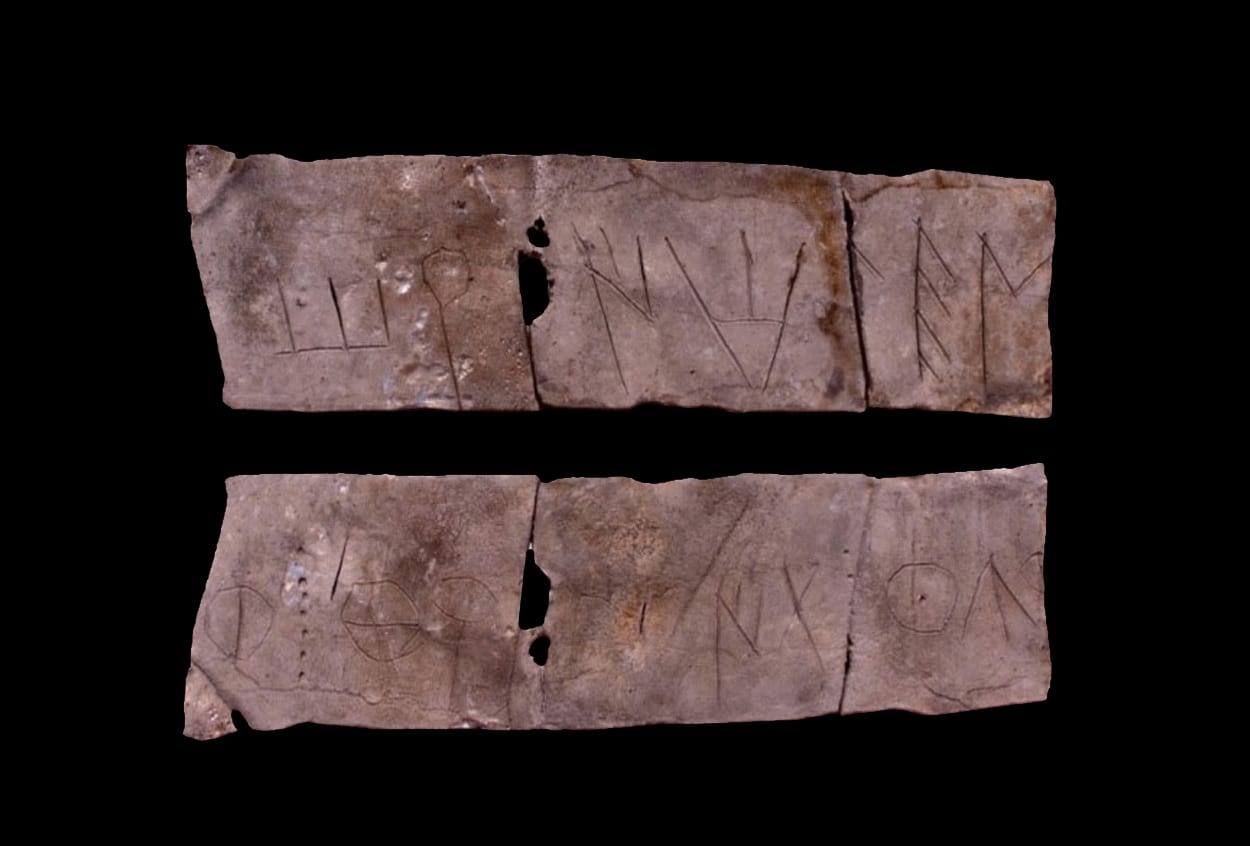
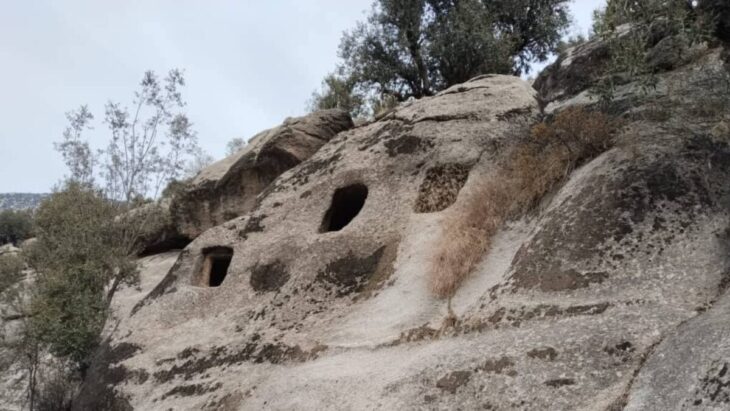
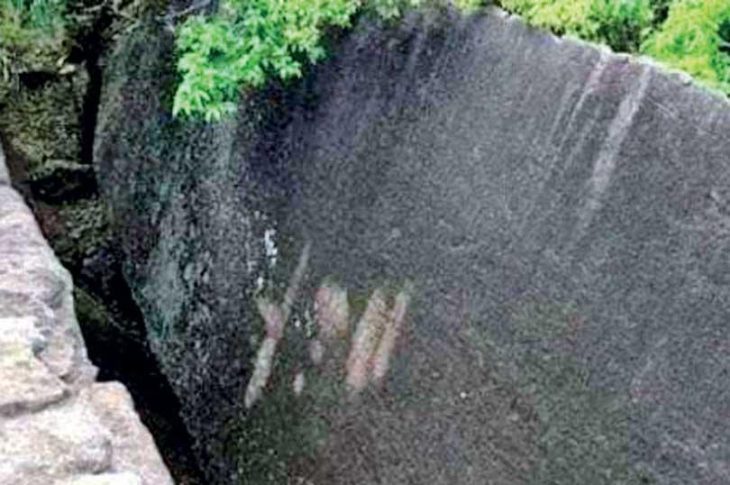
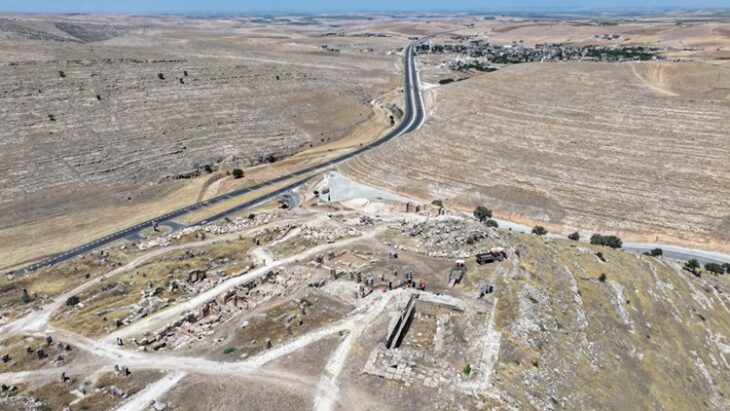
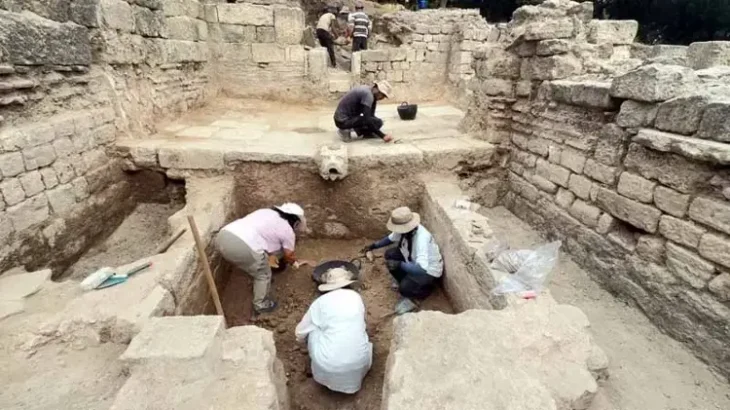
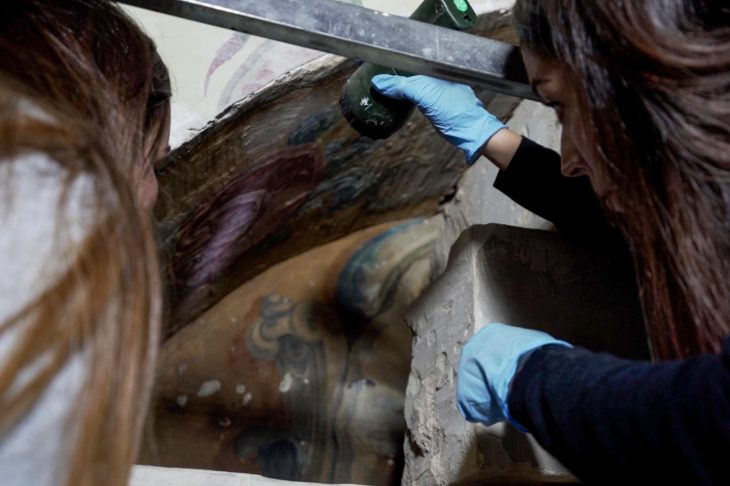
At the Pico de Los Ajos site in Valencia, Spain, a rare lead sheet engraved in ancient Iberian was unearthed.
While there are more inscribed lead sheets known, nearly all of them were unlawfully dug. This is one of just a few uncovered by archaeologists during controlled excavation, and its setting is especially important here since paleographic evidence shows it is far older than the site.
The lead plaque was found bent and has inscriptions on both sides to form a single text, with specialists have been able to identify Iberian symbols written between the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, while other similar plaques generally date back to later centuries.
“This site has one of the largest sets of texts written in Iberian on the entire peninsula”, says David Quixal. The sheets of lead used as writing support are relatively common in the deposits of the Iberian culture. The Pico de los Ajos, a town located in the town of Yátova, was inhabited at least since the 7th century BC and was later abandoned between the first century BC and the first century AD.
Although it has been researched in terms of phonetically, it is still not clear what information the section contains, nor is it clear the context in which it should be placed. The researchers ruled out any relationship with a commercial or administrative nature, implying that it may be a religious text. The team identified a person named “tořaibeleś” in the text, who may be the author or commissioned the writing of the text.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
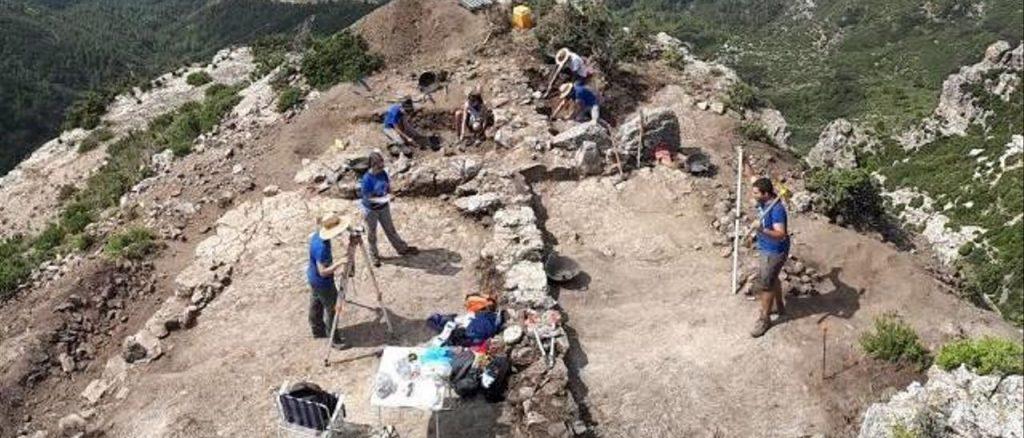

There are no complete parallels among Iberian lead sheets. It has a one-of-a-kind mix of properties, including its small size, folding, and incorporated brief text on both sides. Plates unearthed in El Amarejo’s votive well are the closest cognates, however, they are only written on one side. Even so, it seems likely this sheet had a votive purpose as well, as its text and morphology rule out that it is correspondence, commercial, or a label.
“Iberian is a language that still cannot be translated, but which experts are making gradual progress to identify words to interpret what type of texts they were”, explains David Quixal, professor of Archaeology and one of the authors of the article.
A study detailing the discovery and interpretation of a lead plate with Iberian writing, the first obtained in a regulated excavation in Pico de Los Ajos (Yátova), one of the most important Iberian sites, has been published by a multidisciplinary research team from the University of Valencia (UV), the Prehistory Museum of Valencia (MPV), and the University of Barcelona (UB).
Source: Ruvid