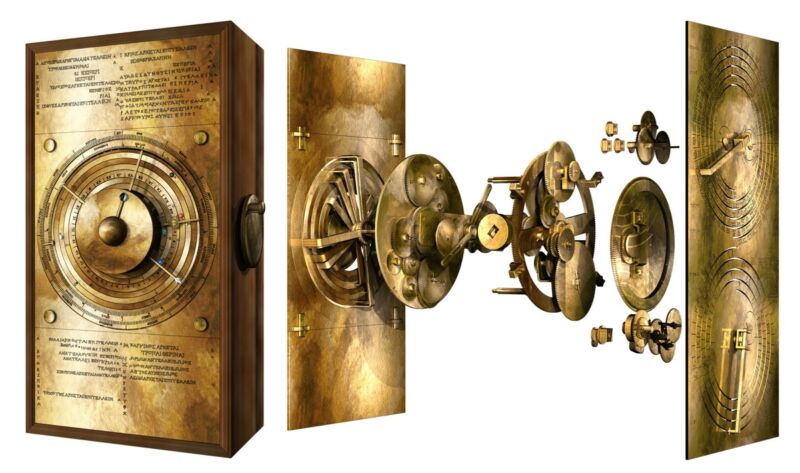
Scientists may have finally made a complete digital model of the 2000-year-old Cosmos panel of a mechanical device called the Antikythera mechanism, which is considered the world’s first computer.
The fragments of the shoebox-sized device were first discovered by Greek sponge divers in a Roman shipwreck in 1900. They were once filled with gears and used to predict the movement of celestial bodies.
The fragments found accounted for only one-third of the larger equipment: a highly complex manual gearbox capable of accurately predicting the movements of the five planets known to the ancient Greeks, as well as the phases of the sun, moon, and sun. Solar eclipses and lunar eclipses-display them relative to the time of ancient events (such as the Olympics).
However, despite years of arduous research and debate, scientists have not been able to fully replicate the mechanism that drives this amazing device or the calculations used in its design from the corroded brass fragments found in the sunken ship. But now, researchers at University College London say that they have completely recreated the design of the device from the ancient calculations used to create the device, and are now putting together their own devices to see if their design works.
“Our work reveals the Antikythera Mechanism as a beautiful conception, translated by superb engineering into a device of genius,” the researchers wrote March 12 in the open-access journal Scientific Reports. “It challenges all our preconceptions about the technological capabilities of the ancient Greeks.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Why should Antikythera be made?
Because of all the mysteries surrounding the device, the researchers hope to recreate the device to solve the root of many problems. In addition, no one has created a so-called model of the universe that is consistent with all physical evidence.
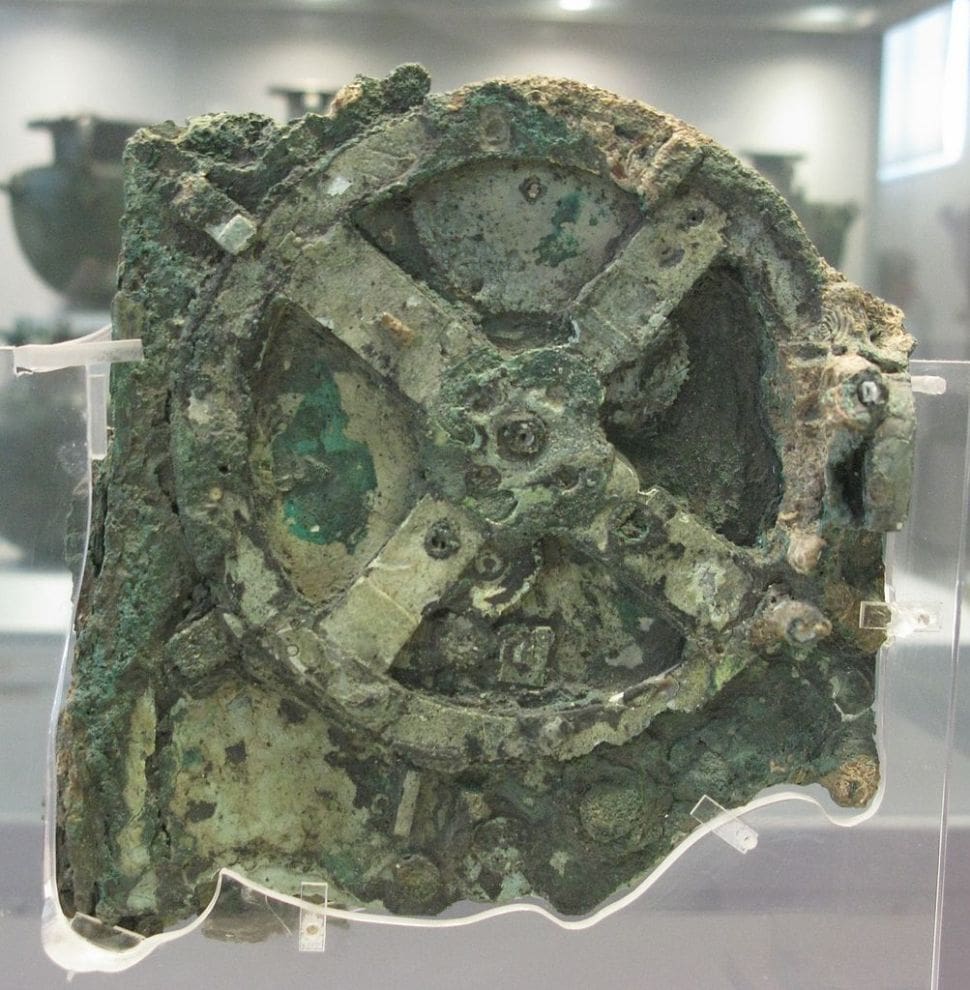

The size of the complex gears that make up the mechanism of the device can be found in the grandfather clock, but the only other gears found in the same period were larger gears such as ball guns or longbow bos, and catapults. This complexity raises many questions about the manufacturing process that can create such a unique and intricate manufacturing process, and why it was discovered on an ancient shipwreck near Antikythera Island as the only equipment of its kind.
Now that the computer model has been made, the researchers hope to make a physical version, first using modern technology so that they can check whether the equipment is working properly, and then use the technology that the ancient Greeks might use.
Wojcik, one of the researchers told Live Science, “There’s no evidence that the ancient Greeks were able to build something like this. It really is a mystery. The only way to test if they could is to try to build it the ancient Greek way”
“And there’s also a lot of debate about who it was for and who built it. A lot of people say it was Archimedes,” Wojcik said. “He lived around the same time it was constructed, and no one else had the same level of engineering ability that he did. It was also a Roman shipwreck.” Archimedes was killed by Romans during the Siege of Syracuse, after the weapons he invented failed to prevent them from capturing the city.
It also remains a mystery whether the ancient Greeks used similar techniques to create other as yet undiscovered devices, or whether copies of the Antikythera mechanism are waiting to be found.