Numismatists from the Faculty of Archaeology at the University of Warsaw have examined thousands of previously ignored small coins (Nummi Minimi) discovered in the ancient city of Marea, located 45 kilometers southwest of Alexandria. Their findings are reshaping the literature’s established understanding of monetary circulation in Egypt at the end of antiquity.
Marea, known as Filoksenite during the Byzantine period was a large port town located to the south-west of Alexandria. In Ancient times it was famous, among other things, for its excellent wine which was sold in all parts of the Mediterranean.
Located on Lake Mariut near Alexandria, it was an important port in the Roman and Byzantine times, and probably existed already in the Ptolemaic times. As it was linked by canals to the Nile and the Mediterranean Sea, also products from Upper Egypt were brought there.
The importance of Marea is evidenced by the four long piers, the longest of which (125 m) was built from strong stone ashlars bound with waterproof mortar. It developed remarkable infrastructure and architecture during the reign of Emperor Justinian, and it became an important place of rest for pilgrims en route to the tomb of Saint Menas, one of the most famous martyrs in Christian history, which is situated in the Egyptian desert.
The Polish Centre of Mediterranean Archaeology UW (University of Warsaw) has been conducting archaeological research in Marea since 2000. The current work is supervised by Professor Tomasz Derda.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Currently, excavations are underway in the extensive bath complex. Excavations also continue in the large basilica built during Justinian’s reign.

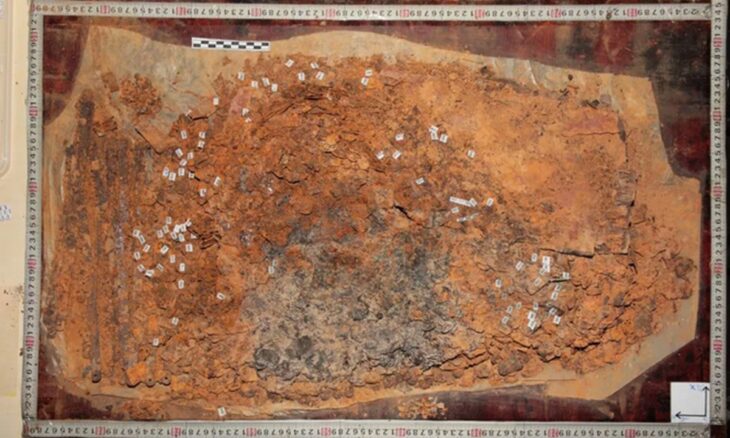
A team of numismatists from the Faculty of Archaeology of the University of Warsaw, led by Dr. Piotr Jaworski, examined nearly 8,500 Byzantine and Umayyad coins. Among them, they discovered several treasures, such as the remains of pouches and thousands of coins lost by the city’s inhabitants and pilgrims who stayed in the city before the last stage of the pilgrim trail to Abu Mena.
‘The importance of the research we conduct in Marea cannot be overestimated, because the material culture of this rich Byzantine city gives an idea about the most important city in the region – Alexandria. Due to the rapid development of the city in the 19th and 20th centuries, the possibilities of conducting archaeological research there are extremely limited, and the state of research on monetary finds is far from satisfactory,’ says Dr. Piotr Jaworski.
The results of numismatic research conducted in Marea (Filoksenite) are surprising because they paint a picture of monetary circulation in Egypt at the end of antiquity that differs from that known from literature. Most existing publications focus on the coinage of Byzantine Alexandria.
An important exception and basic reference material for Polish numismatists is the body of finds from nearby Abu Mena, compiled by Hans-Christoph Noeske. Research findings show that before the Umayyad caliphs took power, Egypt seemed to be part of an economic zone extending far beyond the territory of the country and covering large areas of the eastern Mediterranean, and the closest similarity of the monetary circulation model can be found in today’s Israel.
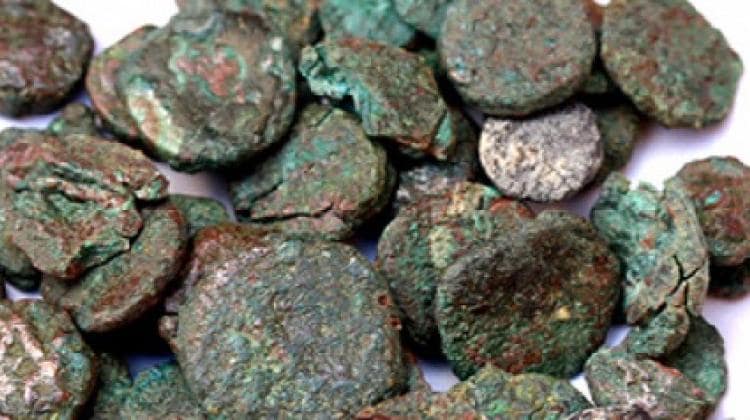
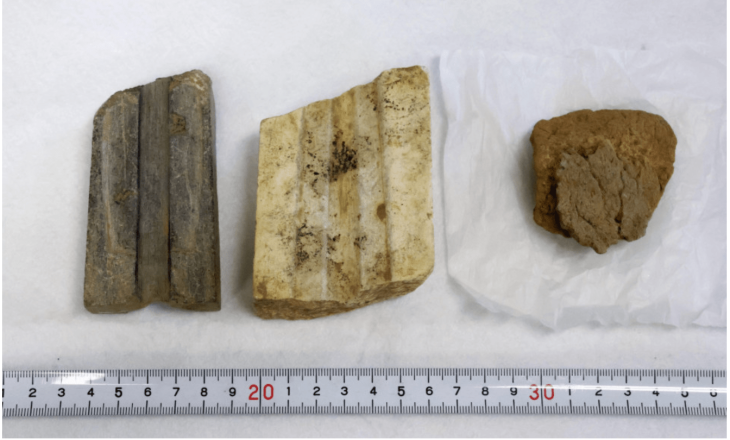
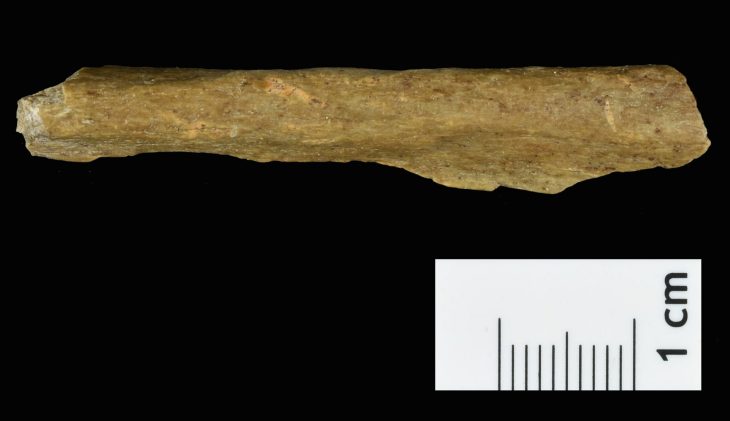
According to the University of Warsaw press release, these important findings were possible primarily due to focusing on the most numerous (approximately 75 percent of the total number of finds), although seemingly least attractive group of coins: those with a diameter of only a few millimeters, called nummi minimi.

The majority of “nummi minimi” were stored in bags, numerous remnants of which were discovered at the site. These coins have been largely marginalized in scientific publications until now. However, numismatists from the University of Warsaw decided to examine each specimen, even the smallest and poorly preserved ones.
Thanks to this, they discovered that in the group of “nummi minimi” found in Marea (Filoksenite), coins minted in Carthage by the Vandal kings predominated and, subsequently, after the recovery of Africa from the barbarians, by Justinian.
The researchers also identified Ostrogothic small coins, which – like Vandal coins – began to flow widely into the eastern Mediterranean after the Ostrogothic kingdom was ended by Justinian.
Among the coins found in Marea, a significant percentage are local Egyptian imitations. They include coins inspired by the coinage of the Kingdom of Aksum and imitations of Byzantine coins minted in Alexandria. A surprisingly large number of them are called “blanki,” that is, empty coin discs made of copper or lead that functioned as spare coins.
Cover Photo: Piotr Jaworski, University of Warsaw