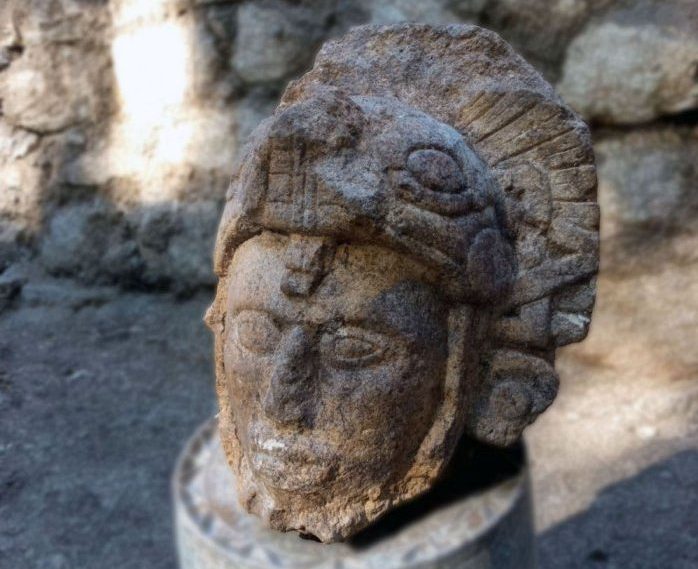
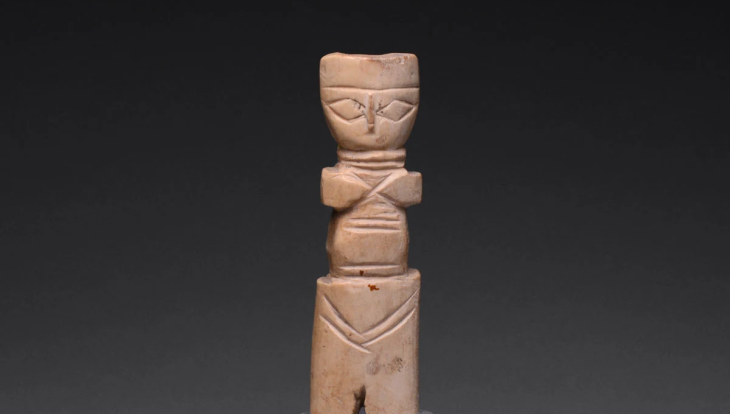
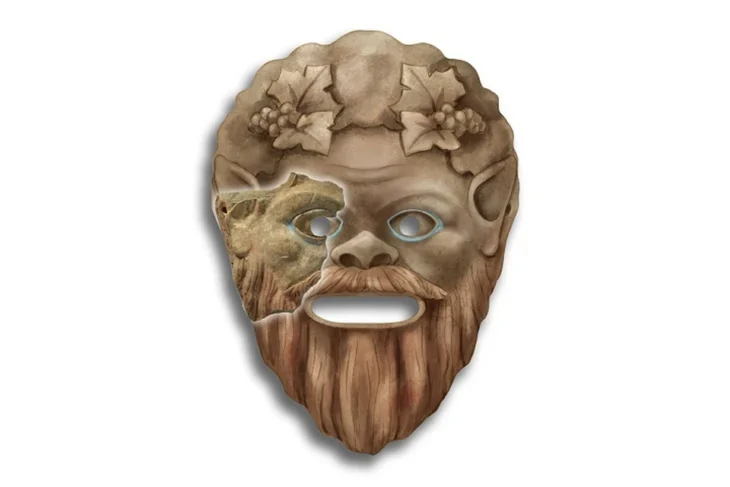
In the Casa Colorada archaeological complex within the premises of Chichén Itzá in Mexico, a sculpture of an anthropomorphic face with a snake headdress was found.
On Thursday, November 9th, during the morning conference of President Andres Manuel Lopez Obrador, the director of Mexico’s National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH), Diego Prieto Hernández, reported on the discovery of said sculpture, made last Tuesday.
Dated to the Late Classic period, the rare sculpted artifact was discovered during excavations by the Archaeological Areas Improvement Program (Promeza), in “Temple 6 of Maudslay,” which is part of the Casa Colorada complex of Chichén Itzá.
The statue is 33 cm (13 in) tall and 28 cm (11 in) wide. It appears to depict a warrior wearing a feathered dress and a helmet shaped like a serpent with its jaws open, and scholars suspect it may have once been part of a larger sculpture built about 1,000 years ago.
The feathered serpent was one of the most important gods in Mesoamerica. The Aztecs called him Quetzalcoatl, and the ancient Maya called him Kukulkan. The K’iche’ group of Maya named him Gukumatz.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
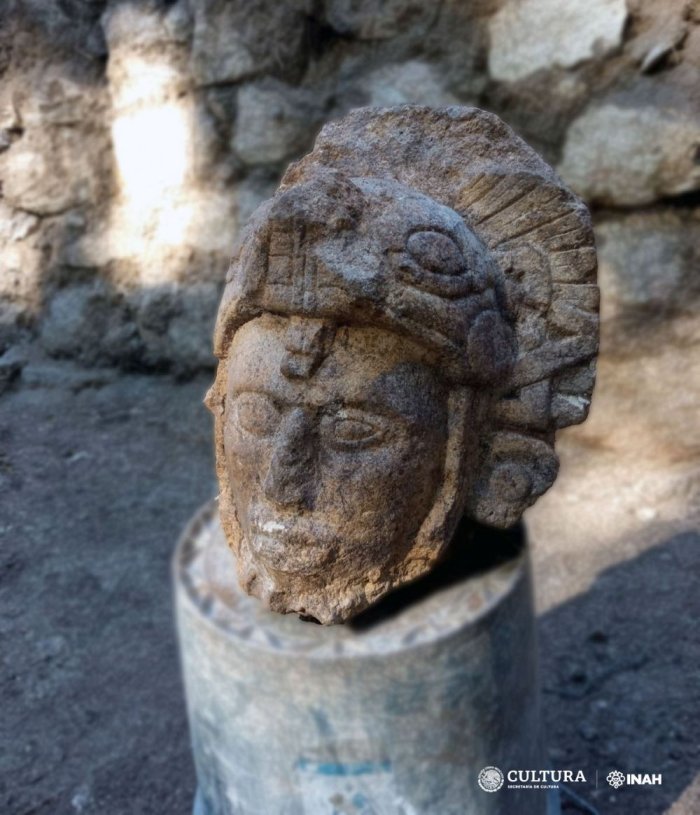

The National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH), Diego Prieto Hernández, described the head as a “very interesting find.” “It was customary to represent warriors with a headdress, with a kind of helmet,” he said. “In this case it is a snake figure from which the face of this character emerges, and a feathered headdress, so it is probably alluding to Kukulcán, the feathered serpent of the Maya.”
The pre-Columbian civilization was one of the most important Mayan centers of the Yucatán peninsula, flourishing between the ninth and thirteenth centuries AD. Chichén Itzá is thought to have housed tens of thousands of people at its peak.
Serpent warriors were people who dressed like serpents and participated in religious rituals in Maya culture. As go-betweens for the worlds of the supernatural and the earth, these warriors were essential to fertility and rain-related ceremonies. The elaborate headdresses, among other costumes, showcased the artistry of the Maya people and their deep spiritual and natural connections.

The excavations are part of an archaeological rescue project carried out in its conclusive phase in the works of the Mayan Train.
The warrior’s sculpture, unearthed at the Casa Colorada complex in Chichén Itzá, was discovered during this archaeological survey accompanying the railway line construction.
“As of Nov. 9, Prieto Hernández said that archaeological salvage work on the seven sections of the Maya Train had recovered 57,146 building structures, 1,925 movable artifacts, 660 human burials and 2,252 natural features associated with human settlements.