Egyptologists at the University of Bonn and the University of Aswan want to systematically record hundreds of petroglyphs and inscriptions dating from the Neolithic to the Arab period and document them in a database.
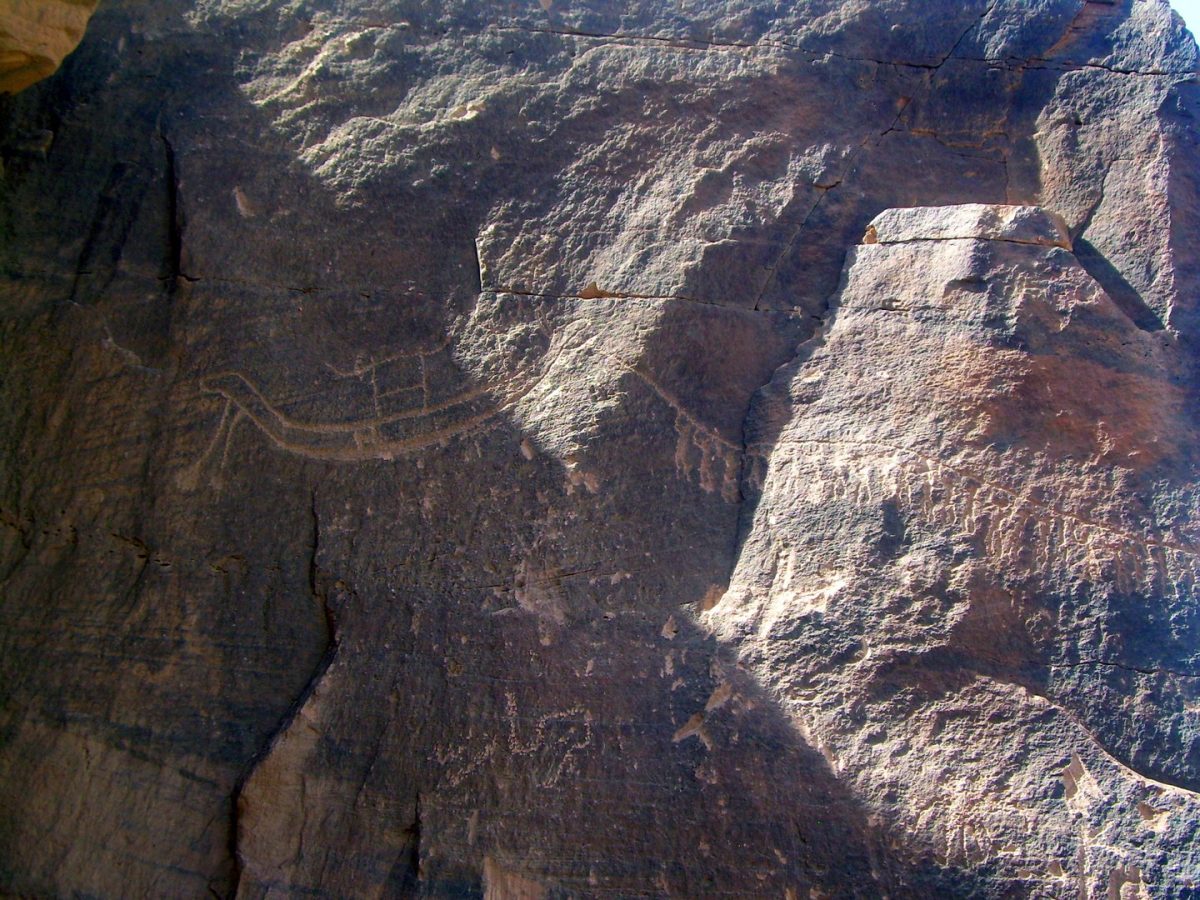
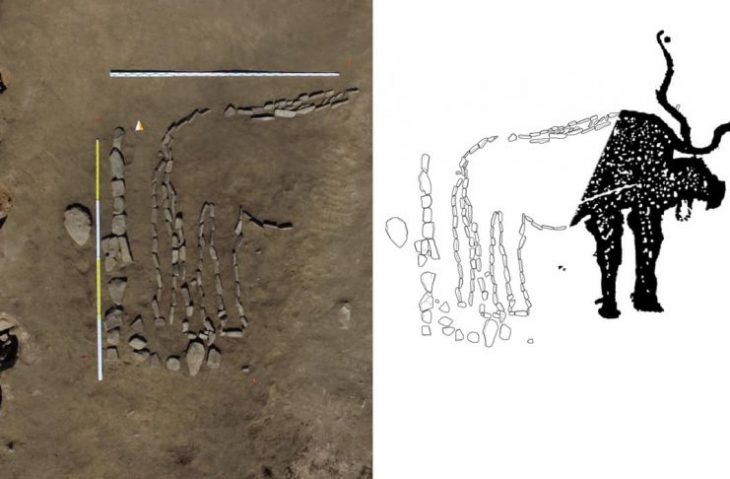
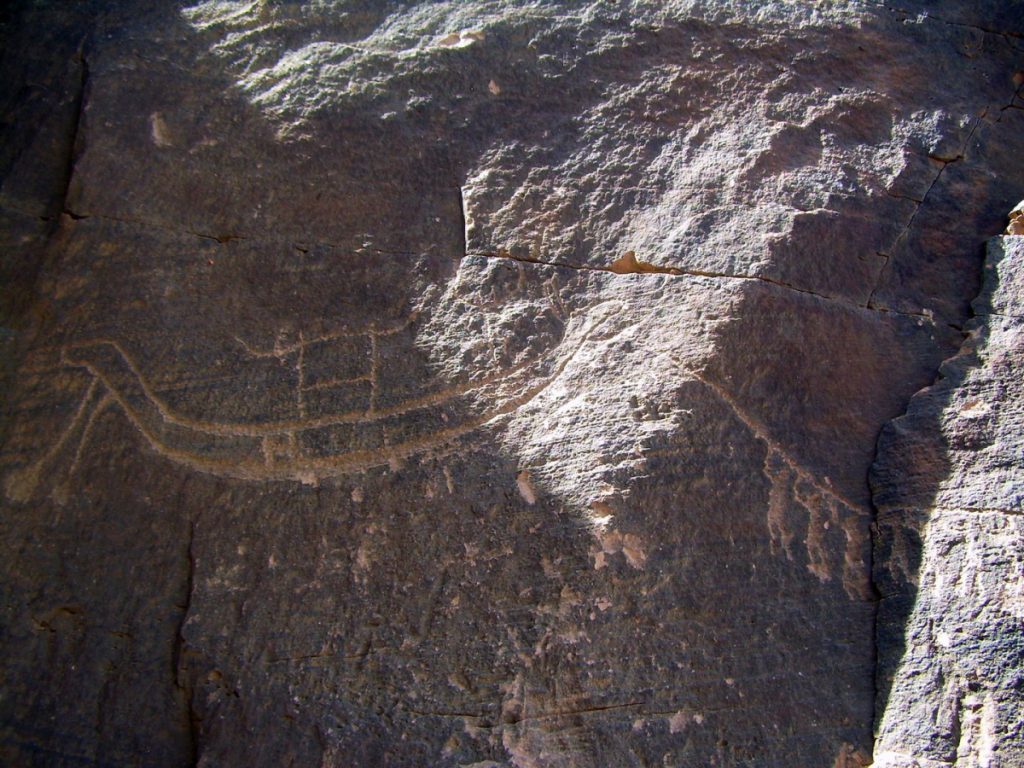
The desert in southern Egypt is filled with hundreds of petroglyphs and inscriptions oldest dating from the fifth millennium B.C. and few have been studied. A more than 5,000-year-old rock painting that shows a boat being pulled by 25 men on a rope among them stands out in particular.
“The first newly discovered sources shed new light on the pre-Pharaonic period of the Fourth Millennium and the importance of the socio-cultural periphery,” says Egyptologist Prof. Dr. Ludwig Morenz of the University of Bonn.
Mohamed Abdel Hay Abu Baker, who was specifically responsible for researching the rock images at the Aswan Inspectorate, among the images that captured during his explorations in the field, one, in particular, stood out to the Egyptologist from the University of Bonn.
It is depicted over the bumps and edges of the rock, how a boat is pulled by 25 men with raised arms on a rope. A ritual is obviously impressively shown here – namely the great procession of an image of the gods, according to Morenz.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
This is clear from image details, he said: the boat with shrine and standard and, in particular, the cattle horns, which are typical of sacred imagery. “This rock image gives us insights into the sacred design of an apparently remote landscape, the Wadi al Agebab, which is still largely unknown in research,” says the Egyptologist.
The entire later Pharaonic culture is based on the beginnings of the pictorial staging of religion. Morenz: “Here, the high importance of religion and especially the cult of the gods in the still pre-Egyptian society of the second half of the Fourth Millennium is revealed as a culture-creating factor.”

Documentation
“This cultural treasure in the northeast of Aswan has been largely undocumented, let alone published,” says Egyptologist Prof. Dr. Ludwig Morenz of the University of Bonn.
The petroglyphs are found in numerous and often remote locations in dried-up river valleys, called “wadis” in Arabic. At the same time, the petroglyphs, which are sometimes inconspicuous at first glance, are under severe threat, especially from current quarrying activities in the desert.
“Especially in recent years, there has already been serious destruction of this cultural asset,” says Morenz, who is also a member of the Cluster of Excellence Bonn Center for Dependency and Slavery Studies (BCDSS) and the Transdisciplinary Research Area “Present Pasts” at the University of Bonn. “Such losses can hardly be prevented completely, given the vastness of the area, but all the more important is at least good documentation.”
In the course of his doctoral studies at Aswan University in Aswan, Abu Baker will now work together with the University of Bonn to create a comprehensive database with an image archive on rock images. For this purpose, the University of Excellence Bonn supports the inspector of the Egyptian Ministry of Antiquities for one year with a scholarship from excellence funds of the federal and state governments. Prof. Morenz is the second supervisor of the dissertation.
Cover Photo: Rock image – with ruler boat procession, ca. 3200 BC, Wadi al Agebab. © Photo: Mohamed Abdel Hay Abu Baker