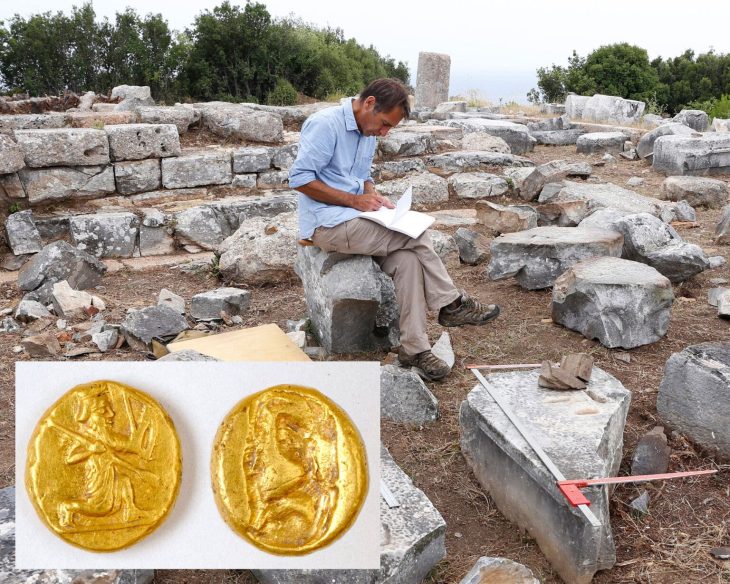
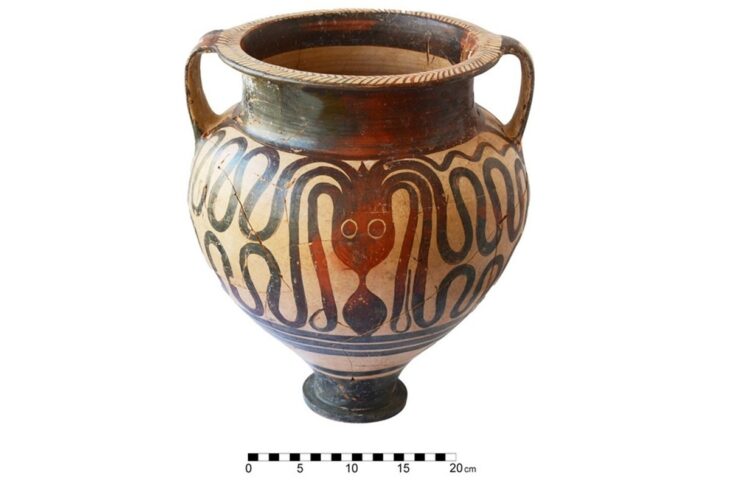
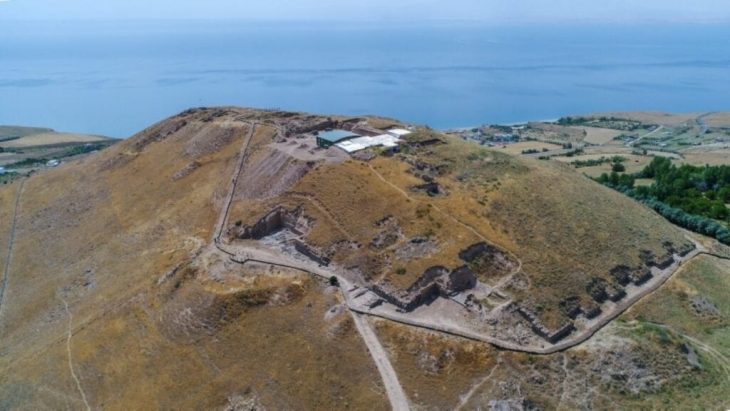
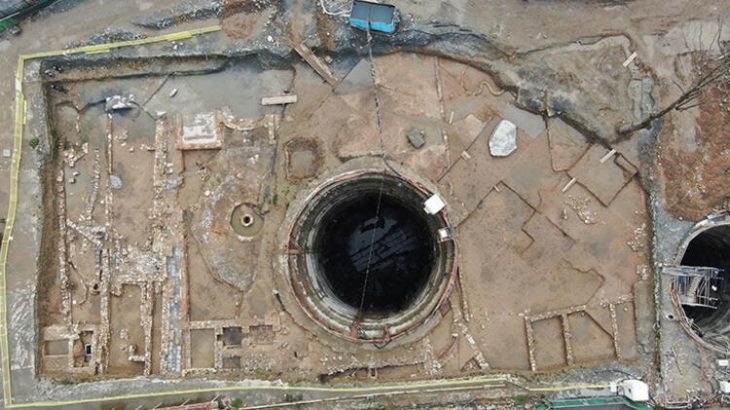
During the most recent excavations at Sırçalıtepe Mound (Sırçalıtepe Höyük) in Türkiye’s central Niğde province, archaeologists discovered traces of a permanent settlement dating back at least 9,300 years.
Head of the Excavation Team, Associate Professor Semra Balcı, told Anadolu Agency (AA) that the mound is located in an area close to obsidian sources in the volcanic Cappadocia region.
Sırçalıtepe Mound is located in the Volcanic Cappadocia region, within the borders of the Kayırlı village in the province of Niğde. With its location, it can be characterized as the nearest site to the Göllüdağ and Nenezi Dağ obsidian sources in the region.
Balcı stated that in the first surveys conducted in 2016, the obsidian processing area, bone, and ground stone tools attracted their attention.
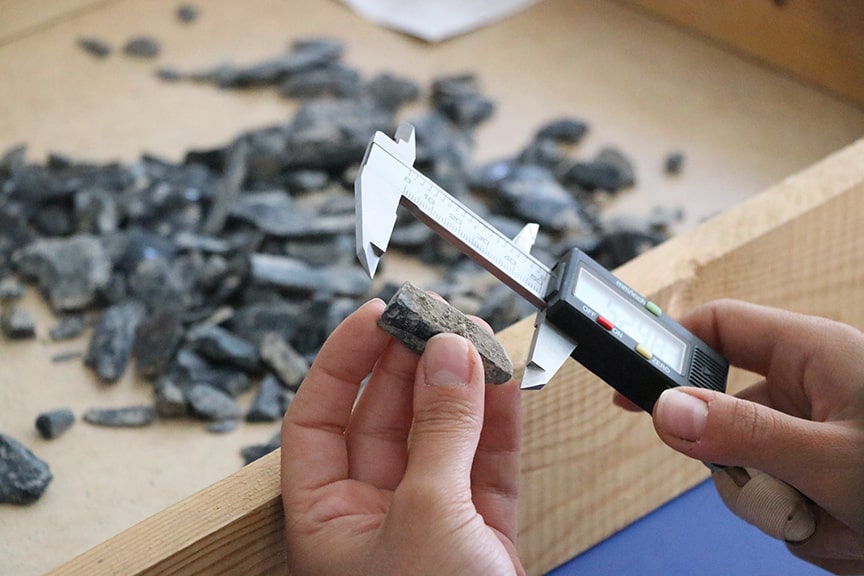

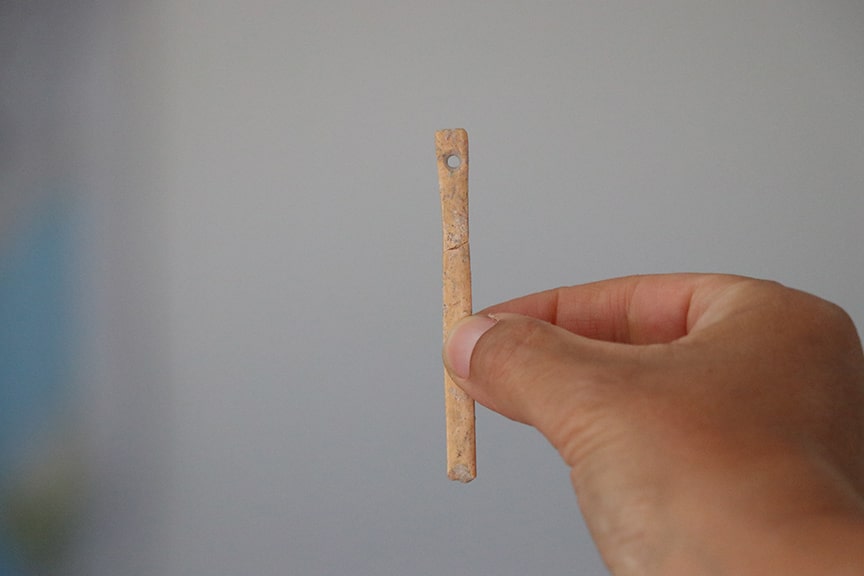
This year at the excavation site Balcı, of Istanbul University, said her team had found bone and obsidian tools used in daily life, along with beads and other objects thought to be for ornamental purposes.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Balcı stated that now that the dig season is over, she and her team will continue to analyze their findings in artifacts and new architectural field data in their workshops.
She added that the two samples they found had been radiocarbon dated, revealing they were 9,600-9,300 years old.
Noting that the dig also yielded specimens of oval arrowheads, she said: “Another important point is that no other site has so far been excavated with an obsidian working area and settlement together.”

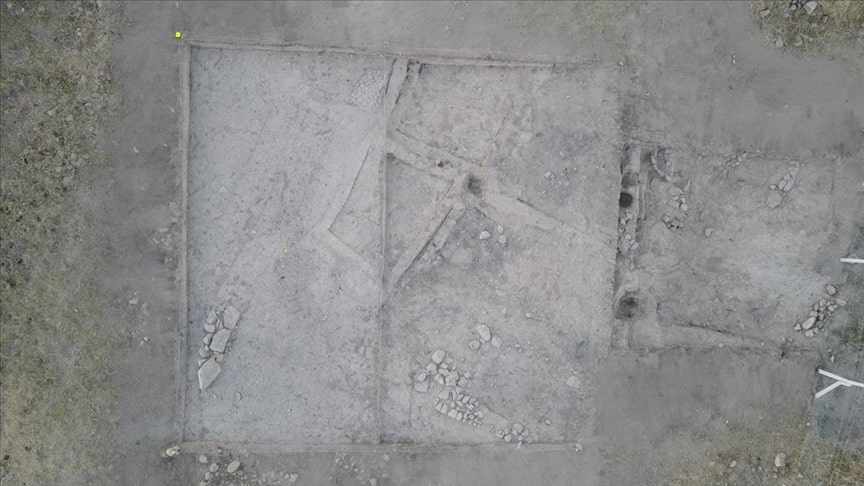
At Sırçalıtepe, excavations were conducted in two different locations on the mound. Both trenches contain obsidian knapping debris in proportions typically found in workshop areas. One trench is from the slope and contains documented architectural remains and finds related to daily life. The other trench is from the top of the mound.
Mudbrick walls, lime-plastered floors, and substantial ovens are among the architectural relics that were found in the slope trench. However, the investigated area from the top trench with abundant cores and knapping debris reveals the difference between Sırçalıtepe and other contemporaneous sites in the region.
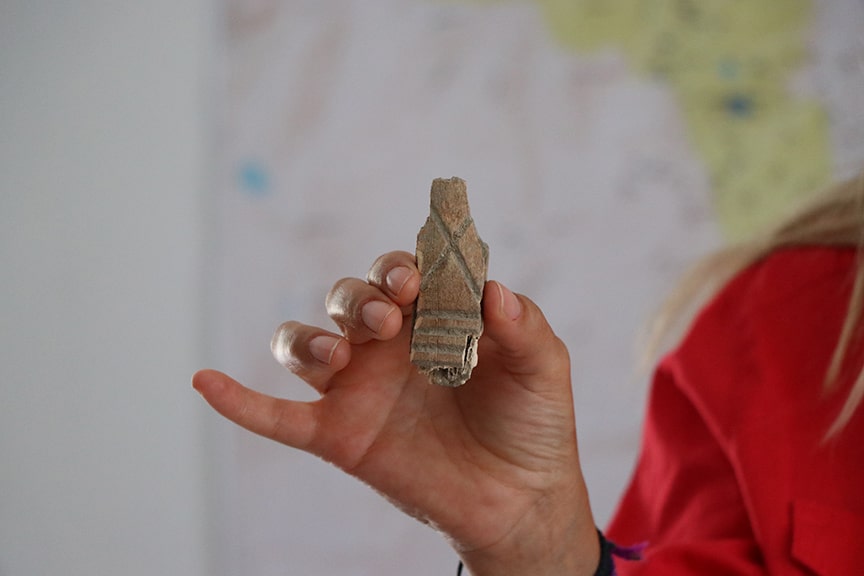

With its obsidian artifacts, in particular, Sırçalıtepe may be able to shed light on the connection between the workshop and the site. On a collection of obsidian artifacts, portable XRF analyses revealed that the inhabitants of the settlement used obsidian sources from Acıgöl, Nenezi Dağ, and Göllüdağ.