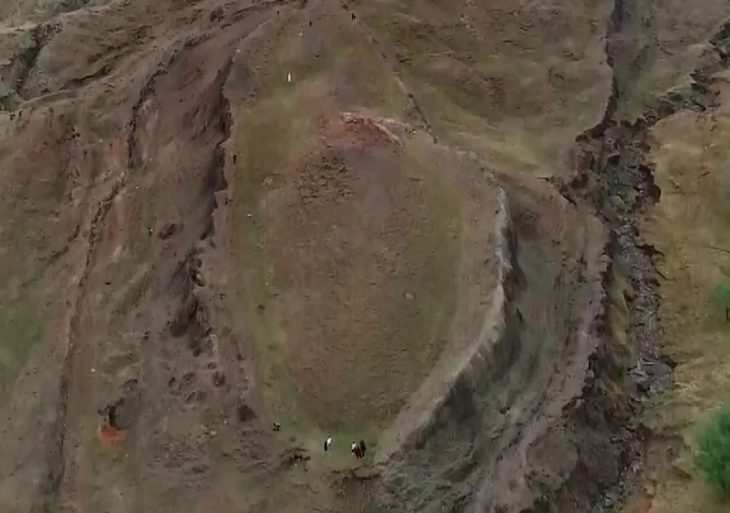
Hiding deep beneath the Baltic Sea, an architectural wonder of the Stone Age has been discovered by researchers. This megastructure, which is situated 21 meters (69 feet) below the surface of the sea in Germany’s Bay of Mecklenburg, is thought to be over 10,000 years old. It is almost a kilometer (0.62 miles) long and is made up of big stones that have been thoughtfully placed.
The wall, which may be the largest Stone Age megastructure in Europe, is believed to have been constructed some 11,000 years ago to direct reindeer into areas where they could be killed more easily.
The German research team, led by geophysicist Jacob Geersen of Kiel University, hypothesizes that the structure was part of a wall used by ancient hunter-gatherers for hunting. The structure has been named the Blinkerwall.
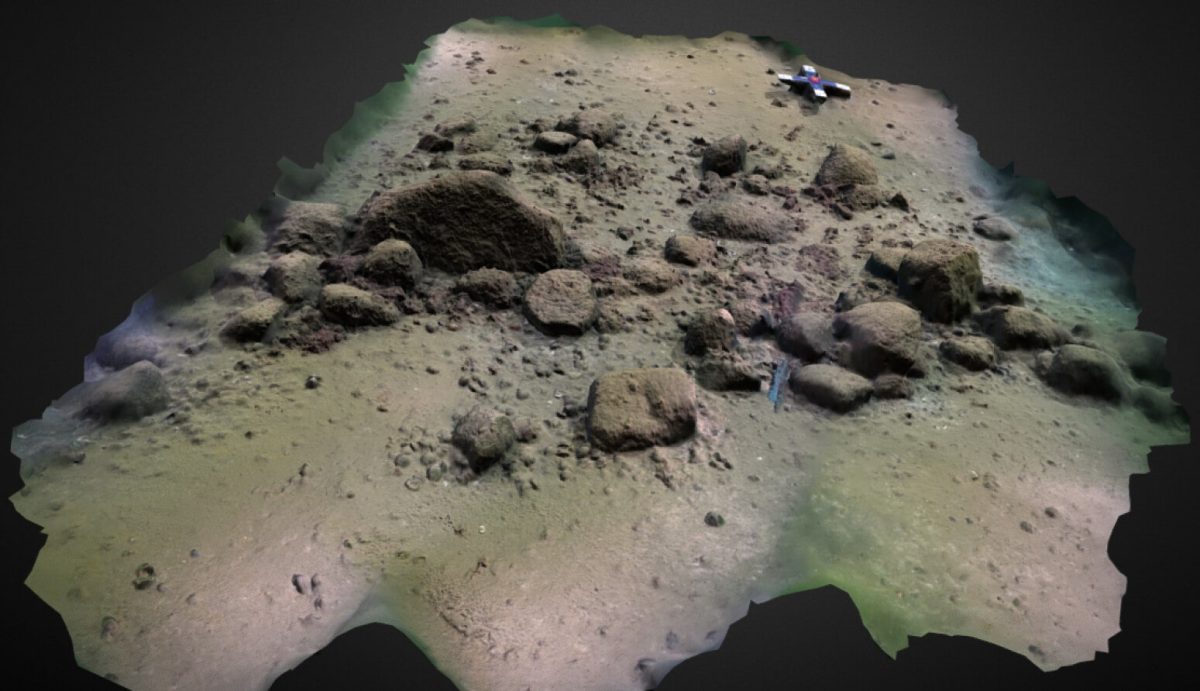
Researchers used a combination of ships and submarine drones to survey the area, collecting sonar data on the shape and size of the long-lost structure. The sheer number of rocks, as well as their organized placement, told the researchers that the formation was not crafted by natural processes.
Tectonic movements, erosion, and changes in climate, including sea level and glaciation, have all contributed to the gradual shifting of Earth’s landscape over time, resulting in the sea swallowing up numerous coastal settlements and structures. Technological advances have now made it possible to discover these lost structures.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
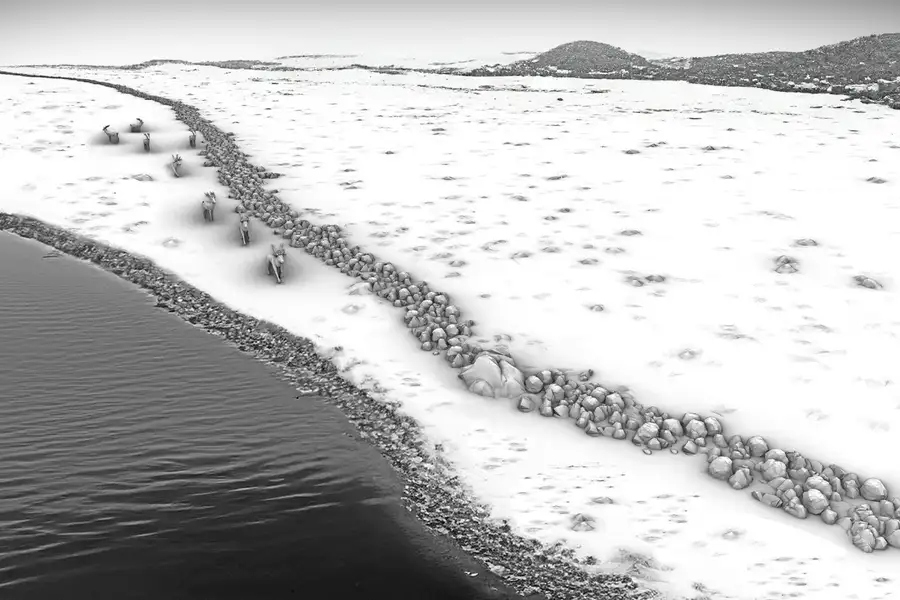

While the Blinkerwall was on dry land around 10,000 years following the end of the last Ice Age. However, it was ultimately flooded due to sea level rise sometime between 8,600 to 8,000 years ago.
Examination of the site indicates 1,670 stones organized over a 971-meter (3,186-foot) stretch, with each stone being under a meter in height and 2 meters in width. So the team thinks the structure was built by linking large stones that were too heavy to move with smaller stones that could be shifted.
The researchers rule out the Blinkerwall being used as a fish weir or coastal defense because the structure does not meet the requirements for these uses, despite its proximity to an ancient shoreline or bog. Instead, they suggest that the wall could have been used to corral large animals like reindeer or bison for hunting.
Team member Marcel Bradtmöller, an archaeologist at the University of Rostock, believes it was probably made by hunter-gatherers belonging to what is known as the Kongemose culture, named after a site in Denmark where artifacts such as stone tools have been found.
The Kongemose culture (Kongemosekulturen) was a mesolithic hunter-gatherer culture in southern Scandinavia ca. 6000 BC–5200 BC and the origin of the Ertebølle culture.
Similar low walls, also known as desert kites, have been discovered under the Great Lakes in North America, as well as in numerous locations throughout Africa and the Middle East. Some are up to 5 kilometers long, and it is now widely accepted that they were used for hunting.
The new study is published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Cover Photo: 3D model of a section of the Blinkerwall adjacent to the large boulder at the western end of the wall. Photographs were taken by Philipp Hoy, Rostock University.