An amateur archeologist has found a big treasure trove of over 1,290 priceless, ancient Roman coins dating back to the 4th Century AD near Bubendorf, a municipality in the district of Liestal, in the canton of Basle-County, in Switzerland.
The hoard was discovered by volunteer archaeological scout Daniel Lüdin in a forested area near Wildenstein Castle in September 2021.
The finder, Daniel Lüdin, was searching a forest with a metal detector near Bubendorf, a municipality in the district of Liestal, in the canton of Basle-County, in Switzerland, when he made the discovery.
When his metal detector signaled a strong alert, Lüdin dug down a little and found a few Roman coins and some potsherds, not enough to explain the strength of the signal. He dug down a little more and hit the jackpot.
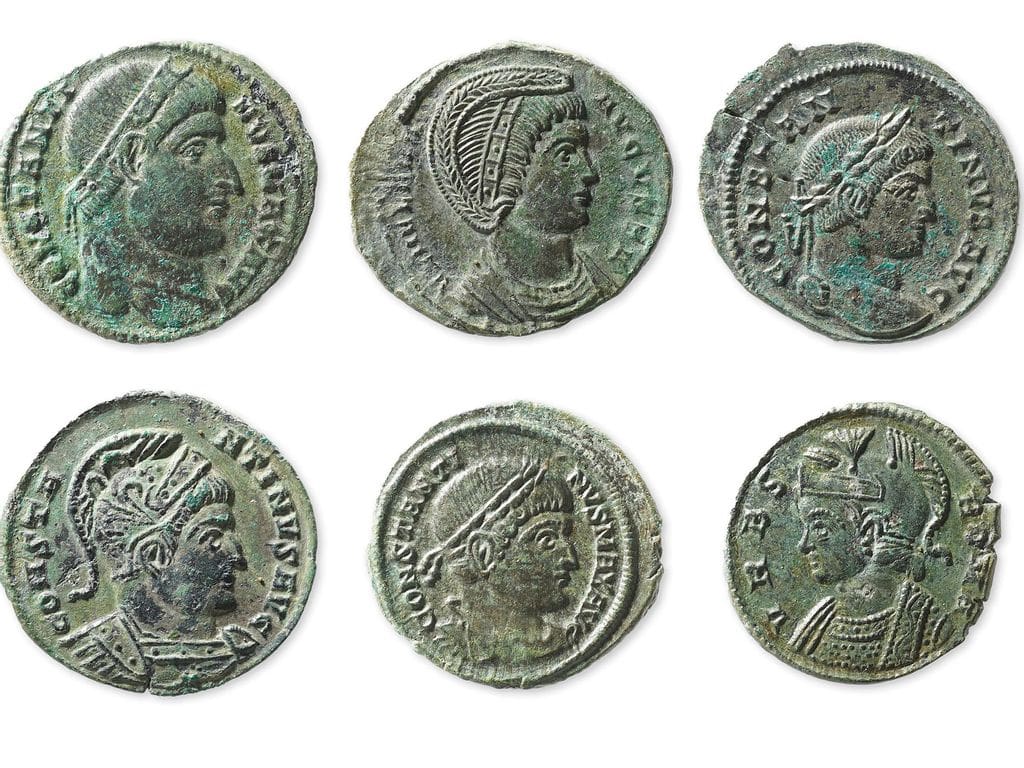

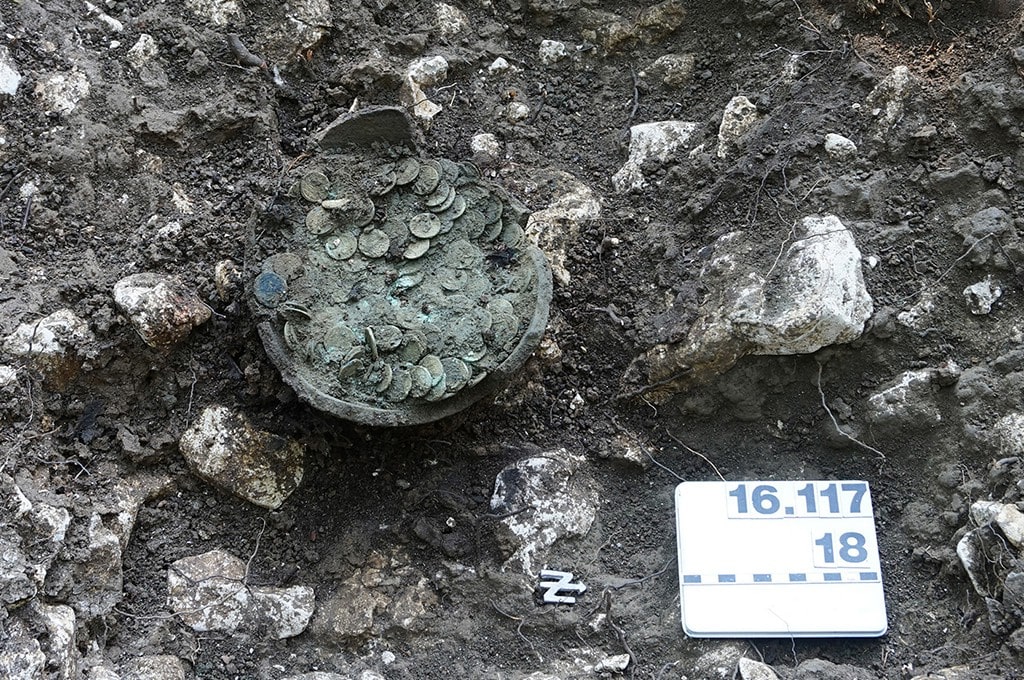
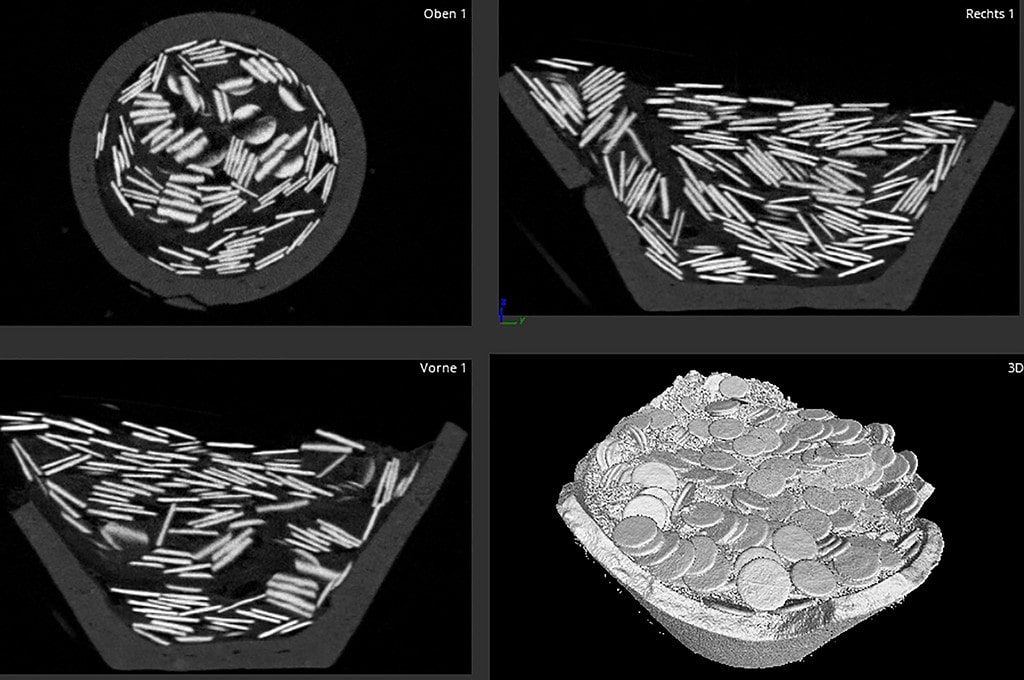
Daniel Lüdin was very careful. He reconsidered the find, filled in the hole, and informed Archeologie Baselland. Thanks to this professional approach, they removed the pot in a soil block so that all of the coins, pot fragments, and any invisible archaeological treasures like traces of organic remains could be excavated under laboratory conditions. The block removal also allowed researchers to CT scan the soil block to map out the contents.
They revealed that the coins in the pot had been separated in two by a piece of cowhide at the time of their burial, although it is currently unclear why and what purpose this served.
Andreas Fischer, of Archaeologie Baselland said: “One can only speculate about the meaning and purpose of this separation.”
What is clear, however, is that these coins are made of a copper alloy and of silver, and they were all “minted during the reign of Emperor Constantine the Great (306-337 AD). The youngest specimens date from the years 332-335 AD.”
The total value of 1290 coppers was the equivalent of a gold solidus or about two months’ salary for a soldier in the legions.
The expert said that often, there are simple explanations as to why people would bury their valuables, but none of them appear to apply here.
What makes the hoard so unusual is that it was buried during a time of political and economic stability. Coin hoards from the 4th century were typically buried during periods of unrest, but Constantine’s reign was not among them. Hoards from this period are vanishingly rare throughout the Empire.
3D model of the hoard after the external soil was cleaned but before the contents were excavated in the laboratory. Jan von Wartburg.
It seems likely that this one was buried for other reasons. One possibility is a religious offering as the find site was on the border between three known Roman estates, so it could have been a boundary line sacrifice.
Cover Photo: The ceramic pot with the coins after professional excavation by employees of Archeology Baselland in Switzerland. (Archaologie Baselland)