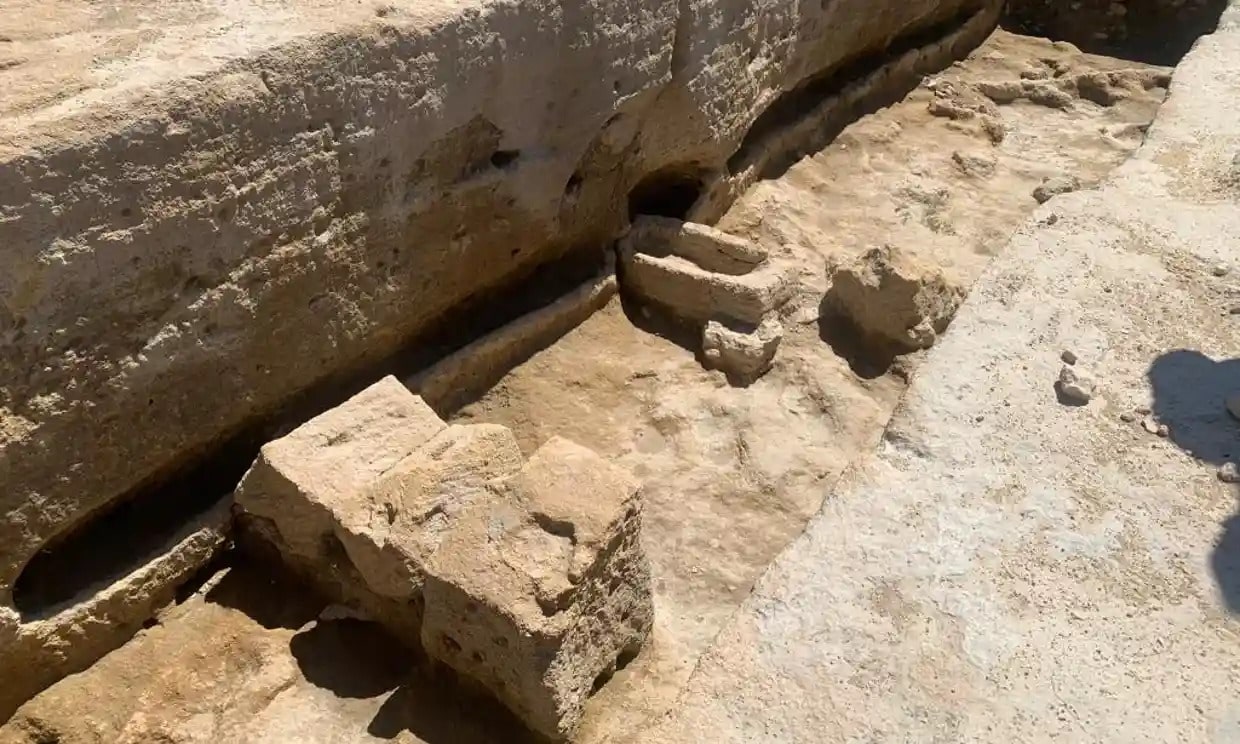
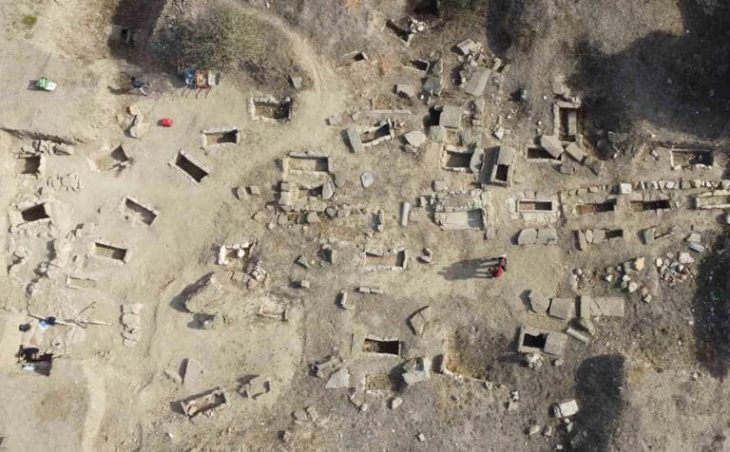
A 4th or 5th-century B.C Phoenician necropolis has been found at Osuna in Southern Spain. A well-preserved underground limestone vault necropolis, where the Phoenicians living in the Iberian peninsula buried their dead, was discovered during water utility upgrades.
Council workers have found a well-preserved necropolis from the Phoenician era with at least eight subterranean limestone burial vaults and a staircase.
Archaeologists said the “unprecedented” Phoenician-Carthaginian cemetery. Such sites are normally found in coastal areas rather than so far inland, they say.
It is a unique find because the only comparable necropolises that have been unearthed so far are coastal, dotting the area around the ancient Phoenician colony of Cádiz. Osuna is inland, about 55 miles east of Seville.
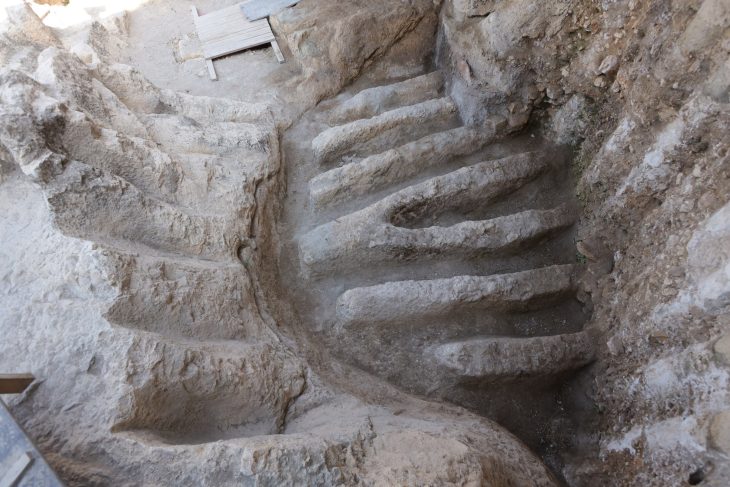
Preliminary surveys have so far turned up eight burial vaults as well as staircases and areas that are thought to have served as atriums. These were elite graves, and unprecedented in what would have been practically the hinterlands of Phoenician Spain.
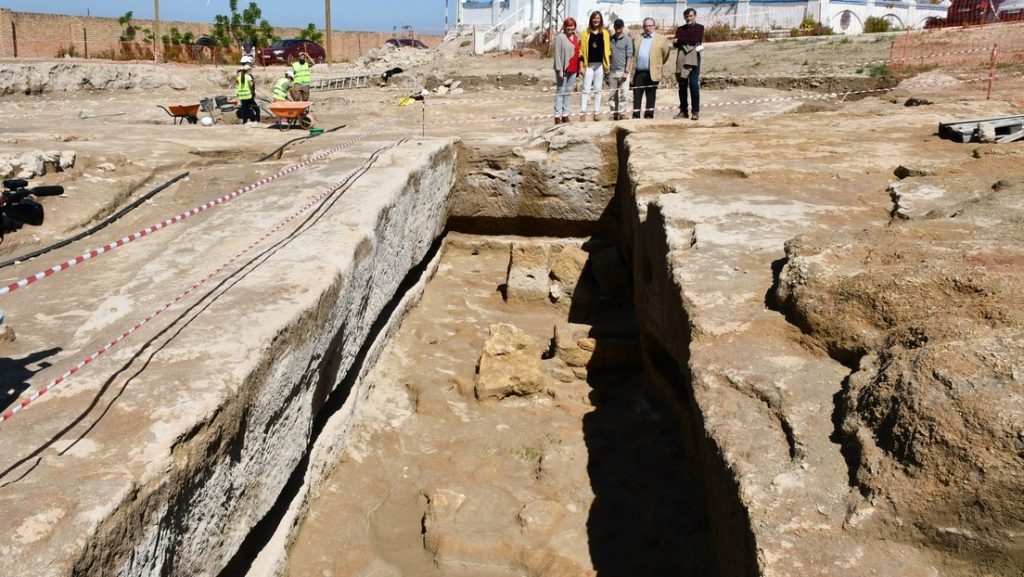

The lead archaeologist, Mario Delgado, described the discovery as very significant and very unexpected. “To find a necropolis from the Phoenician and Carthaginian era with these characteristics – with eight well tombs, atriums, and staircase access – you’d have to look to Sardinia or even Carthage itself,” he said.
“We thought we might find remains from the imperial Roman age, which would be more in keeping with the surroundings, so we were surprised when we found these structures carved from the rock – hypogea [subterranean vaults] – perfectly preserved beneath the Roman levels.”
Rosario Andújar, the mayor of Osuna, said the find had already prompted a re-examination of the area’s history.
The mayor said that while more research needed to be done, the luxurious nature of the necropolis suggested it had been built for those at “the highest level” of the social hierarchy.
Excavation work is currently underway in order to reach the ground levels of a possible atrium, officials said.
The Phoenicians were amongst the greatest Mediterranean traders from approximately 1,500 to 600 BC. Based on archaeological remains, the consensus now is that colonisation began around 800, when settlements were founded along the south coast of the peninsula. They settled southern Spain, not long after the founding of Phoenicia’s greatest colony, Carthage.
They set to work exploiting the region’s rich and untapped deposits of tin, gold, and silver and expanding their trade networks. The trade of metals and consumer goods (fish, textiles) made the Phoenician settlements of what is now Andalusia enormously prosperous. Archaeologists believe that the rich tombs found on the coast were built for the shipping dynasties that ran Phoenician commerce.
The Spanish town of Osuna came to the spotlight when it became the location for parts of the fifth season of HBO series, Game of Thrones.
Cover Photo: Andalucía regional government