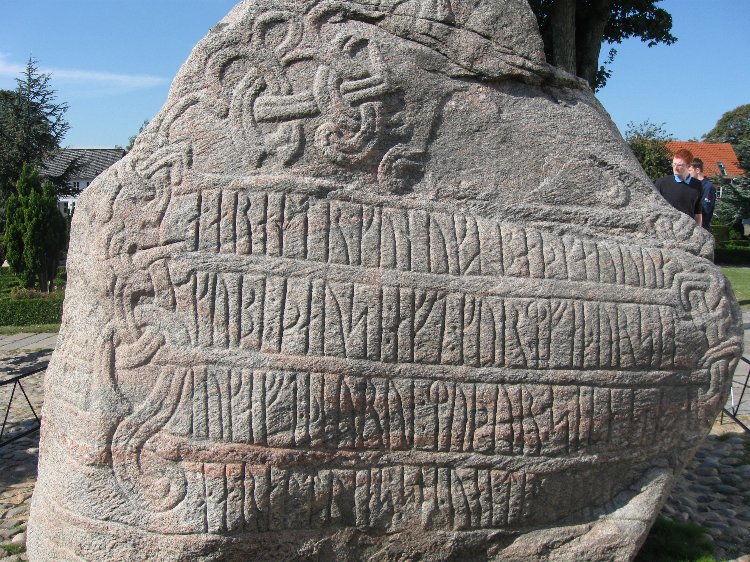
Researchers at the National Museum of Denmark using 3D scans have identified who carved the Jelling Stone Runes, located in the town of Jelling, Denmark. The discovery shows that Queen Thyra was far more important than was previously assumed.
Today, the details of our individual writings, from the way we compose our letters to the pressure we apply to pen and paper, can be used to define us. The same, it seems, is true for ancient runesmiths, which has allowed archaeologists to finally identify the person who carved the amazing Jelling stones in Denmark.
The Jelling stones are located in the town of Jelling, near the eastern coast of Denmark. They consist of two massive stone monuments that date back to the 10th century AD. The oldest was erected by King Gorm the Old to honor his wife Thyra, while the second stone was raised by his son, Harald Bluetooth to commemorate his parent’s memory. This second stone also contains intricate carvings that describe Harald’s achievements. It celebrates his conquest of Denmark and Norway and how he converted the Danes to Christianity.
Harald Bluetooth on the second stone describes himself as “that Haraldr who won for himself all of Denmark and Norway and made the Danes Christian.”
Featuring in every Danish passport, the Jelling Stone is known as the ‘birth certificate’ of Denmark.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
3D scans of runestones enable researchers to gain a close-up view of traces of the carving process. This means they can tell the carving technique of the different rune stones apart. Every experienced stonemason holds his chisel at a certain angle and strikes the hammer with a specific force: this is visible in the angle of the traces of the carving and the distance between them. The motor function developed in such work is individual. The name is Ravnunge-Tue. A runicist from the Viking Age, whose name is hardly well-known among the general public, but who, on the other hand, is quite well-known among professionals.
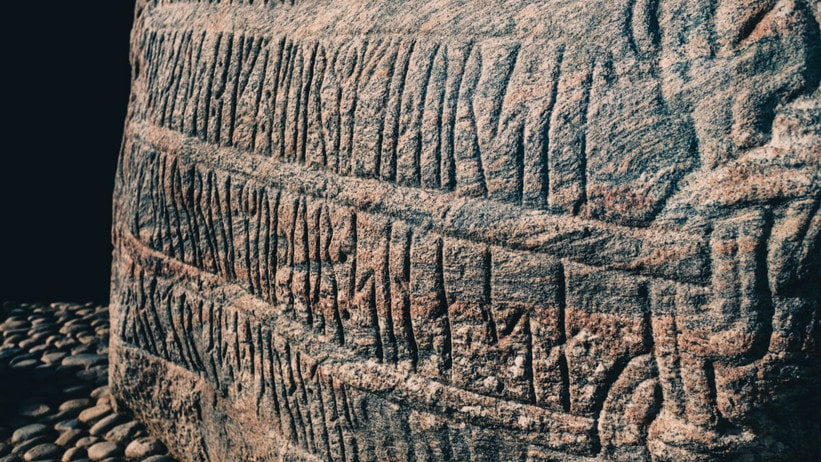

By analyzing these unique features and the distance between them, the team were able to compare the runes on the Jelling stones with others, such as the Laeborg Runestone, which is located about 30 kilometers (18.6 miles) away.
This comparison has been invaluable. It turns out the Jelling stones display the same carving techniques as those on the Laeborg Runestone.
For this project, seven Jutland runestones were 3D scanned: the two Jelling stones, the two Baekke stones, the Lborg stone, the Home stone, and the Randbl stone. The runes on the smaller Jelling Stone were too worn to see the signature chiseling techniques. It’s possible Ravnunge-Tue carved that one too.
Queen Thyra’s Power
The discovery is in itself interesting because it can link another person to the Jelling dynasty, but it is especially interesting because the realization brings with it another startling revelation, explains Lisbeth Imer, runologist and senior researcher at the National Museum in Copenhagen.
“The fact that we now know the name of the rune carver of the Jelling Stone is incredible; but what makes the discovery even more amazing is the fact that we know who Ravnunge-Tue’s boss was. She was Queen Thyra of Jelling – mother of Harald Bluetooth, wife of Gorm the Old,” says Lisbeth Imer.
The two Jelling stones mention Queen Thyra as the mother of Harald Bluetooth, wife of Gorm the Old and ‘Denmark’s salvation’. However, the name Thyra also appears on two other rune stones: the Læborg Stone, which Ravnunge-Tue carved in memory of Thyra; and Bække 1, which bears the inscription, ‘Ravnunge-Tue and Fundin and Gnyple, these three made Thyra’s mound.’

For many years, researchers have been debating whether the Queen Thyra of the Læborg Stone is the same as the Jelling Thyra. However, based on the new research, the likelihood of two different Thyras is significantly less, because, according to the researchers who conducted the analyses, Ravnunge-Tue carved both the Læborg Stone and the Jelling Stone.
That means Queen Thyra was on at least four rune stones, more runic mentions than anyone else in Viking-era Denmark, twice the number of mentions her husband and son got. Lisbeth Imer believes that this also highlights just how important Queen Thyra was.
“This means that Queen Thyra was far more important than we previously assumed. She probably came from a nobler, older family than Gorm the Old, whom we usually refer to as the first King of Denmark. This is extremely interesting when it comes to understanding the power structure and the genesis of Denmark as a nation,” says Lisbeth Imer.
All four rune stones that mention Thyra are located in Southern Jutland, implying that her power was based in this area, while Gorm the Old may have come from elsewhere.
Cover Image Credit: Drew Parsons – Megalithic Portal