Researchers have successfully sequenced the whole genome from the skull of Peştera Muierii 1, women who lived in today’s Romania 35,000 years ago, for the first time.
Her high genetic variety demonstrates that the migration out of Africa was not the major bottleneck in human history, but rather happened during and after the most recent Ice Age. This is the conclusion of new research headed by Uppsala University’s Mattias Jakobsson and published in Current Biology.
“She is a bit more like modern-day Europeans than the individuals in Europe 5,000 years earlier, but the difference is much less than we had thought. We can see that she is not a direct ancestor of modern Europeans, but she is a predecessor of the hunter-gathers that lived in Europe until the end of the last Ice Age,” says Mattias Jakobsson, professor at the Department of Organismal Biology at Uppsala University and the head of the study.
Other experts have found that the form of her cranium is comparable to both contemporary people and Neanderthals in prior investigations. As a result, they concluded she had a higher proportion of Neanderthal heritage than other contemporaries, making her stand out from the crowd. However, the present study’s genetic examination reveals that she has the same low level of Neanderthal DNA as most other people alive at the time. When compared to the bones of people who lived 5,000 years ago, such as Peştera Oase 1, she had barely half as much Neanderthal heritage.
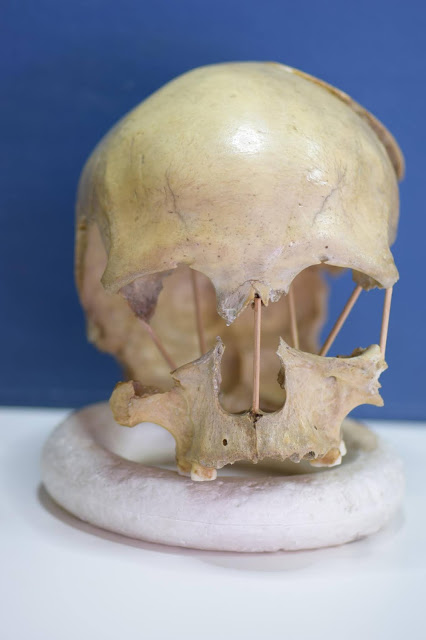
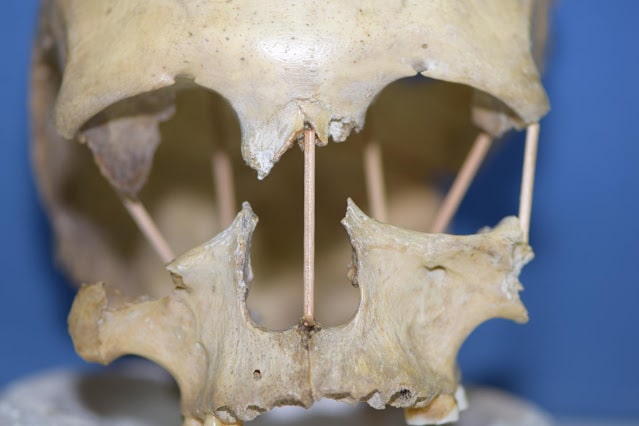
The skull of Pestera Muierii 1. Now researchers have successfully sequenced
the entire genome from the skull of Pestera Muierii 1, a woman who lived
in today’s Romania 35,000 years ago [Photo: Mattias Jakobsson]
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The exodus of modern humans from Africa around 80,000 years ago was a watershed moment in human history, and it is commonly referred to as a genetic bottleneck. Populations migrated from Africa to Asia and Europe. The consequences of these migrations may still be observed today. Outside of Africa, genetic diversity is lower than in Africa. The fact that Peştera Muierii 1 has a high genetic diversity suggests that the largest loss of genetic variety happened during the last Ice Age (which ended around 10,000 years ago) rather than during the out-of-Africa migration.
“This is exciting since it teaches us more about the early population history of Europe. Peştera Muierii 1 has much more genetic diversity than expected for Europe at this time. This shows that genetic variation outside of Africa was considerable until the last Ice Age and that the Ice Age caused the decrease in diversity in humans outside of Africa.”
The researchers were also able to follow the genetic variation in Europe over the last 35,000 years and see a clear decrease in variations during the last Ice Age. The reduced genetic diversity has previously been linked to pathogenic variants in genomes being more common among populations outside of Africa, but this is in dispute.
“Access to advanced medical genomics has allowed us to study these ancient remains and even be able to look for genetic diseases. To our surprise, we did not find any differences during the last 35,000 years, even though some individuals alive during the Ice Age had low genetic diversity.
Now we have accessed everything possible from these remains. Peştera Muierii 1 is important from a cultural history perspective and will certainly remain interesting for researchers within other areas, but from a genetic perspective, all the data is now available.”