A research project headed by Dr. Michael Hölscher of Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU), has uncovered that the book of revelation has some descriptions and phrases similar to ancient curse tablets.
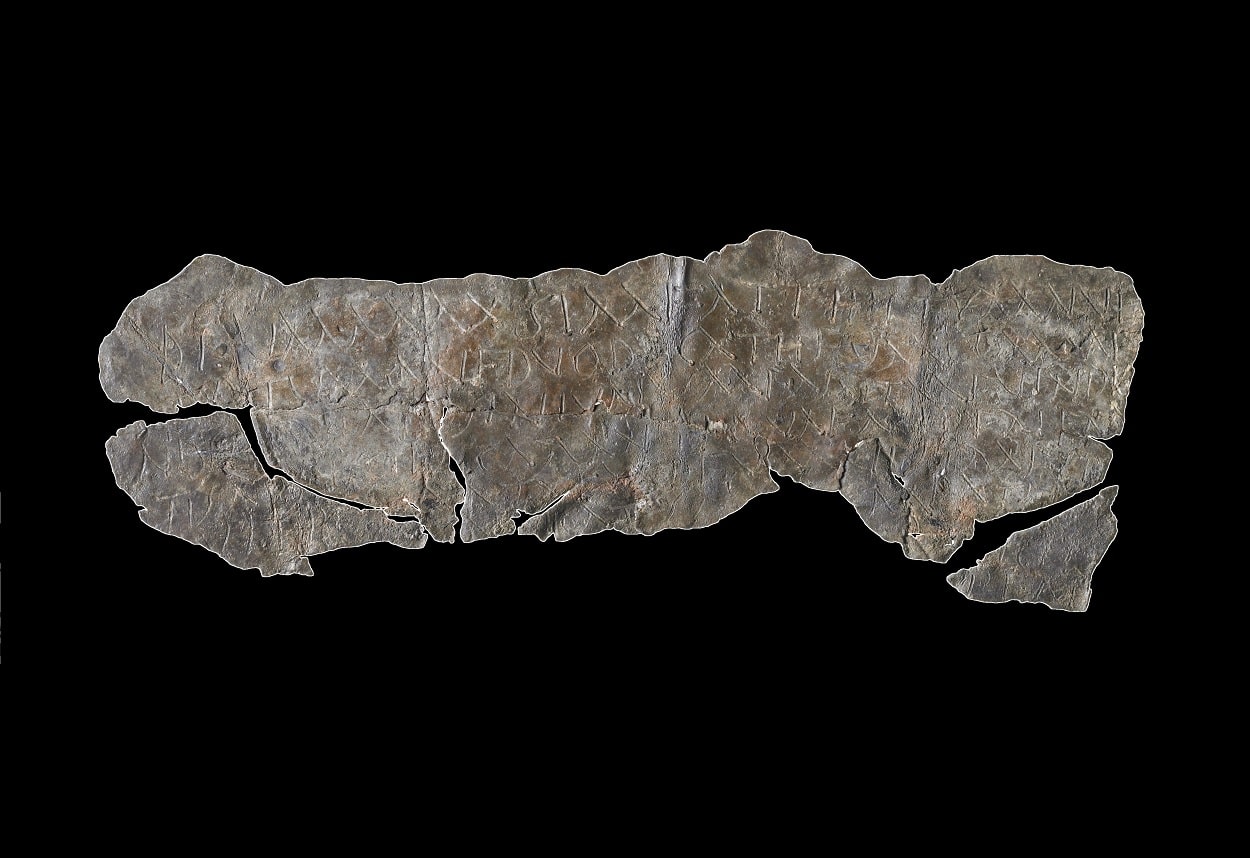
In the ancient world, curse tablets were widely used and in high demand. On thin sheets of lead, the corresponding incantations were frequently written or carved with the intention of harming a foe or rival. Curse tablets and the associated rituals were used widely as the Roman Empire grew; they have been discovered at locations from Egypt to Britain.
Cursed tablets were used by all members of society, regardless of economic or social status, with approximately 1,700 tablets discovered at sites throughout the Roman world dating primarily from 500 BC to AD 500.
The lead tablets with their inscribed curses were often deposited in specific places, such as graves or in the vicinity of sacred locations, the assumed abodes of spirits of the underworld, who would ensure the effectiveness of the curse. “The curse ritual as a whole was not simply restricted to the wording of the spell as such, but would have also involved the act of writing it down, the piercing of the tablets, or their burial in deliberately selected places,” said Hölscher describing aspects of the tabella defixionis practice. The ancients considered it a form of witchcraft or black magic, which were prescribed under Roman law.
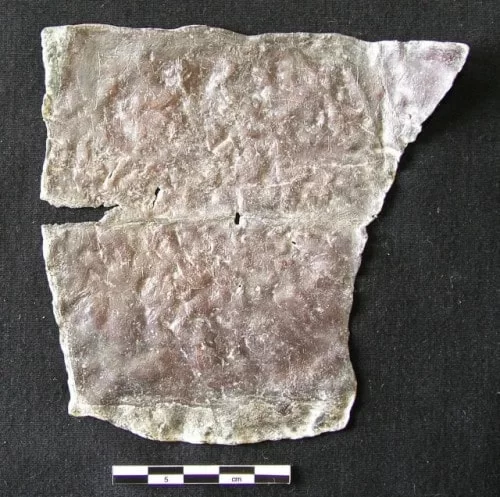

The research project entitled “Disenchanted Rituals. Traces of the Curse Tablets and Their Function in the Revelation of John” has been researching the role cursed tablets played in Roman society, as well as how they use terminology similar to the Book of Revelation.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
There are aspects of curse tablet-related inscriptions and practices in Revelation. This may well have been an indirect expression of the need for segregation and the attempt at self-preservation of an often threatened early Christian community,” explained Dr. Michael Hölscher, a researcher at the JGU Faculty of Catholic Theology.
The Book of Revelation, the last book in the New Testament, is a combination of three different literary genres: epistolary, apocalyptic, and prophetic. Although the precise author’s identity—who simply goes by “John”—has long been a subject of scholarly debate, the book is generally accepted to have been written sometime during the first century AD.
Aided by his insights into the phrasing used by those employing curse tablets and their expectations as to how their curses were supposed to work, Hölscher has been looking at how these have left their traces in the text of the Revelation of John. “In Revelation, we find wording and phrases that are very similar to those that appeared on curse tablets, although no actual verbatim quotations from the latter appear,” Hölscher pointed out.
As an example, he cites the description of an angel that casts a vast stone into the sea with the words: “Thus with violence shall that great city Babylon be thrown down, and shall be found no more at all.” According to Hölscher, this can be read as a kind of curse ritual. Those confronted with these words at the time could well have directly associated them with the routine use of curse tablets with which they would have been familiar.
In the seven letters of the Book of Revelation, Roman rule and the cult of the emperor are portrayed as demonic, satanic phenomena, from which the Christian minority was striving to isolate itself. “The Book of Revelation contributes to the process of self-discovery, the seeking of a distinctive identity by a Christian minority in a world dominated by a pagan Roman majority that rendered routine homage not only to the emperor but also to the main Roman gods”, explained Hölscher.
“It is possible that those who read or listened to the words of the Apocalypse of John could readily have seen whole passages, single phrases, or concepts in the light of curse spells,” said Hölscher, emphasizing the influence of the curse tablet culture. The project will investigate the overlap of the two sources against the background of how magic on the one hand and religion on the other were perceived in antiquity.
The research project entitled “Disenchanted Rituals. Traces of the Curse Tablets and Their Function in the Revelation of John” is being sponsored by the German Research Foundation (DFG) over the period 2022 to 2025.
Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz
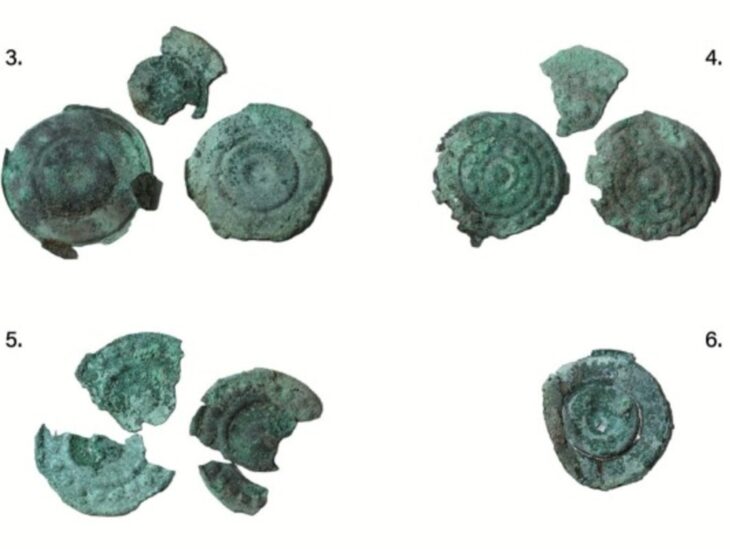
Cover Photo: Curse tablet Priscilla from Groß-Gerau: The lead tablet, here the front side, consists of three fragments and is inscribed on both sides with a prayer for revenge in Latin. It probably dates from around 100 AD. René Müller / LEIZA