Roman remains dating back 1800 years have been found in a valley in eastern Turkey.
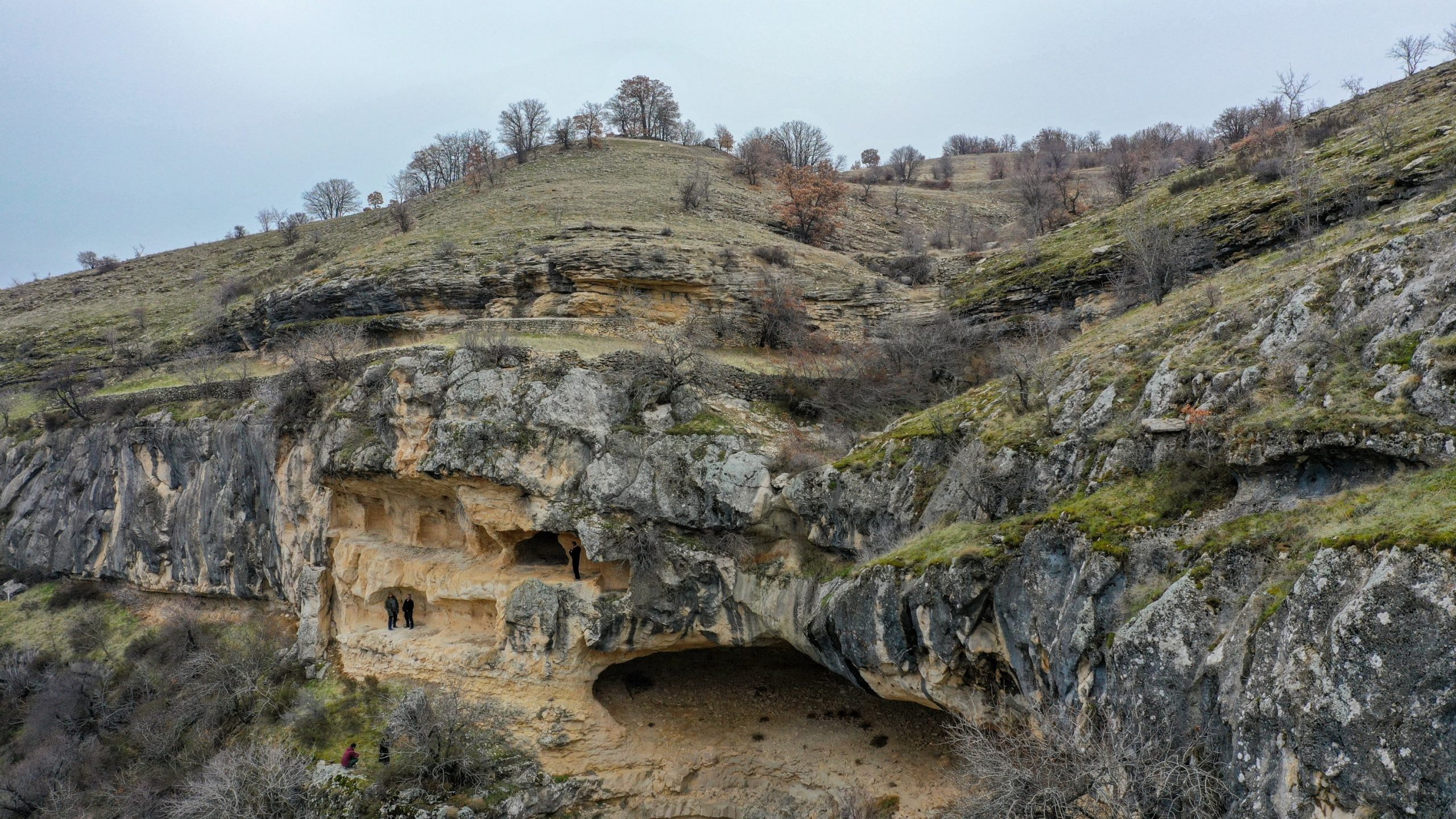
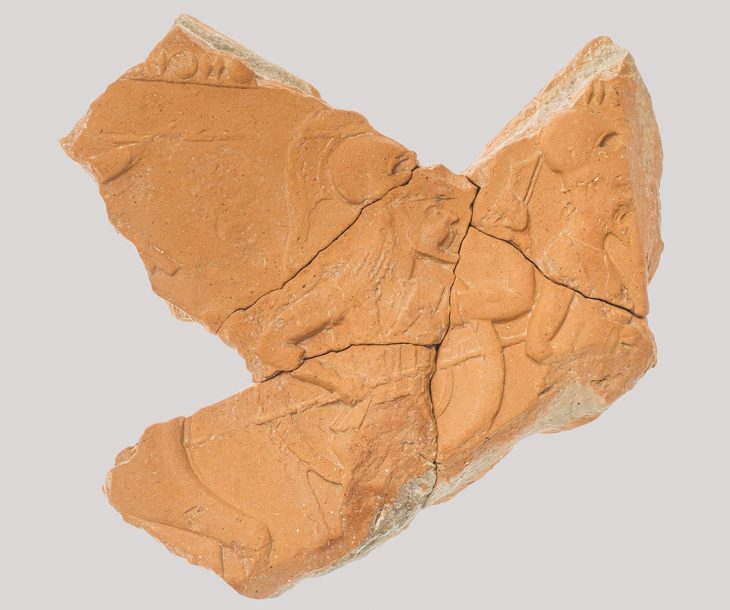
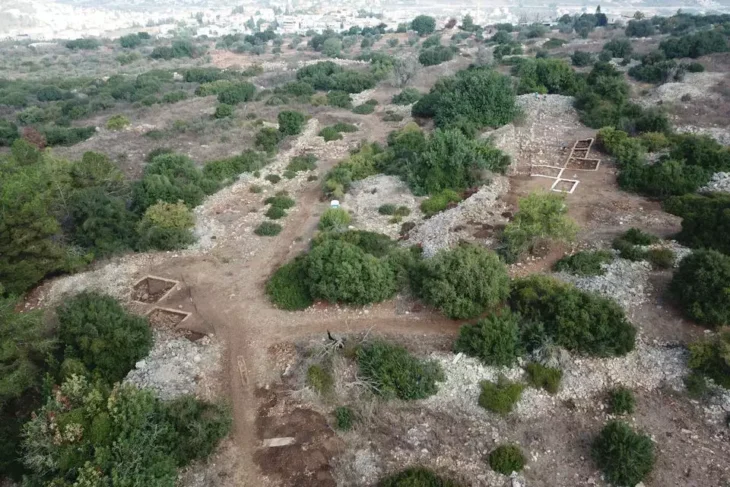
Among the Roman ruins found in a valley near the village of Balkayası in the Ağın district of Elazığ, there are important finds such as rock tombs and underground tombs, and man-made underground passages for religious practices.
Some locals discovered the historical remains while they were strolling in the valley. Thinking that the remains may be of archaeological importance, they contacted Professor Ismail Aytaç, who is both an academician at Fırat University (FÜ) and head of the excavations at Harput Castle.
Aytaç, who conducted research in the region, determined that the valley contains 1,800-year-old remains from the Roman period. He also discovered different findings such as “catacombs” where Christians worshiped in secret and buried their loved ones and grain warehouses carved into the rock floor.
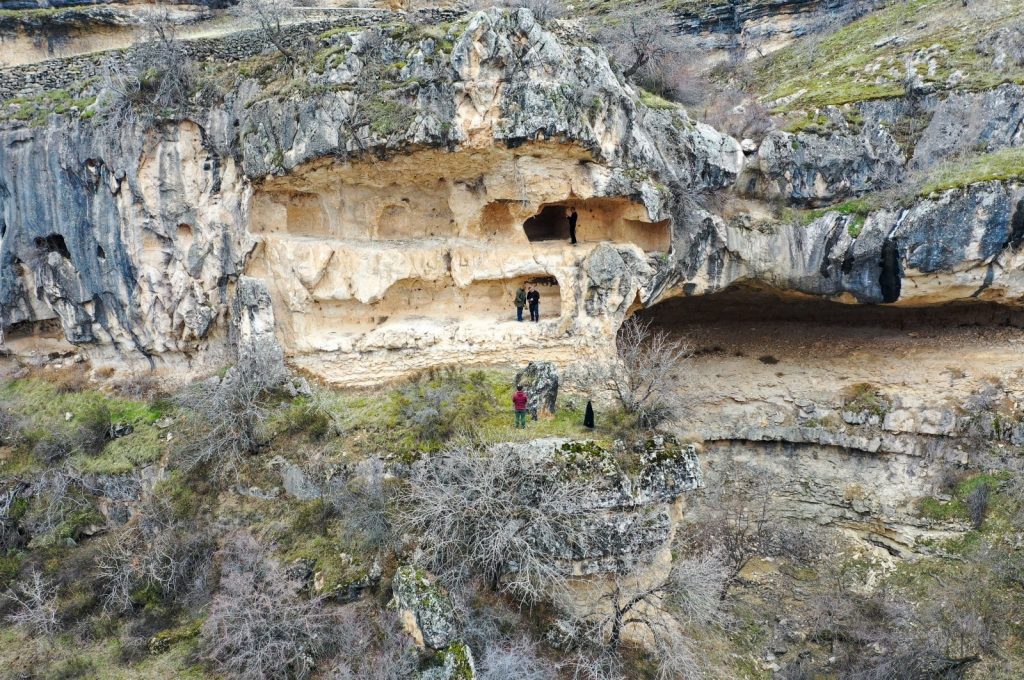

Professor Aytaç told Anadolu Agency (AA) that the region including the Euphrates River has hosted many civilizations throughout history since the Paleolithic Age, and archaeological studies carried out within the scope of the Keban Dam rescue excavations revealed traces of the settlement dating back to 6,000 B.C.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Pointing out that the archaeological remains discovered by the citizens near the Euphrates River basin, including rock tombs and catacombs, are of great importance in terms of the historical and cultural richness of the region, Aytaç noted that they will conduct large-scale archaeological research in the region.
Aytaç stated that the burial sections made for a small child or baby in the rock tombs, some of which were built for a family, are remarkable, and said: “The burial areas for adults and children were carved into the rocks. Although some of them were destroyed, there are also some intact ones among them. These two-story rock tombs have not been recorded previously. These structures were used for secret worship by Christians during the times when Christianity was forbidden. By increasing the surface research, we will ensure that they will be recorded. In the next stage, nature tourism and cultural tourism will be combined to create a wide destination.”