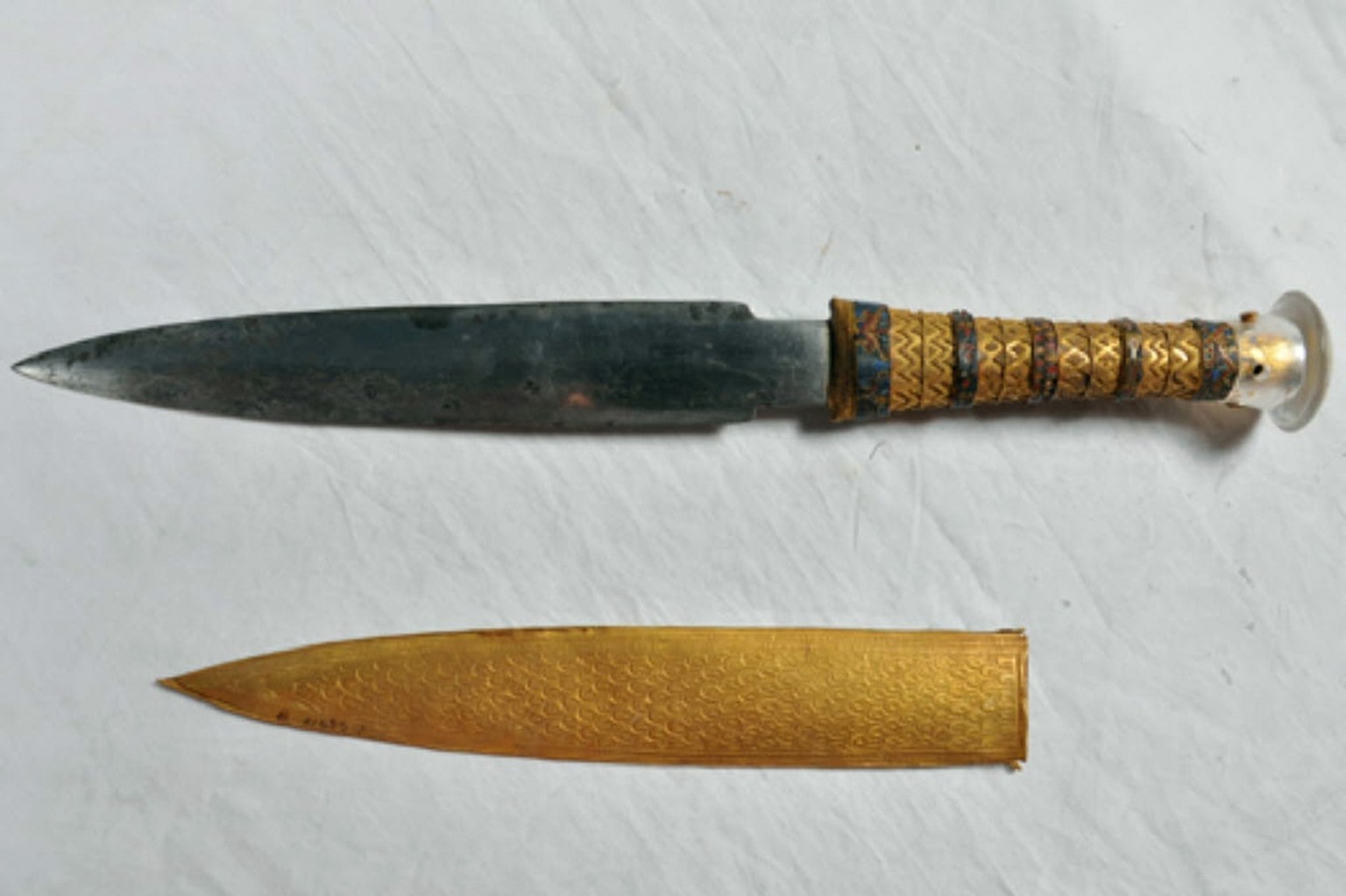
Archaeologists have finally solved the enigma of King Tutankhamun’s dagger, which was discovered 3,400 years ago. A new examination of the weapon recovered in the pharaoh’s tomb in 1922 indicates that it was made from a meteorite found outside of Egypt.
The find supports a prior notion that the beautiful shiv was sent to King Tut’s grandpa as a gift from afar. The artifact’s origins and the way it was manufactured remain one of the great mysteries surrounding Tut’s grave goods.
In 2016, scientists determined that the chemical makeup of the 13-inch blade show that it was expertly crafted from an iron meteorite. Now an analysis from a team at the Chiba Institute of Technology in Japan has revealed that the object was likely made outside of Egypt.
In their paper, the researchers wrote: The gold hilt with a few percent of calcium lacking sulfur suggests the use of lime plaster instead of gypsum plaster as an adhesive material for decorations on the hilt. Since the use of lime plaster in Egypt started during the Ptolemaic period (305–30 B.C.), the Ca-bearing gold hilt hints at its foreign origin, possibly from Mitanni, Anatolia, as suggested by one of the Amarna letters saying that an iron dagger with gold hilt was gifted from the king of Mitanni to Amenhotep III, the grandfather of Tutankhamen.

Researchers described their investigation earlier this month in the journal Meteoritics & Planetary Science.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
They performed X-ray analyses of the dagger, which is housed in the Egyptian Museum of Cairo.
The analyses indicated that the artifact was made using a low-temperature technique heated to less than 950C (1,742F).
The researchers say this “hints at its foreign origin, possibly from Mitanni, Anatolia”.
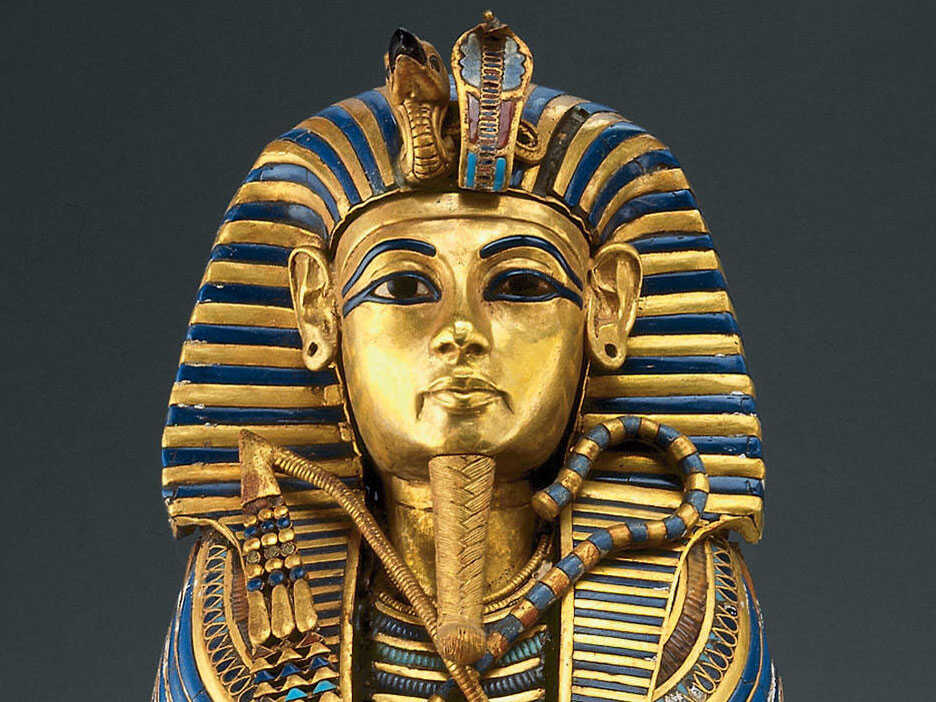
The artifact dates back to the 14th century BC and was found in the wrapping surrounding the right thigh of King Tut’s mummy.
It features a decorated gold handle with a rounded knob of rock crystal. It was encased in a gold sheath that was decorated with a pattern of lilies, feathers, and a jackal’s head.

Another separate gold blade was found under King Tut’s wrapping on the abdomen.
Iron objects were rare and considered more valuable than gold during the Bronze Age and were mostly decorative.
Tutankhamun, a pharaoh of the 18th Egyptian dynasty, ruled Egypt from 1332 to 1323 B.C.
He is most famous for his age – experts believe the boy was nine when he took the reigns of the world’s most powerful empire.
His death aged just 19 has puzzled experts for decades. Some believe he died of a broken leg or other accident, while others suspect he was assassinated.
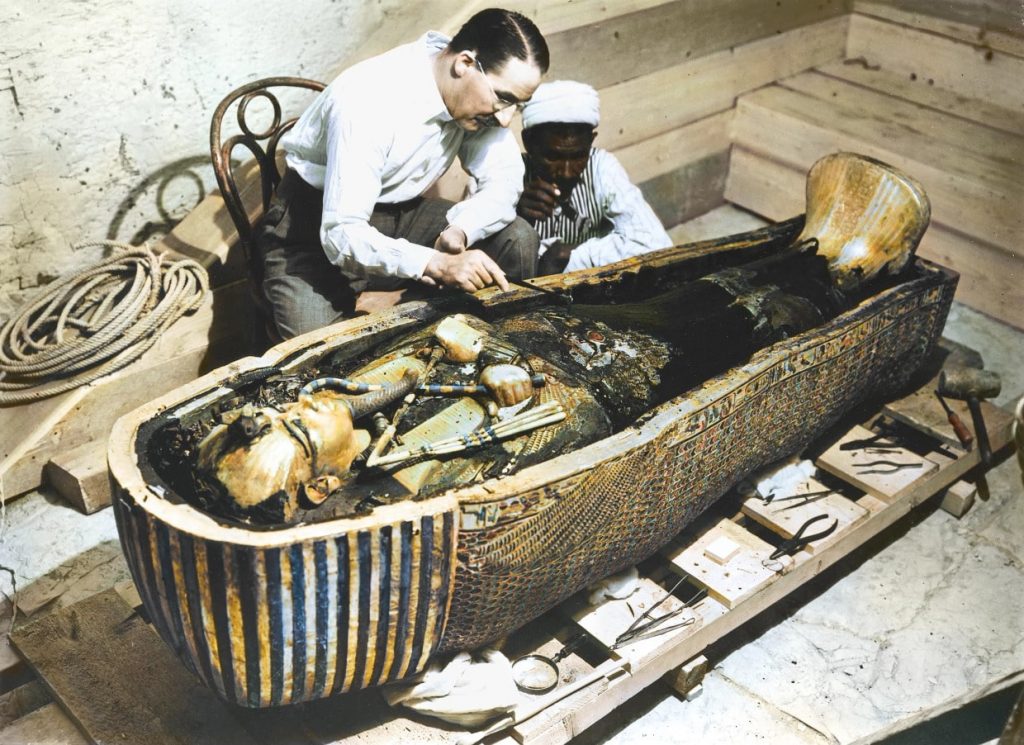
Tut’s tomb was famously unearthed in the East Valley of the Kings near Cario by British archaeologist Howard Carter in 1922.
The find was unusual in that the site had never been visited by looters, leaving the lavish treasures inside undisturbed for 3,300 years.
Cover Photo: University of Pisa