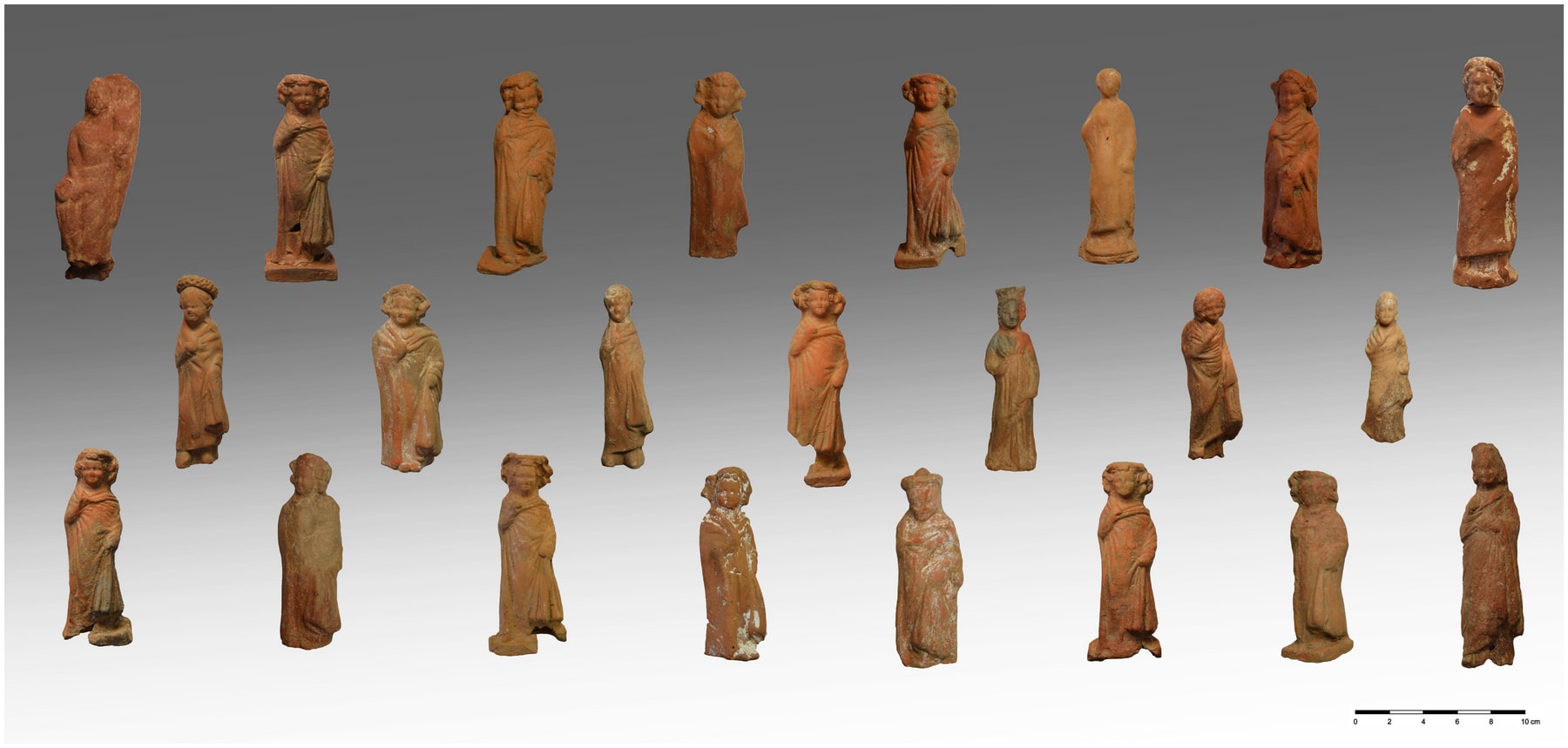
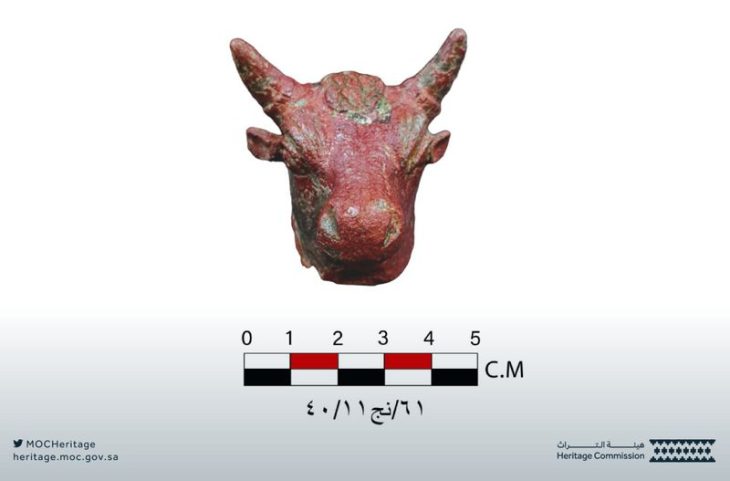
Archaeologists excavating a hilltop temple complex on the Cycladic island of Kythnos (commonly called Thermia) Greece have unearthed more than 2,000 intact votive offerings dedicated by ancient worshippers.
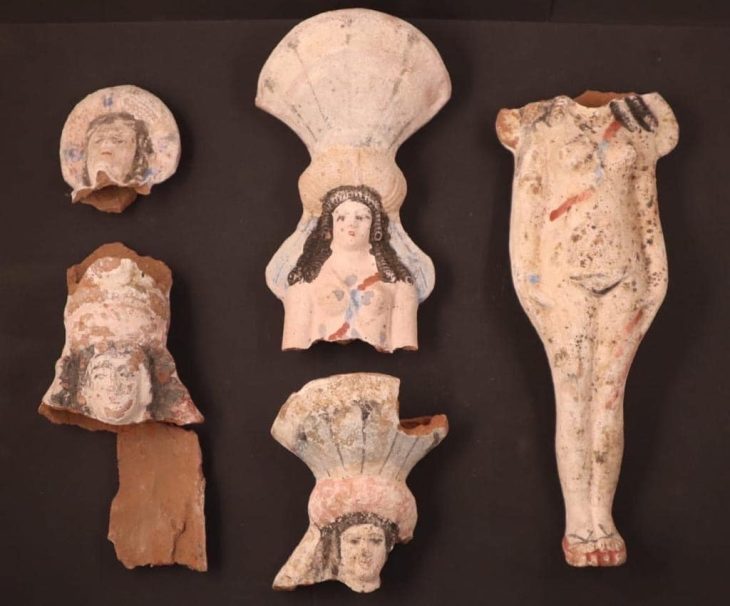
Greece’s Culture Ministry said Wednesday statement said the finds from work this year included more than 2,000 intact or almost complete clay figurines, mostly of women and children but also some of the male actors, as well as tortoises, lions, pigs, and birds.
Several ceremonial pottery vessels discovered are associated with Demeter, the ancient Greek goddess of agriculture, and her daughter Persephone, to whom the excavated sanctuary complex was dedicated.
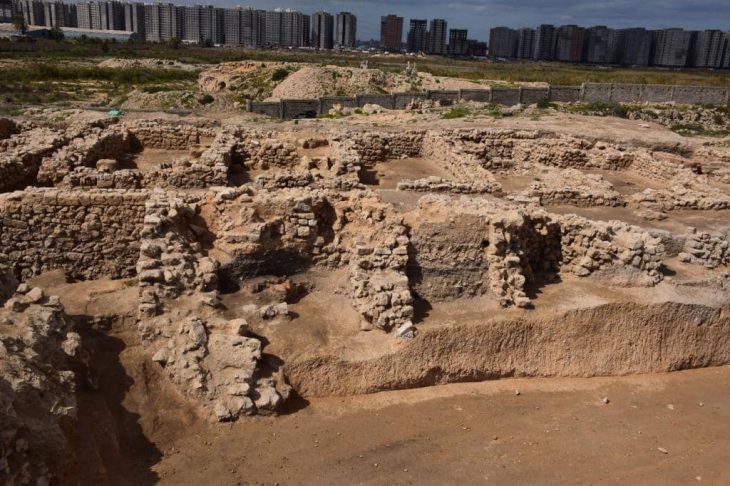
The ancient city of Kythnos, one of the earliest settlements in the Cycladic Islands, was continuously inhabited from the 12th century B.C. to the 7th century A.D. On the northern portion of the plateau, which has a view of the ocean, the sanctuary complex was constructed. The earliest building, which was built in stages, dates back to the seventh century B.C. Up until the fourth century A.D., the temple complex was in continuous use.
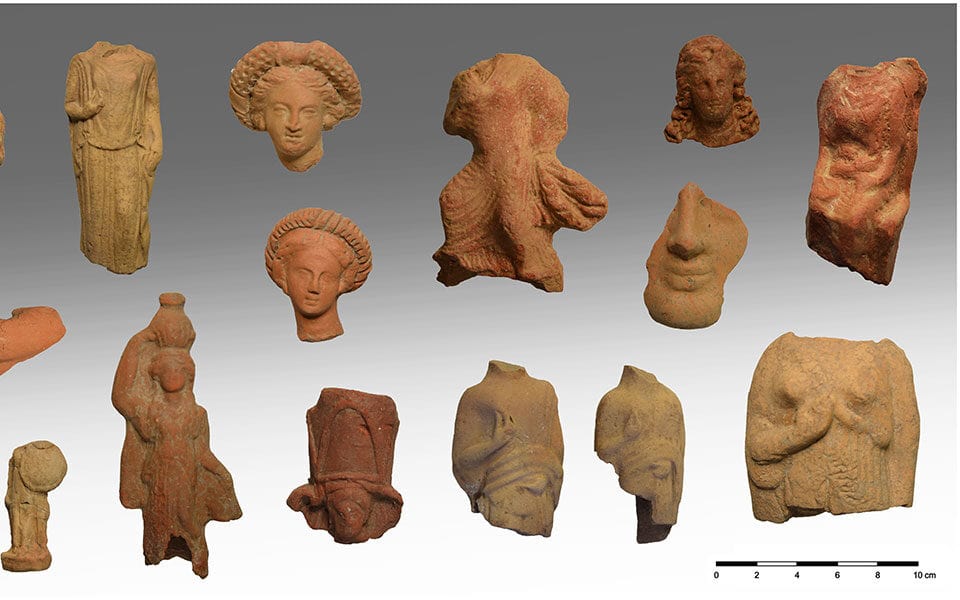

The artifacts were discovered in the scant ruins of two small temples, a nearby long building that may have served as a temple storeroom, and a nearby pit where older offerings were buried to make room for new ones.
The excavation by the Greece’s University of Thessaly and the Culture Ministry also found luxury pottery imported from other parts of Greece, ornate lamps, and fragments of ritual vases used in the worship of Demeter and Persephone at Eleusis, an ancient Athens suburb.
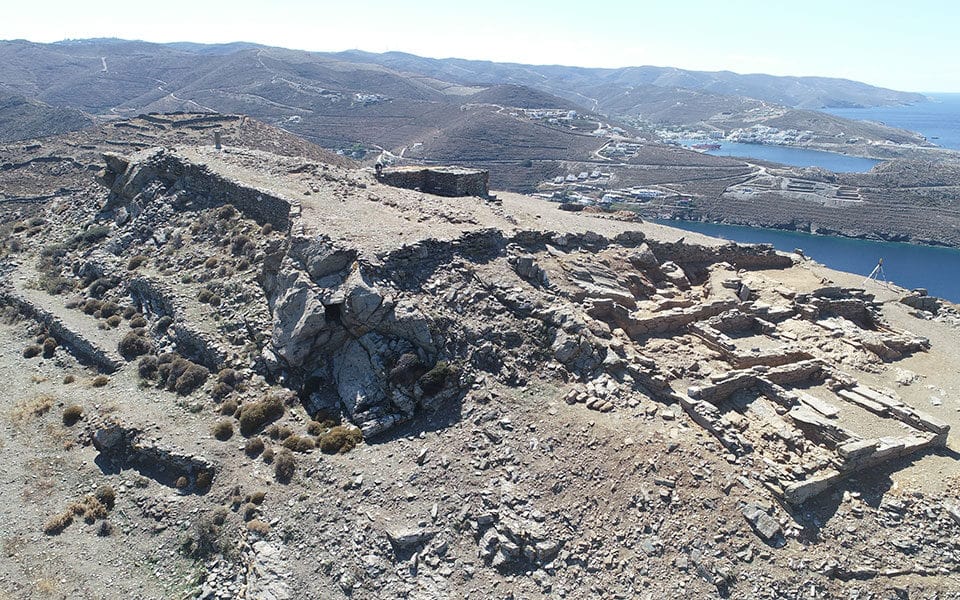

It is unclear how closely the site on Kythnos was linked to Eleusis, one of the most important religious centers in ancient Greece, where the goddesses were worshiped during secret rites open only to initiates who were forbidden to speak of what they saw. The sanctuary at Eleusis is known to have owned land on the island.
Kythnos in Roman times was a place of political exile. The excavations are set to continue through 2025.
Cover Photo: Grece Culture Ministry