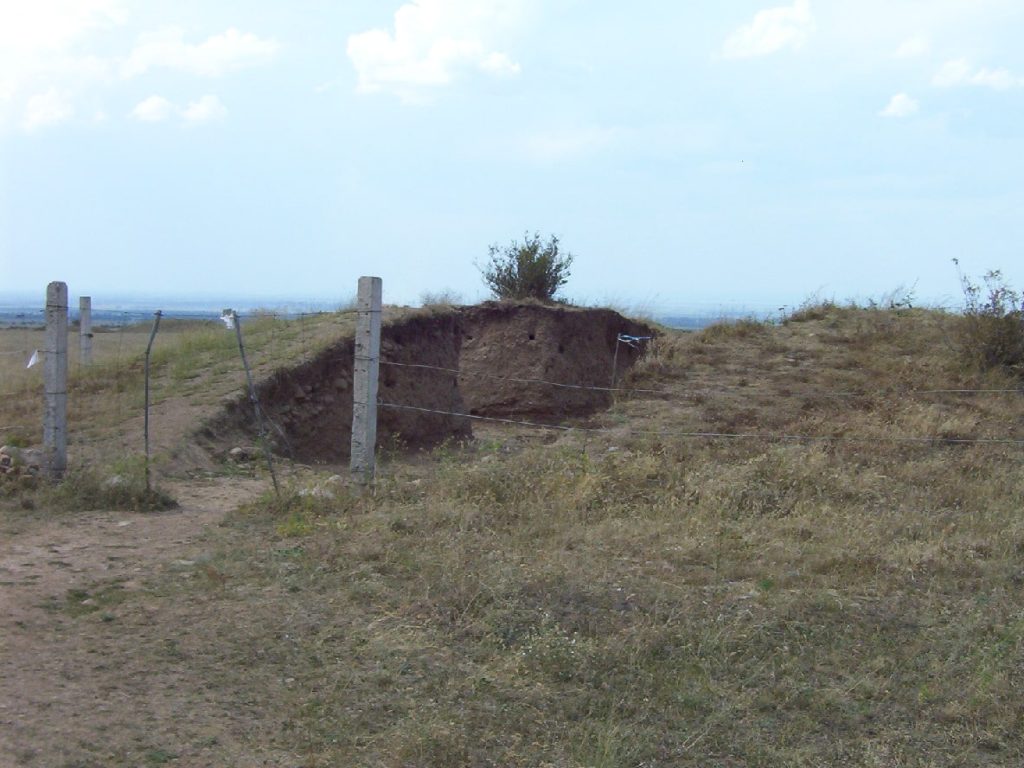
The Golden Man, the main symbol of Kazakhstan’s independence, is a warrior’s costume from about the 5th century BC that was found in a Saka tomb near Issik settlement, about 60km east of Almaty.
When his remains were discovered in 1969 during an excavation at the Issyk burial mound in southern Kazakhstan, along with exquisite gold-embroidered armor and other priceless funerary artifacts, archaeologists quickly nicknamed him the “Golden Man”.
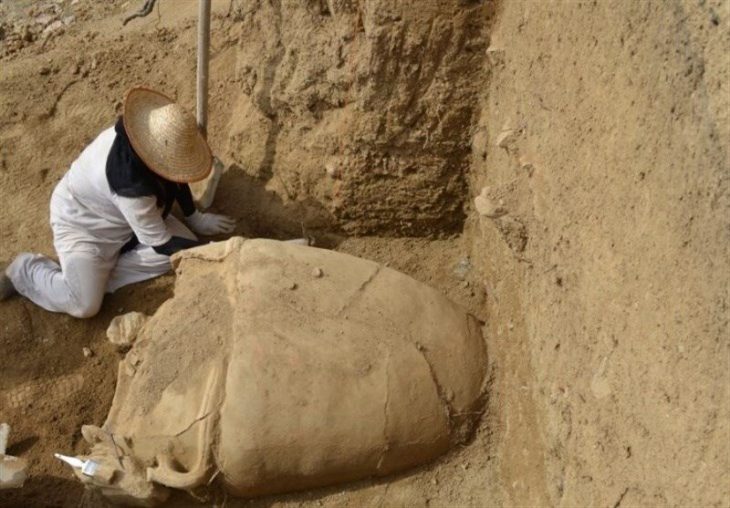
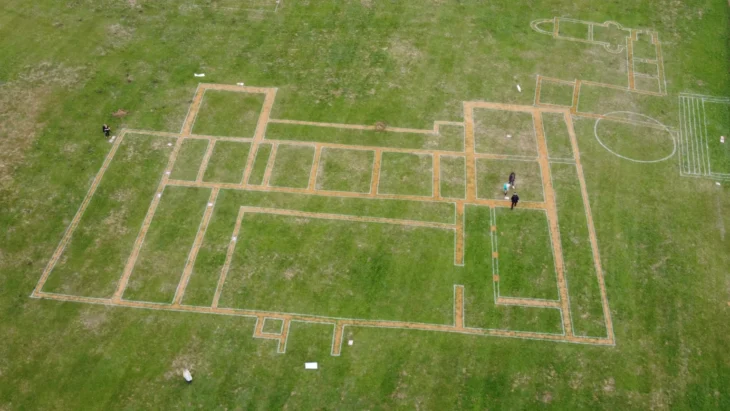
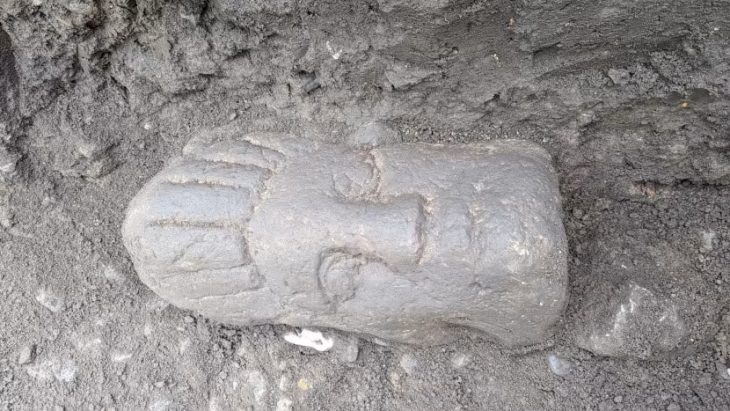
The discovery was made by a farmer from the Issyk collective farm while preparing the land for planting. The central tomb in the kurgan had been plundered in antiquity, but the robbers had missed a rich burial hidden in the side of the mound.
The Kazakh Institute of History, Ethnography, and Archaeology (now the Kazakh Institute of Archaeology) sent Kemal Akishev to Issyk to promptly begin systematic excavation of the kurgan after the farmer discovered it. Within a sarcophagus made of massive fir logs, Akishev and his associates soon found a skeleton covered in 4,000 gold ornaments. The rich find of jewelry left researchers so taken aback that they largely overlooked the human remains.
The so-called Golden Man, dubbed the ‘Tutankhamun of Kazakhstan’ by scientists, is believed to be an 18-year-old Saka soldier. Covered with thousands of pieces of gold, the suit is composed of a shirt, boots, and headgear and it is presumed that the golden earrings and rings from the grave also belong to him.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

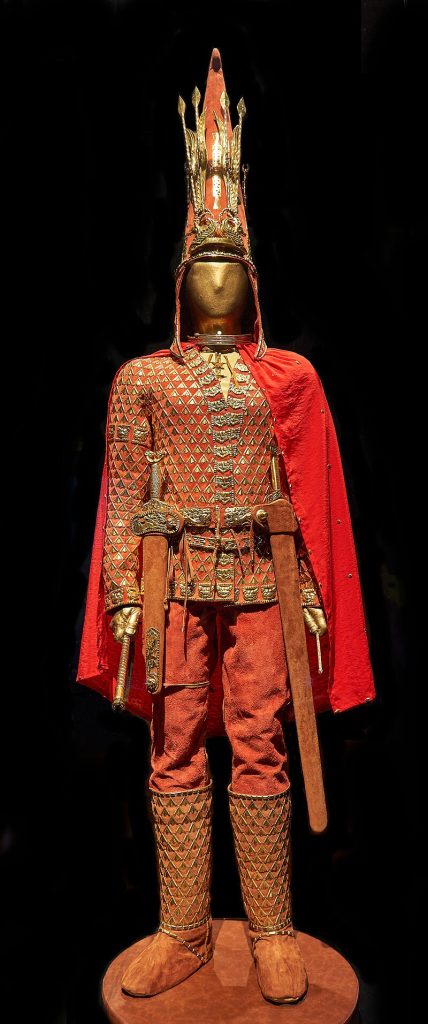
Warrior’s costume is made of more than 4000 separate gold pieces, many of them finely worked with animal motifs, and has a 70cm-high headdress bearing skyward-pointing arrows, a pair of snarling snow leopards and a two-headed winged mythical beast.
The conventional wisdom is that the skeleton found inside the costume was that of a young Saka prince killed in battle. But there is a strong countercurrent of thought that the Golden Man was in fact a Golden Woman, and that Kazakhstan’s nation-makers have deliberately misrepresented the gender to suit Kazakh stereotypes.
In her 2002 book Warrior Women, archaeologist Jeannine Davis-Kimball makes the case that other artifacts found in the tomb indicate the deceased was a woman, even though the body was too severely damaged to identify its gender.

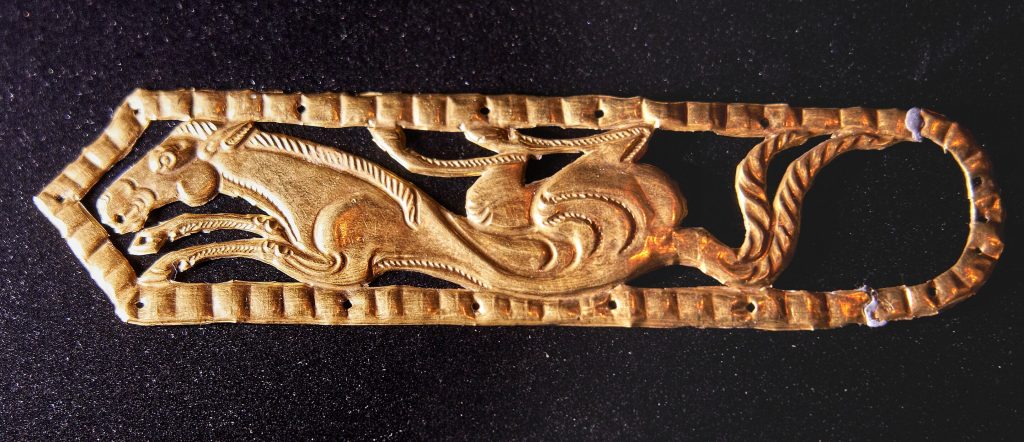
The ‘women’s equipment’ includes a mirror, beads, a spinning wheel for processing wool, and a scoop. The high conical headdress, decorated with branches of gold foil and shoots, is a reference to the fertility ritual. Janine suggests that this is not just a warrior, but a priestess. In her opinion, the gender has been deliberately misrepresented to satisfy stereotypes.
A fascinating school of thought links the Golden Woman to Tomiris, a queen of the Massagetes tribe who drove out the Persian emperor Cyrus the Great’s invading army.

The bones were only rediscovered recently at a forensic institute, stored in a cardboard box with a scribbled note reading “The Golden Man, May He Rest in Peace”. The bones are in a bad state. They have been kept in a cardboard box for 50 years and have been exposed to all sorts of bacteria and viruses, including modern ones. It seems difficult to make a healthy analysis at the moment.
Many archaeologists say this cannot be ruled out, given the rudimentary nature of the study of the remains, and the similarity of some of the Issyk artifacts to those found in female Scythian burial mounds in the southern Urals area of Russia.
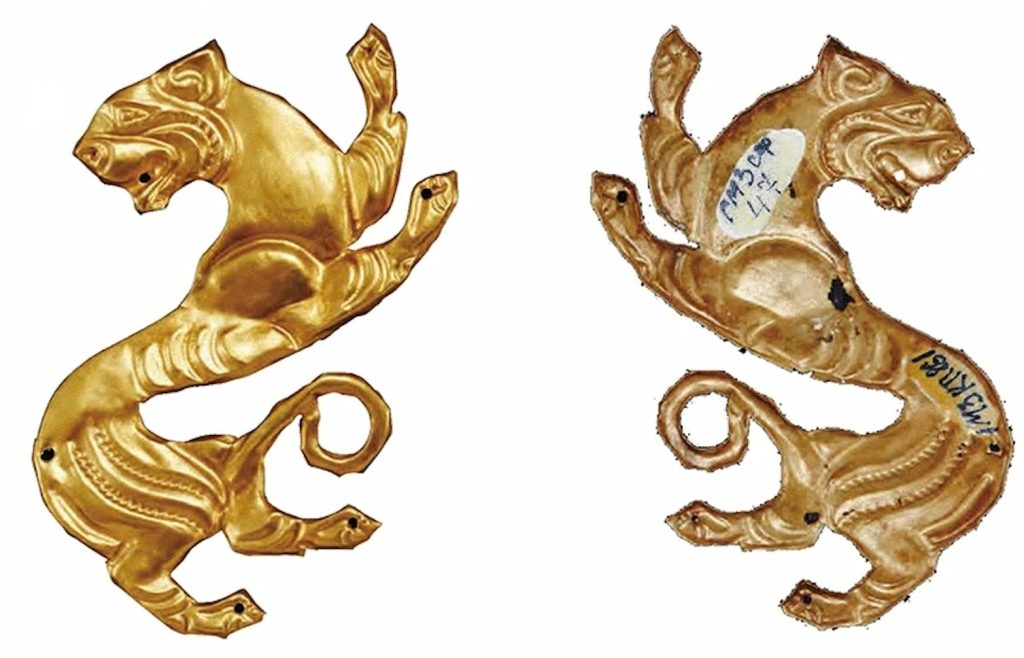

Whoever wears it, man or woman, the suit is created with exquisite craftsmanship using battering, stamping, carving, and granulation techniques. According to the findings, the Golden Man can be dated to the late Bronze Age or early Iron Age.
Since independence in 1991, Golden Man has become a symbol of Kazakhstan’s national heritage. He appears atop independence monuments throughout the country, including Astana and the financial capital Almaty, as well as on the presidential standard and commemorative coins.