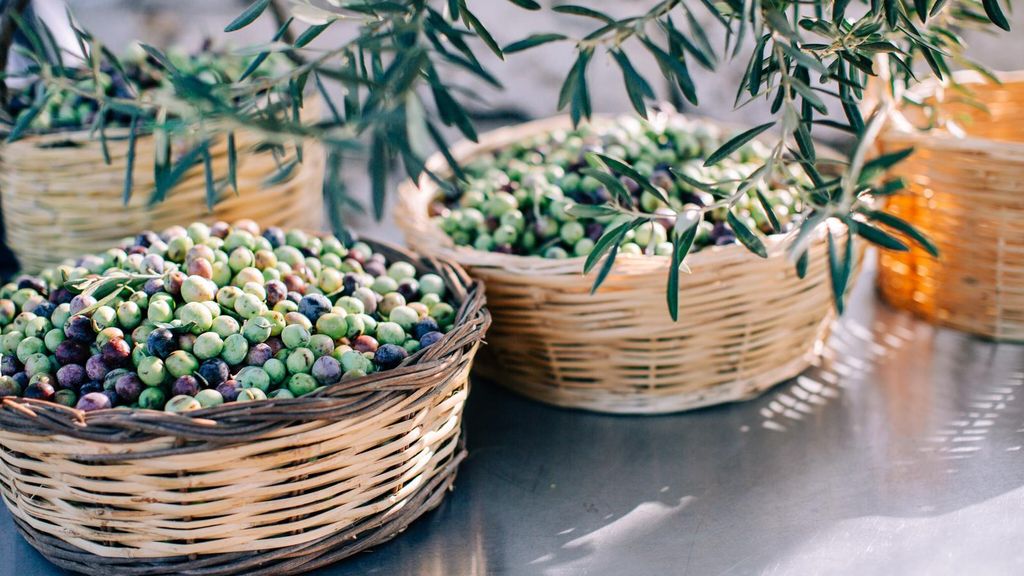
Cover Photo: Ayvalik olive harvest, Türkiye.