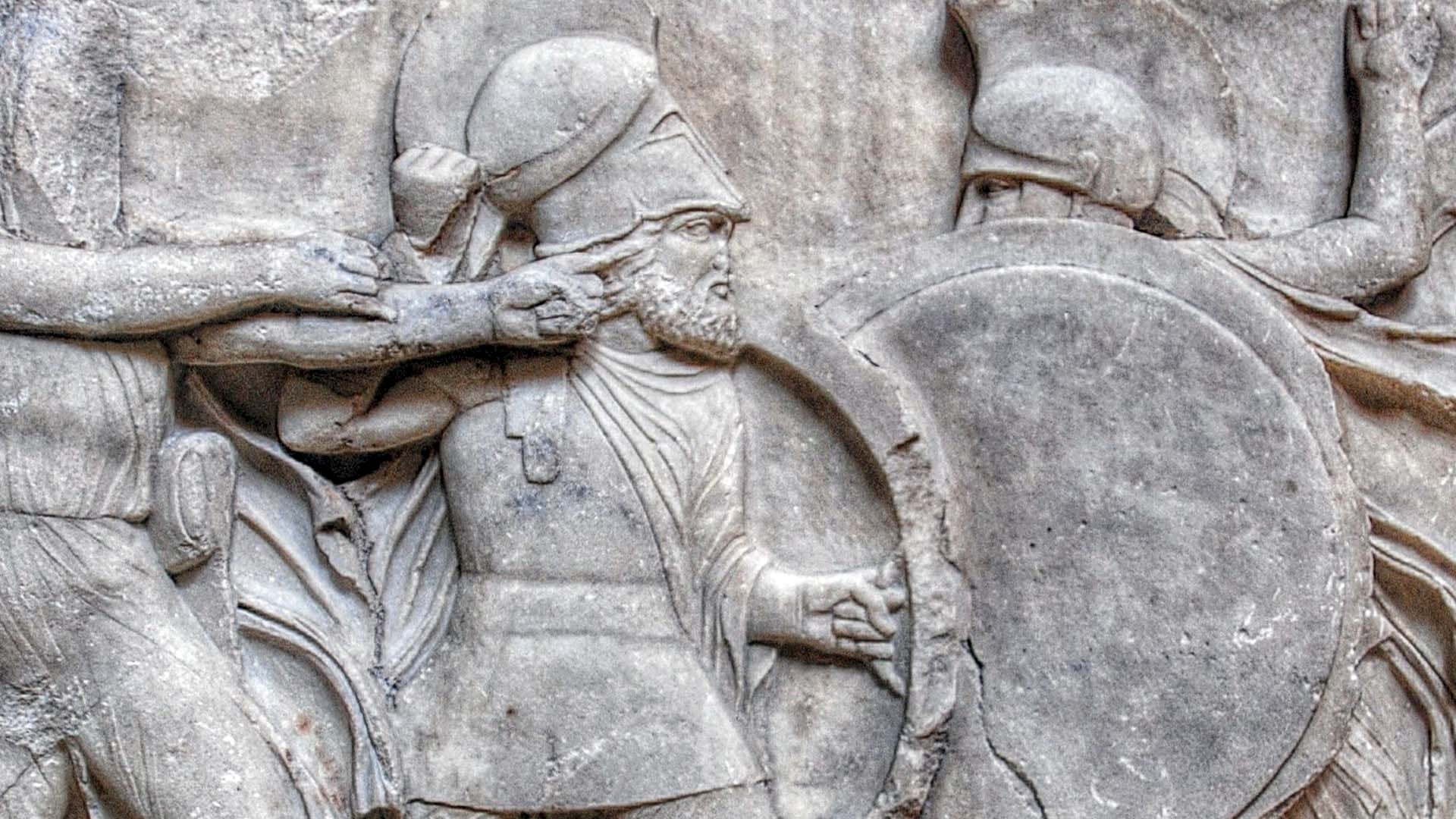
According to the Ancient Greek Historians, victory over the Carthaginians in the Battle of Himera was won by the alliance of the Ancient Greek City-States. However, archaeological evidence suggests that this is a haunted ancient lie. Who were the warriors, and what truth did the ancient historians not write?
According to records in ancient texts, the Carthaginians besieged the ancient Greek city of Himera in 480 BC, but without success. The ancient Greek army, which fought a successful defensive war, repelled the attackers.
B.C. In 409, 71 years later, Carthaginians attacked the city again, but this time the Ancient Greeks could not resist the Carthaginian navy, and Himera fell.
Who really fought in the Battle of Himera?
According to a study published in the journal PLOS ONE by Katherine Reinberger of the University of Georgia, US, and colleagues, geochemical evidence reveals that armies in the Battles of Himera were a mix of locals and outsiders. Certain claims made in historical accounts by ancient Greek writers are contradicted by these findings.
Ancient Greek historians, especially Herodotus and Diodorus Siculus, that Himera was successful in the first war because he received help from the allied Greek City Giants, They wrote that he fell because he fought alone in the second war. However, given the limited and partisan perspective of those ancient historians, these accounts are liable to be incomplete and biased.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
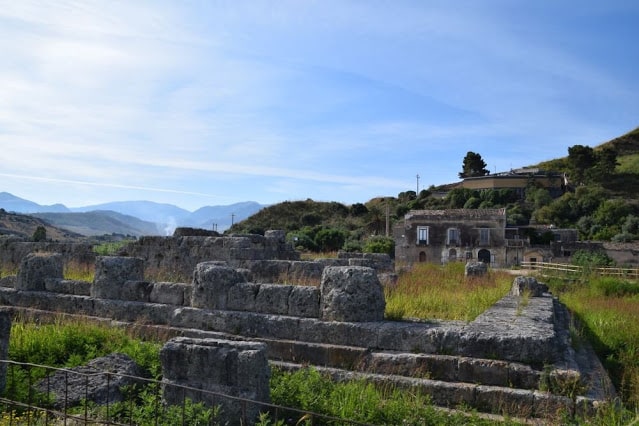

the first Battle of Himera in 480 BCE. Photo: Katherine Reinberger
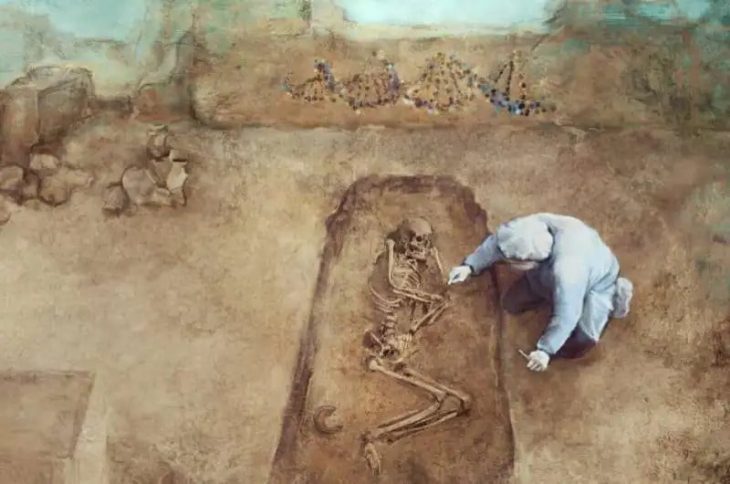
The current study’s authors put these historical arguments to the test against geochemical proof. They took strontium and oxygen isotope samples from the tooth enamel of 62 soldiers who participated in the wars. The soldiers’ tooth chemistry differed depending on where they came from.
The researchers found that only about a third of Himera’s soldiers from the first battle was local in the area, while about three-quarters were local to the second battle, confirming written claims that Himera was more assisted by outsiders on the first occasion than in the second battle. . However, the evidence also shows that, unlike written accounts, many Outsiders were not allies of Greece, but were mercenaries hired from outside Greek territories.
This study demonstrates the power of archaeological remains to examine the claims of historical texts and reveals potential biases in ancient writings. Ancient Greek historians may have deliberately underestimated the role of foreign mercenaries in the Battle of Himera in order to maintain a more Greek-centric narrative and avoid the theme of hiring foreign mercenaries, which may have a negative impact on Greek society.
The authors add: “Here we were able to use isotopes to support ancient historians, while also challenging those sources by finding evidence of mercenaries and potentially foreign soldiers from very diverse geographic origins. This study is also important to future studies of migration in the Mediterranean by expanding the network of comparative isotopic values.”
Source: Public Library of Science